RECON: Secure Your Systems with SAP Solution Manager
US-CERT issued Alert AA20-195A on Monday for the so-called RECON (Remotely Exploitable Code On NetWeaver) vulnerability in SAP NetWeaver Application Server Java (AS Java). RECON impacts versions 7.3 and higher of AS Java including an estimated 40,000 SAP systems. Based on a BinaryEdge search, 4,000 of the impacted systems are internet-facing. The vulnerability is rated 10/10 using the Common Vulnerability Scoring System and can be exploited remotely by unauthenticated attackers to fully compromise SAP systems.
RECON targets a missing authentication flaw in the LM Configuration Wizard of AS Java to execute malicious code that creates administrative users in compromised systems. Attackers can exploit RECON to compromise not only AS Java systems but also connected systems including SAP ERP, CRM, SCM, and BW.
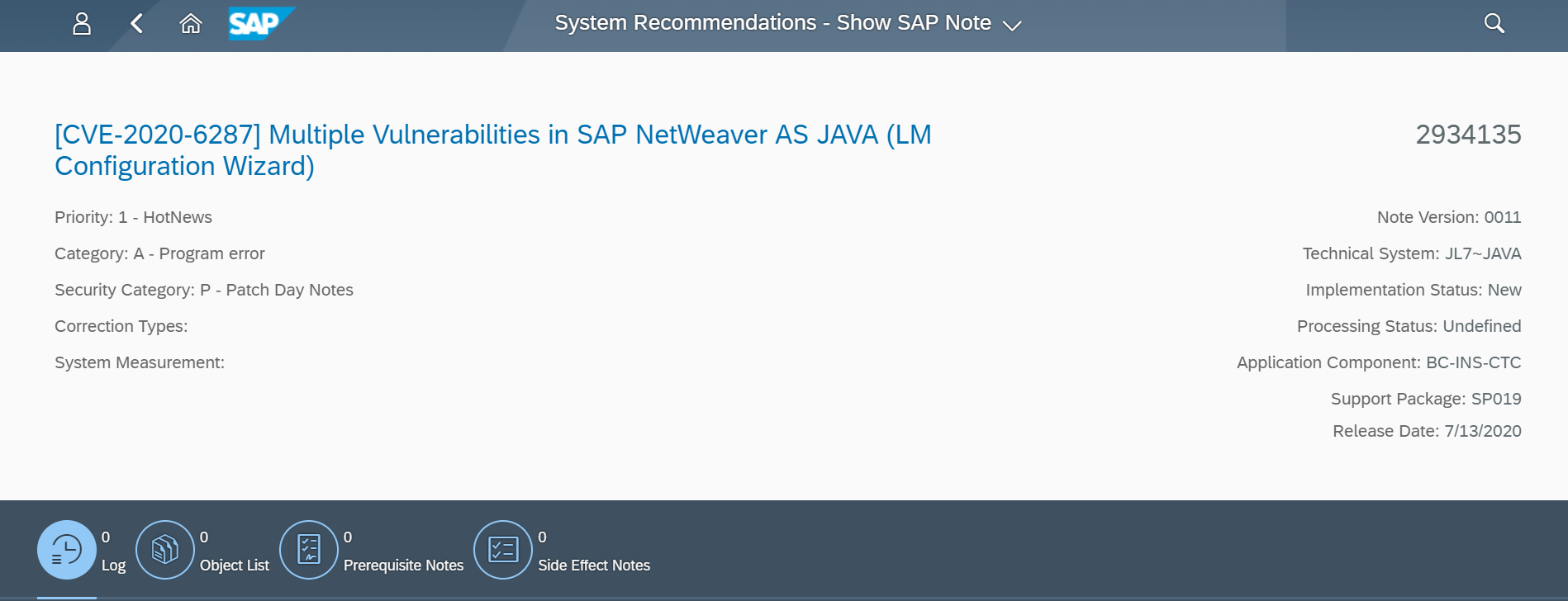
CISA strongly recommends SAP customers to apply SAP Note 2934135 to mitigate RECON. The note introduces authentication and authorization for the LM Configuration Wizard and therefore secures against RECON attacks. As a workaround, the application tc~lm~ctc~cul~startup_app can be disabled if the note cannot be applied. The LM Configuration Wizard is required by SAP Landscape Management. According to SAP, “This application is used by a few SAP Lifecycle procedures only, such as the initial technical setup. It is not needed for a day-to-day operations. You can temporarily activate or enable this application for executing the SAP lifecycle procedures.” Procedures for disabling the LM Configuration Wizard are detailed in SAP Note 2939665.
