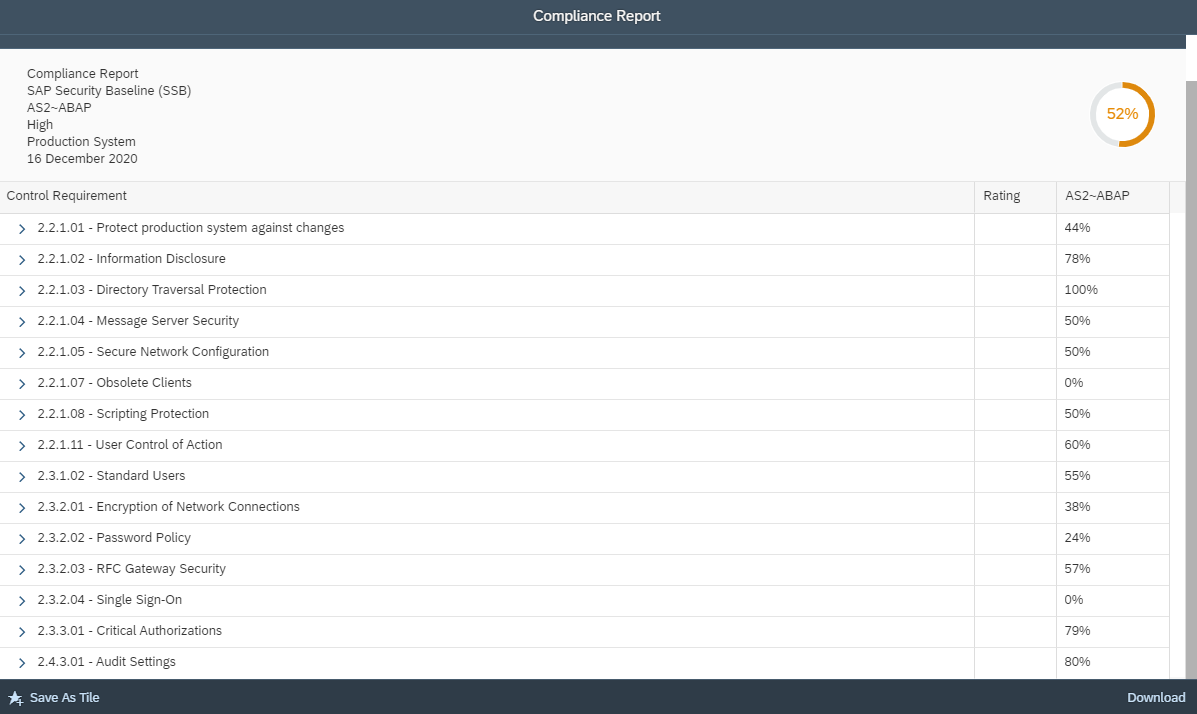
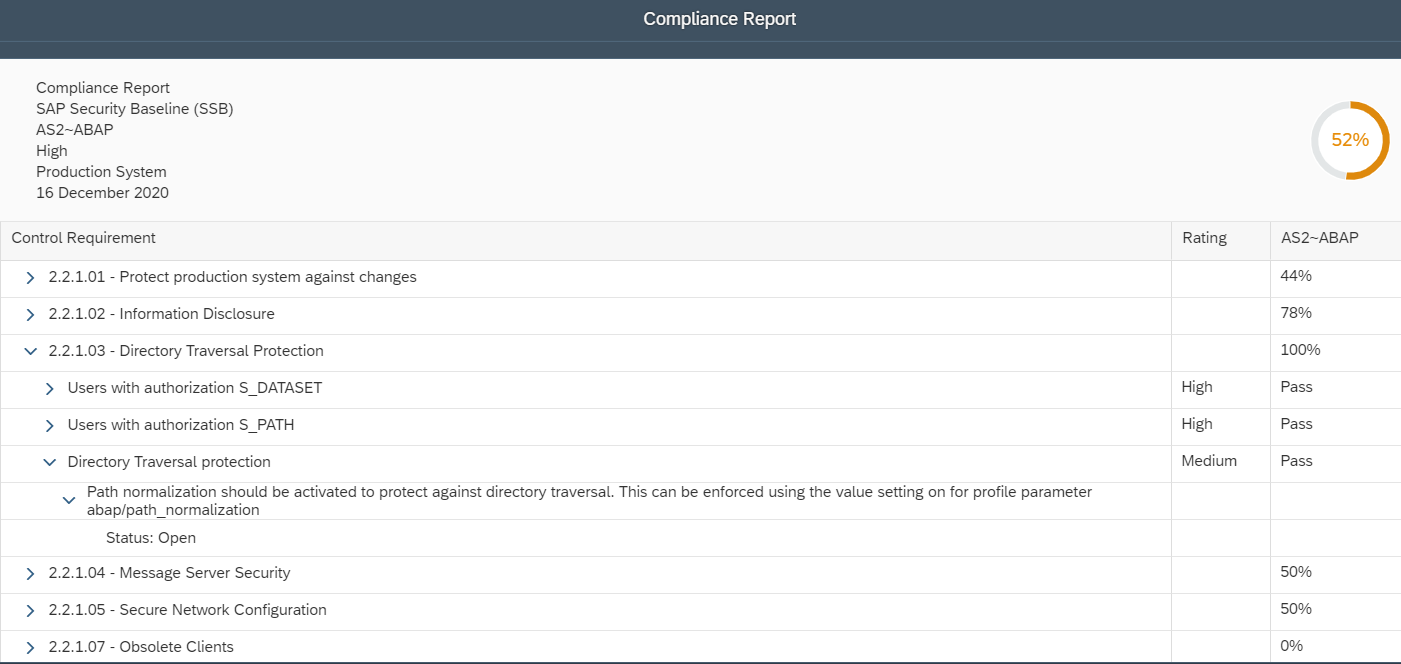
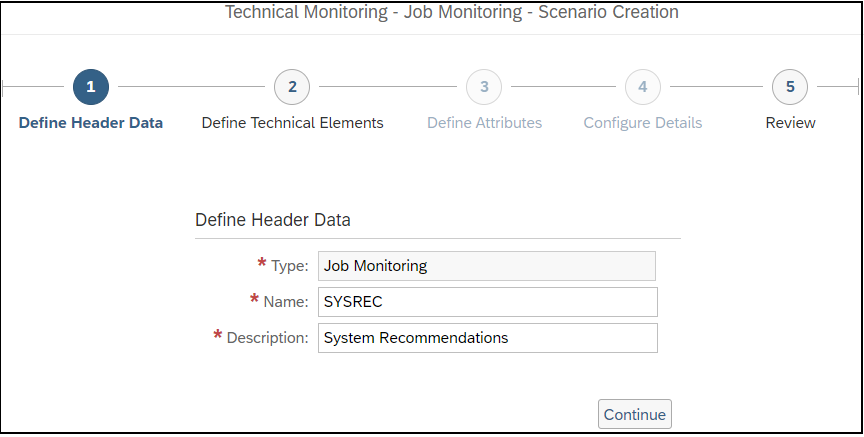
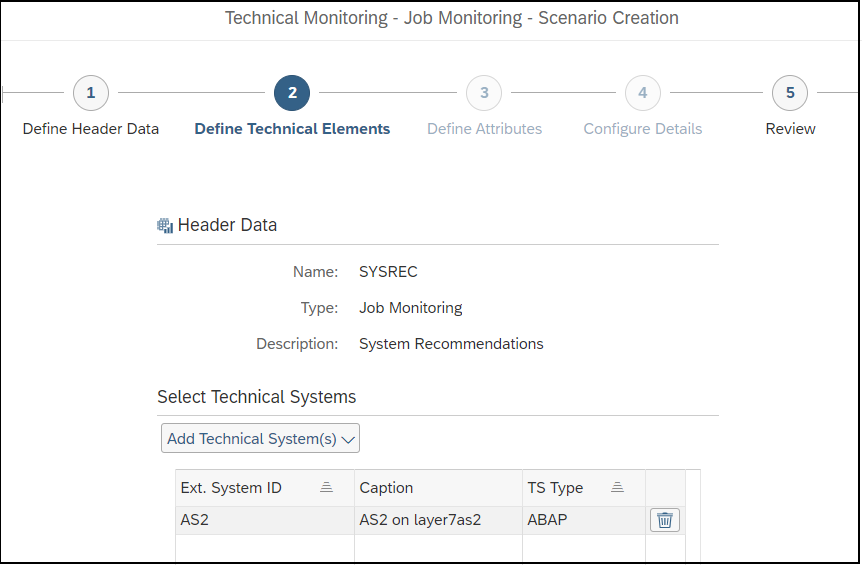
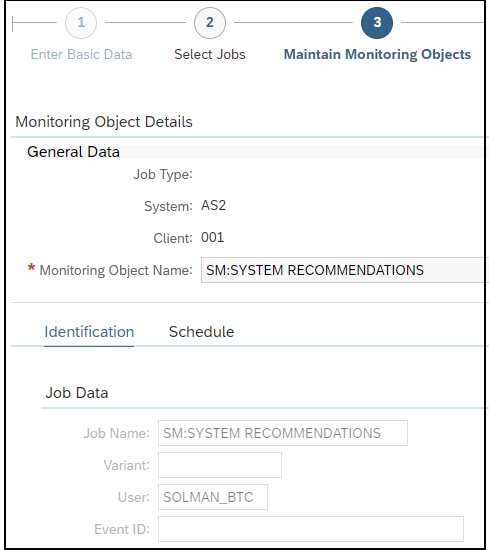
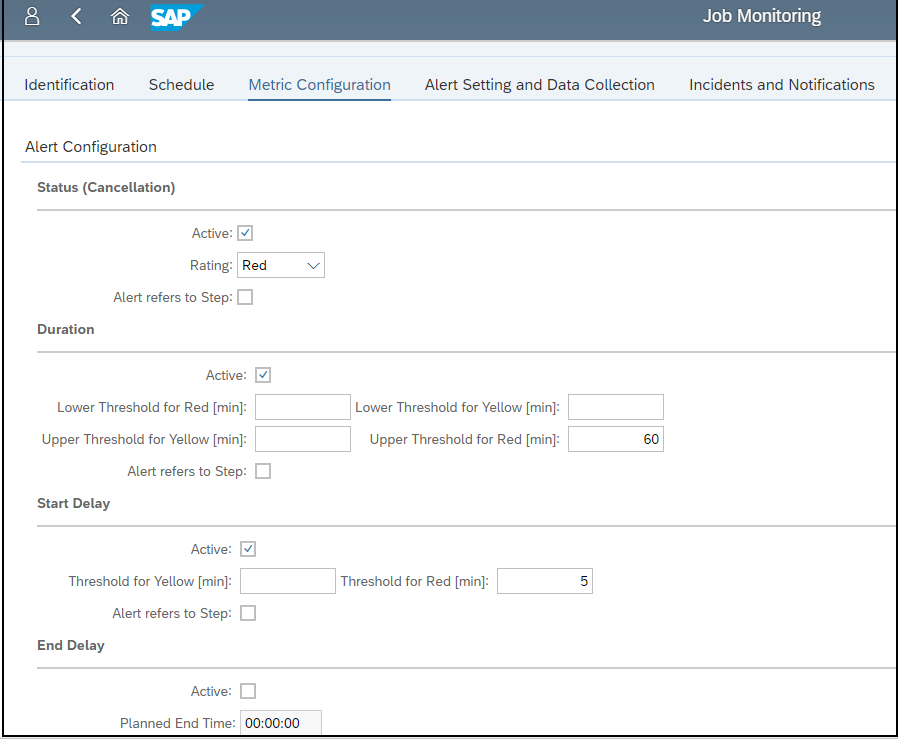
Layer Seven Security’s Cybersecurity Extension for SAP® Solutions Achieves SAP® Certification as Integrated with SAP NetWeaver®
Toronto, Canada – March 8, 2021 – Layer Seven Security today announced its Cybersecurity Extension v3.4 for SAP® Solutions has achieved SAP®-certified integration with the SAP NetWeaver® technology platform. The solution has been proven to integrate with SAP solutions, providing automated vulnerability management, threat detection and incident response for SAP applications and infrastructure.