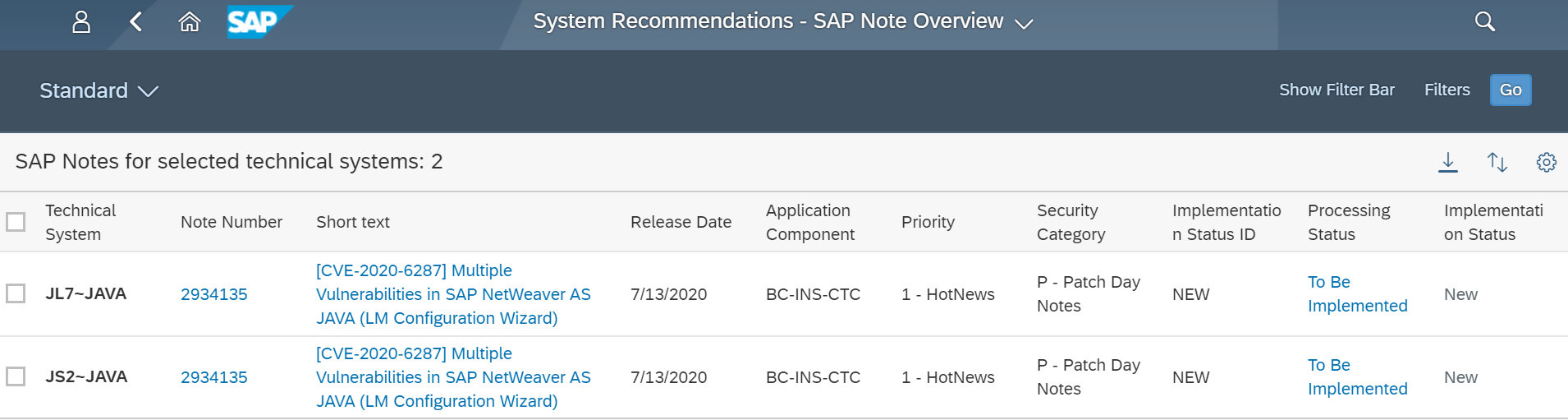
The implementation status of Notes 2934135 and 2939665 for impacted systems should be tracked using System Recommendations (SysRec) in SAP Solution Manager. SysRec connects directly to SAP Support to discover relevant notes for SAP applications, databases and components.
Users can create custom tiles in SysRec to track the implementation status of RECON notes in their SAP landscape from the Fiori launchpad.
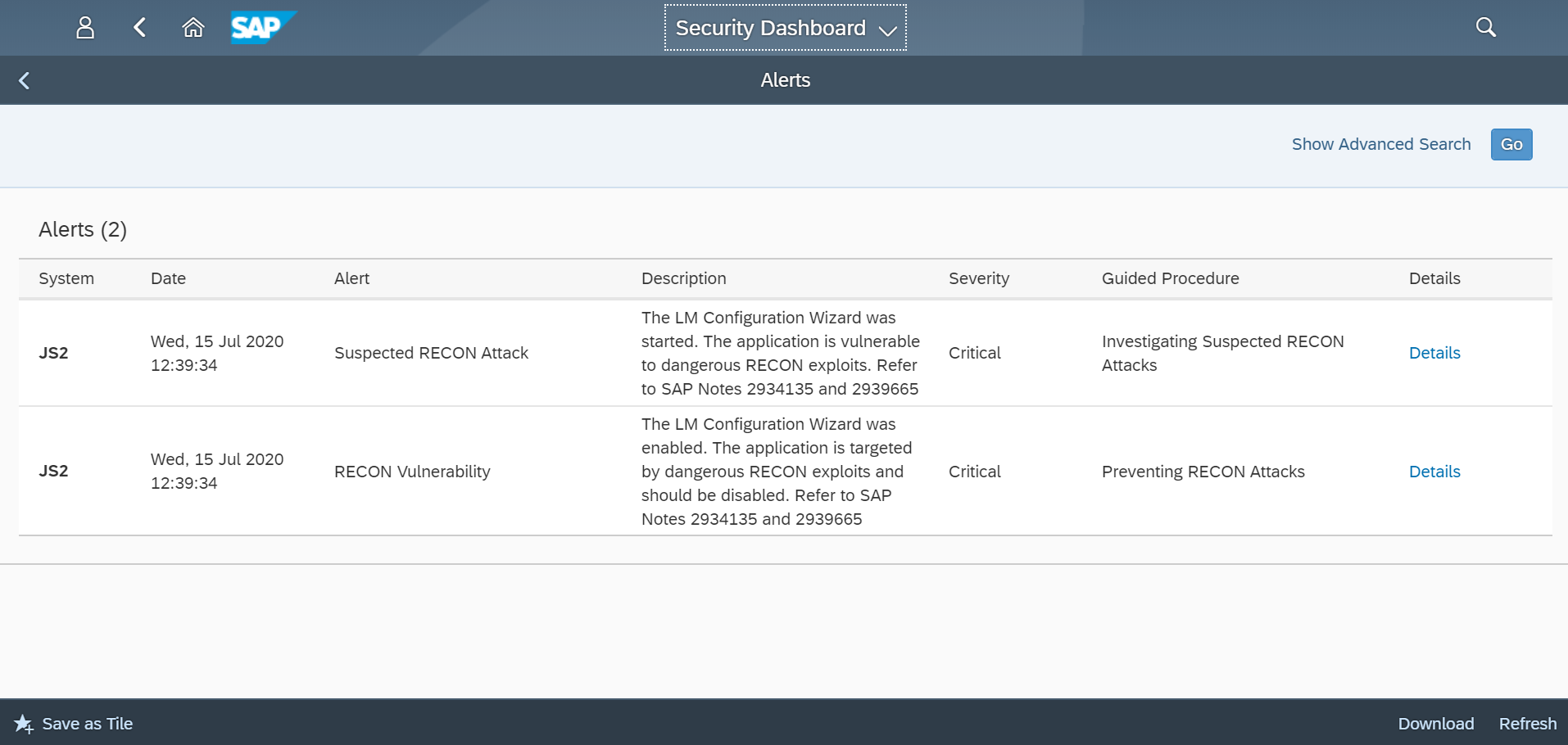
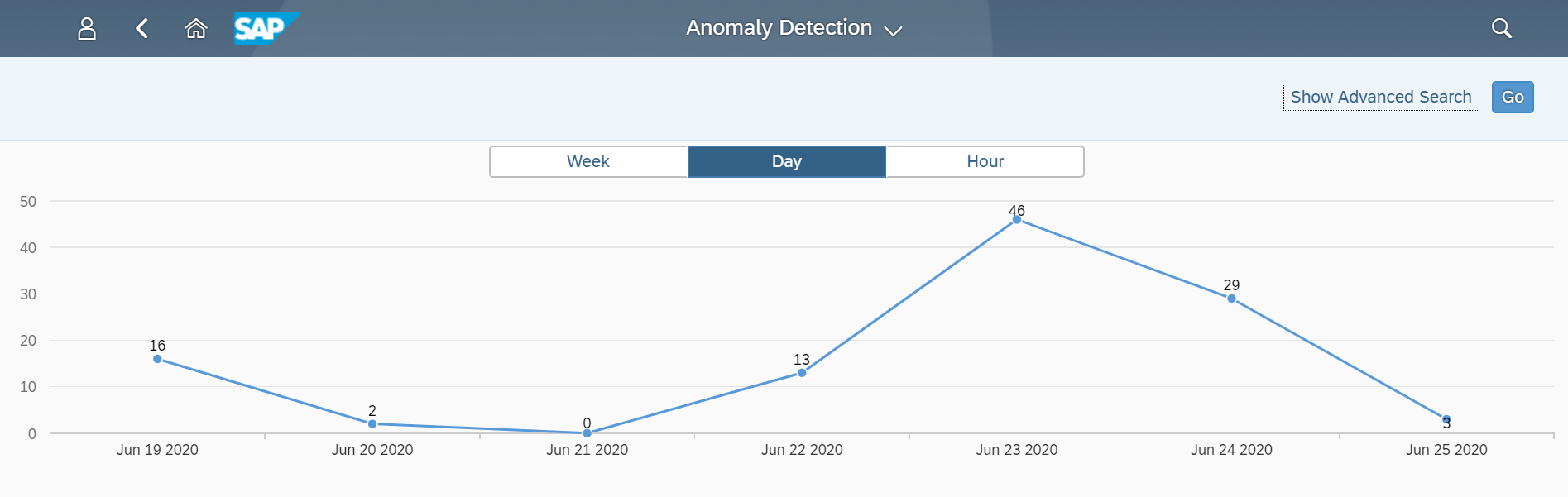
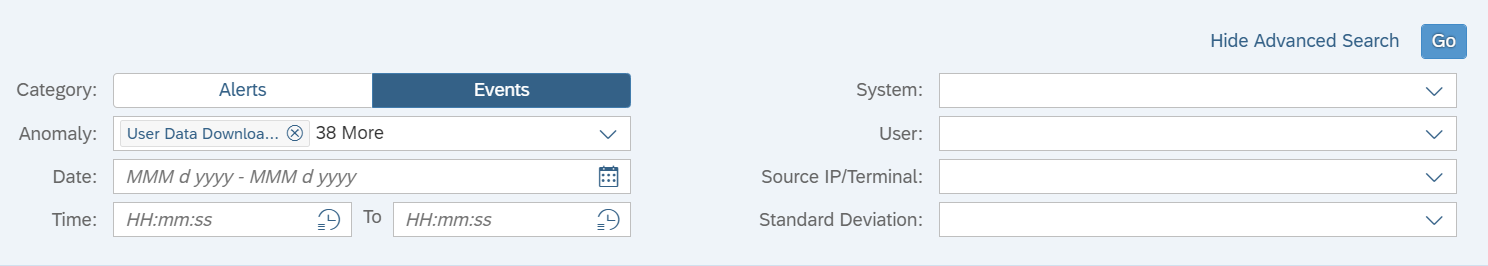
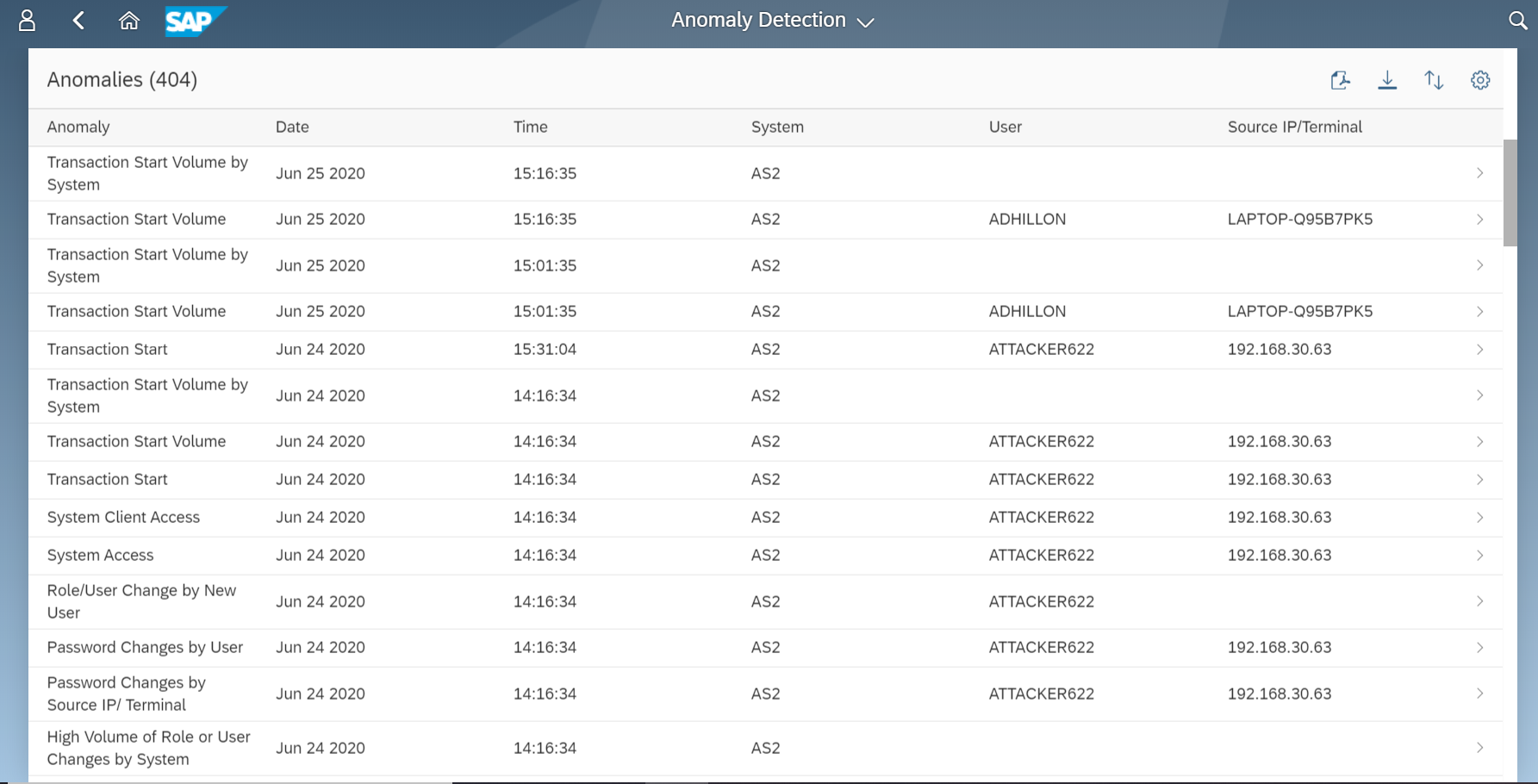
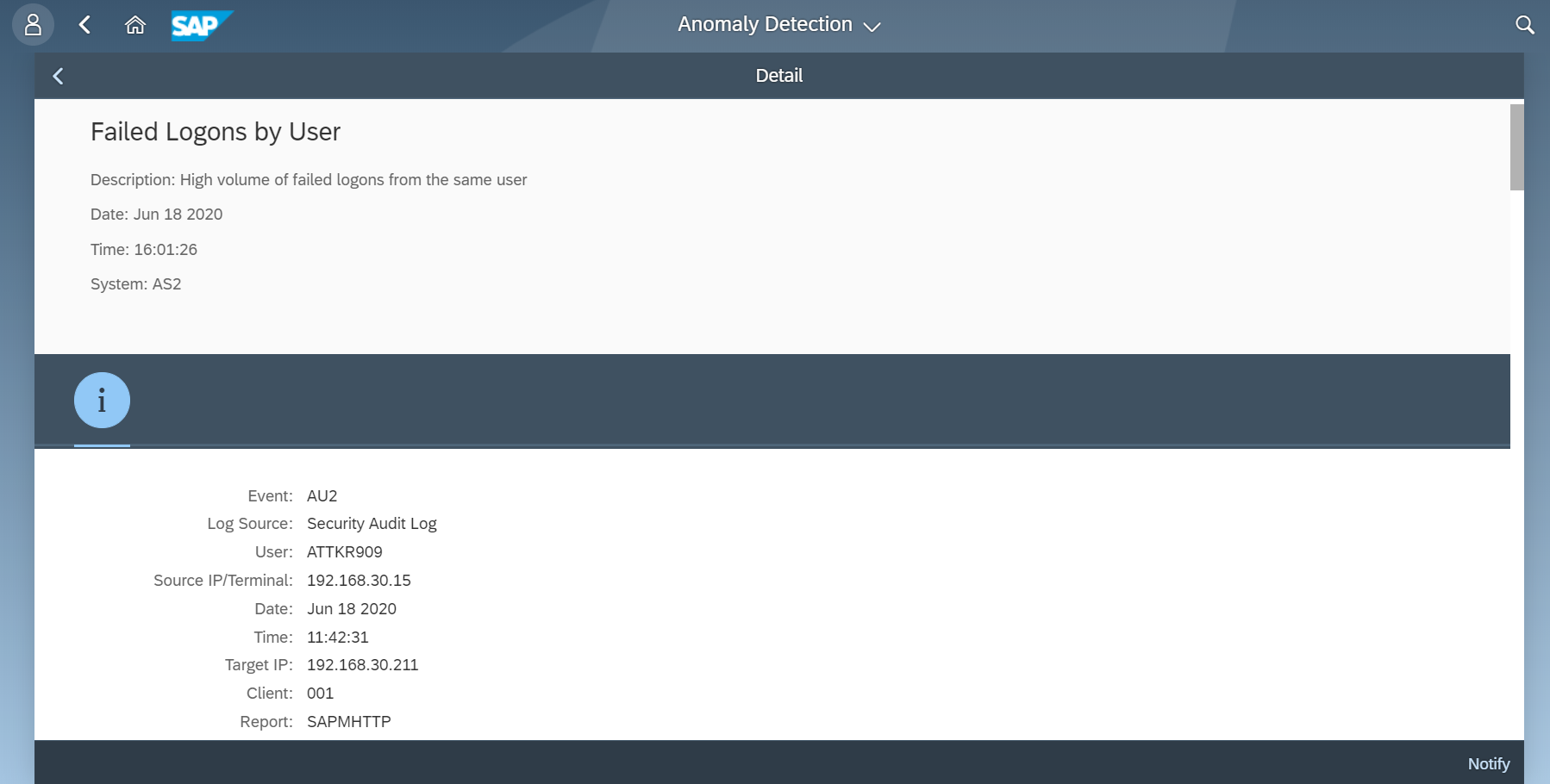
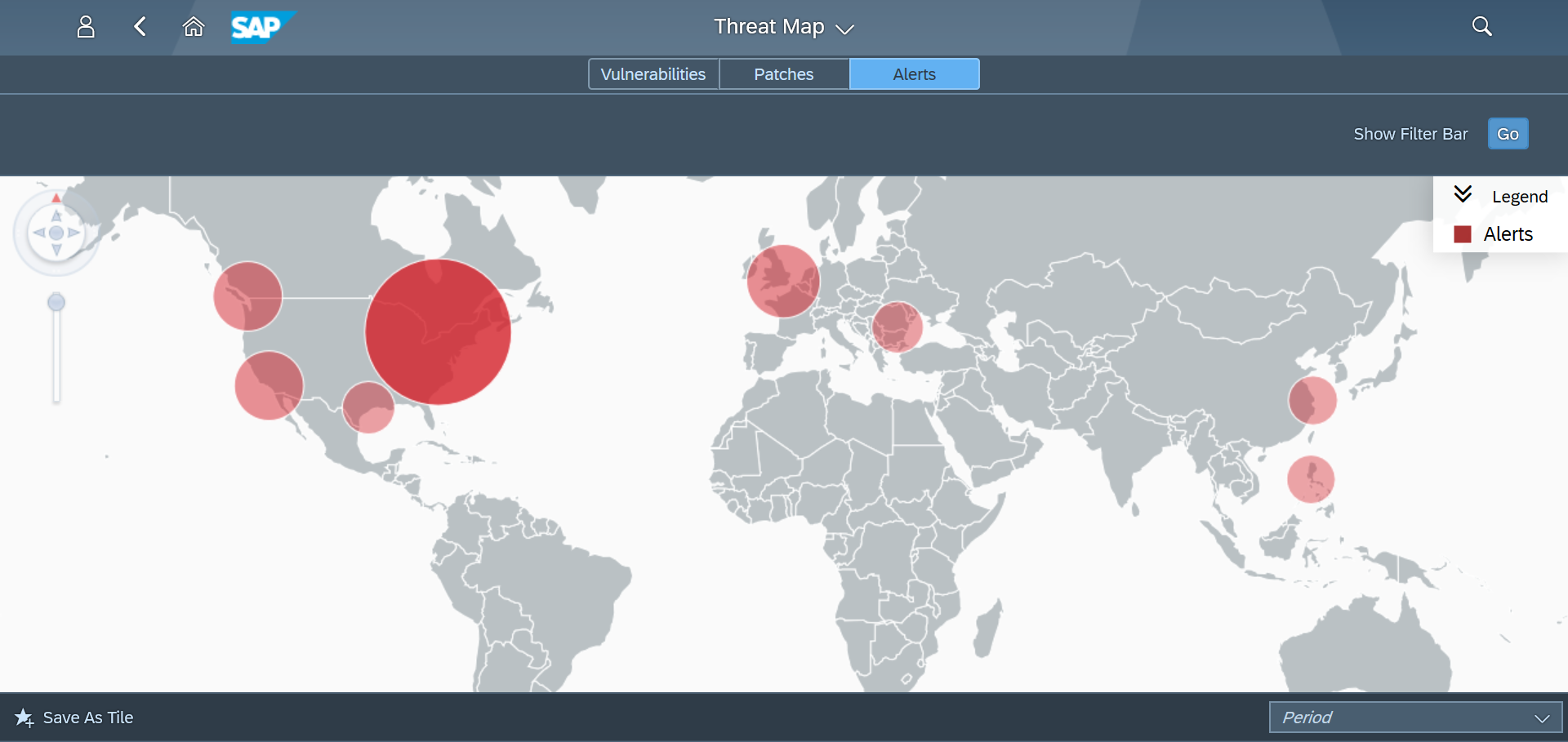
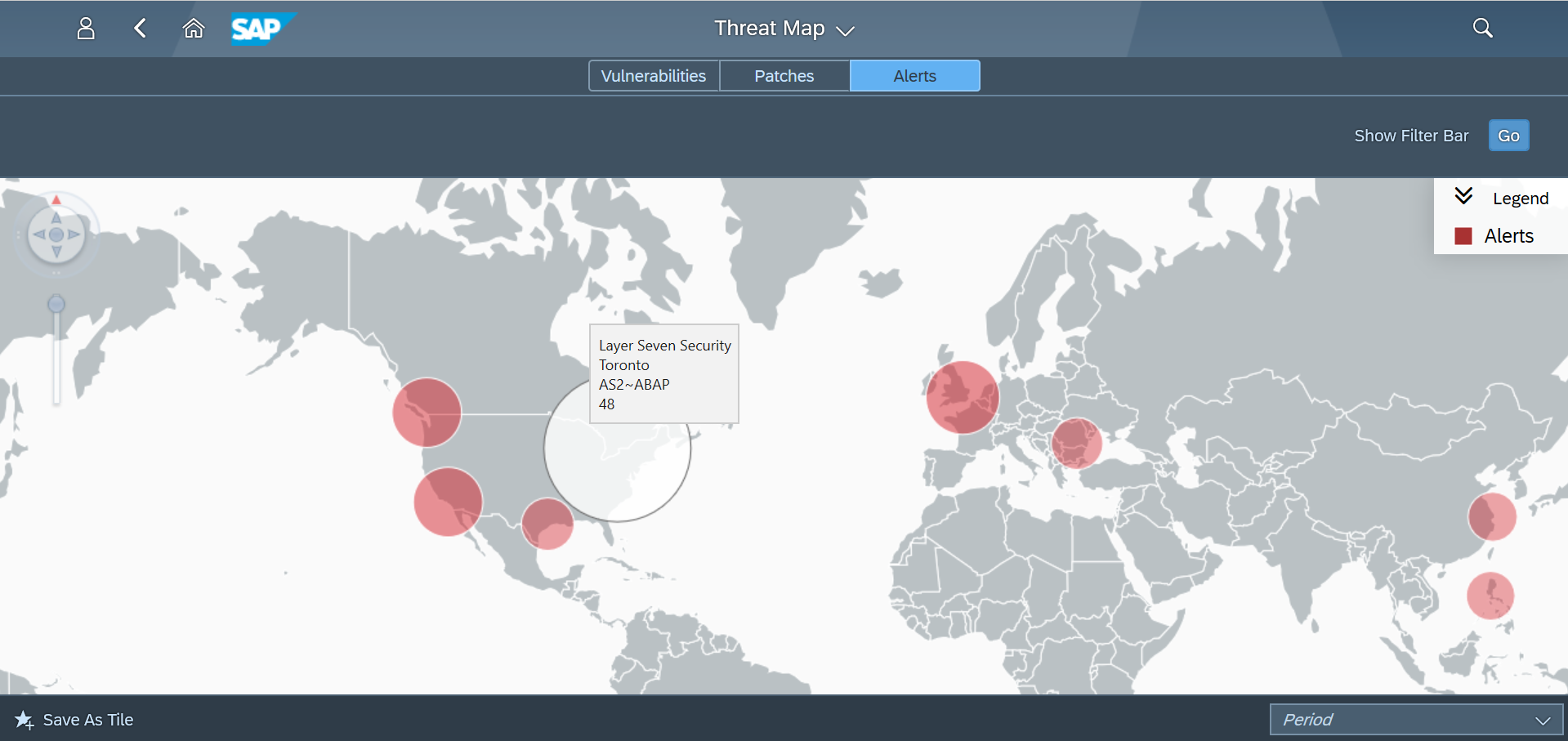
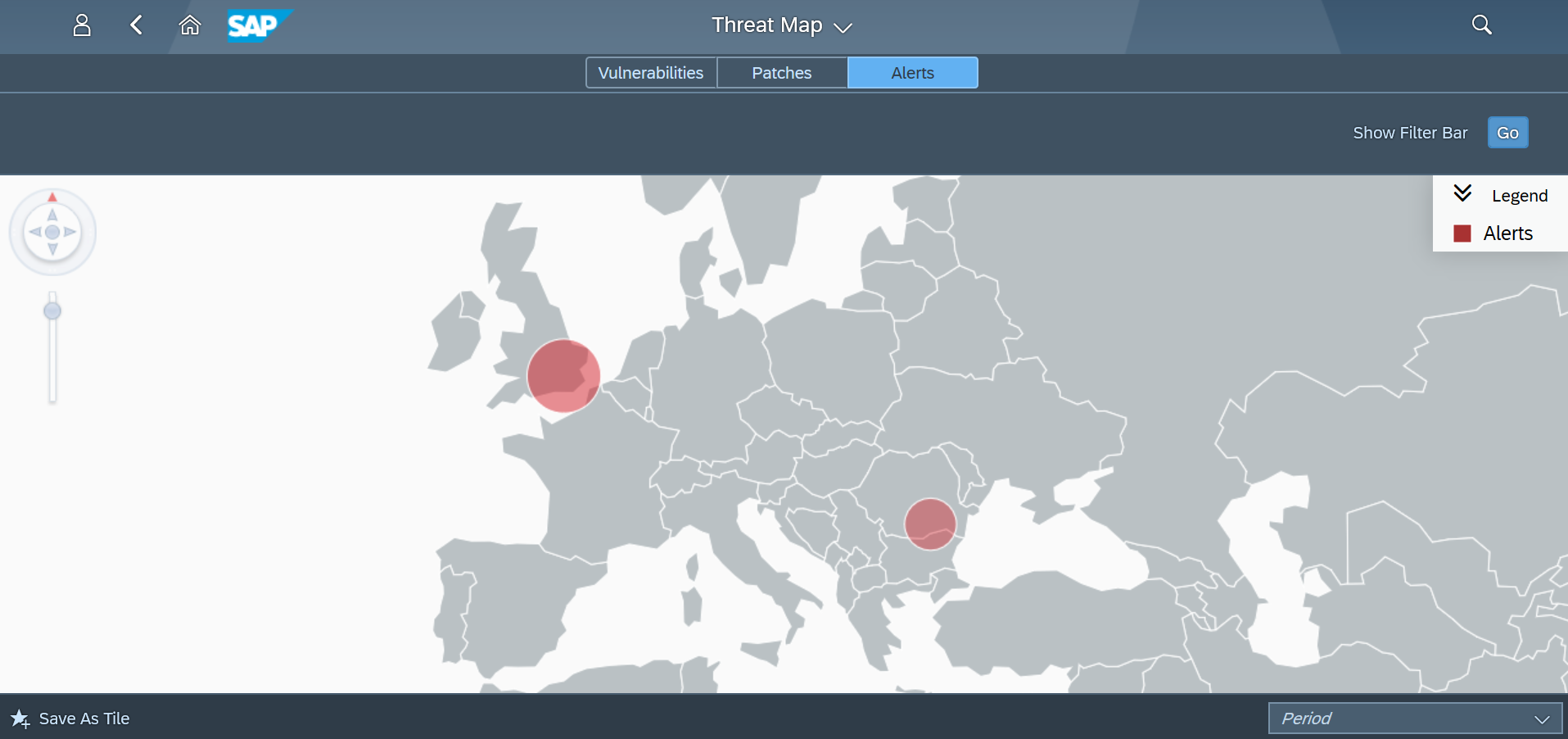
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP Solution Manager monitors Java application logs to detect the signature of RECON exploits. This includes enabling and executing the vulnerable application. The Extension also detects the creation of new administrative users and connections by new users or source IP addresses using anomaly detection. RECON alerts can be investigated using the incident response procedures Preventing RECON Attacks and Investigating Suspected RECON Attacks.
Email and SMS notifications are triggered for RECON alerts. The alerts can also be monitored in Solution Manager using the Alert Inbox, System Monitoring, and other applications. They can also be integrated with SIEM solutions for cross-platform monitoring. Custom alarms can be added to the Fiori launchpad to notify users of suspected RECON exploits.