“We are delighted to announce that our Cybersecurity Extension v3.4 for SAP Solutions has achieved SAP-certified integration with SAP NetWeaver,” said Ian Thomson, Chief Operating Officer at Layer Seven Security. “The certification will support the successful integration of the extension in SAP landscapes, helping customers to protect business-critical SAP systems against the threat of cyber attacks.”
The SAP® Integration and Certification Center (SAP ICC) has certified that Cybersecurity Extension v3.4 for SAP Solutions integrates with SAP NetWeaver. Technology or infrastructure products that have SAP-certified integration with SAP NetWeaver have proven to interoperate with the technology platform.
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP Solutions is now listed in the SAP Certified Solutions Directory.
Layer Seven Security is a partner in the SAP PartnerEdge® program. As such, it is empowered to build, market and sell software applications on top of market-leading technology platforms from SAP. The SAP PartnerEdge program provides the enablement tools, benefits, and support to facilitate building high-quality, disruptive applications focused on specific business needs – quickly and cost-effectively. The program provides access to all relevant SAP technologies in one simple framework under a single, global contract.
About Layer Seven Security
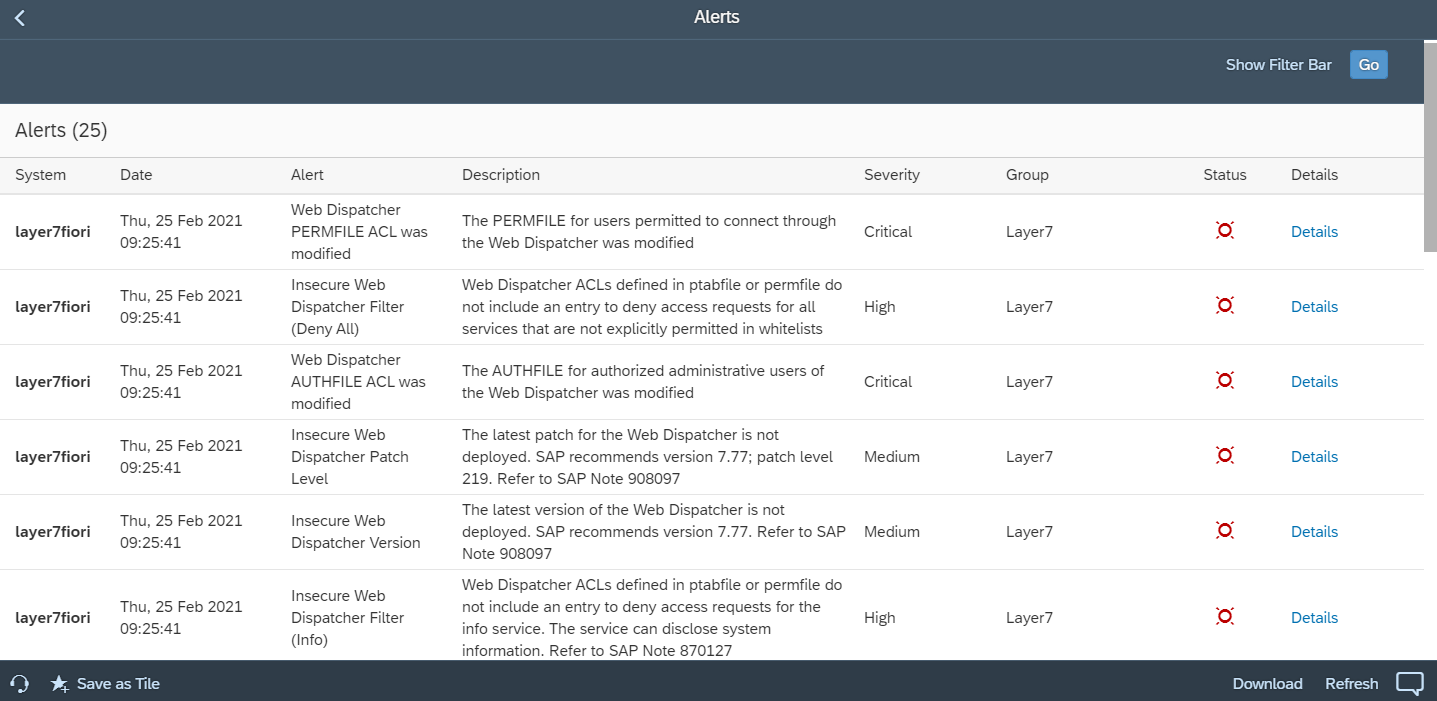
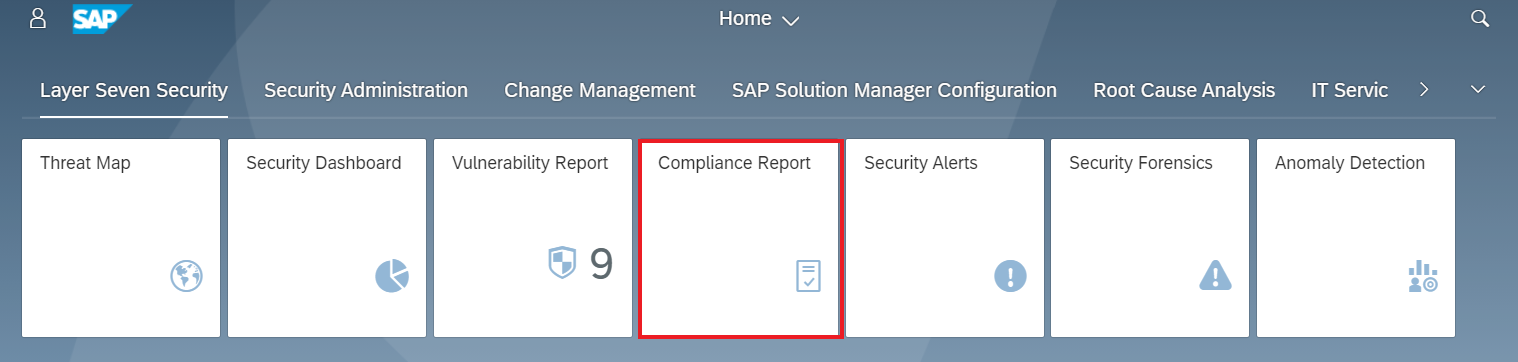
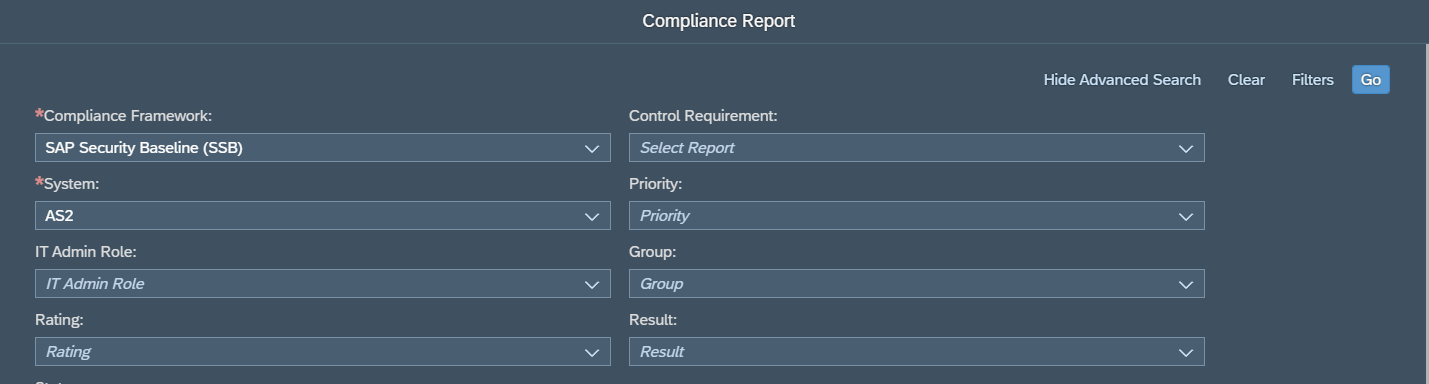
Layer Seven Security is an SAP partner, headquartered in Toronto, Canada. The company’s Cybersecurity Extension for SAP® Solutions performs advanced security diagnostics and monitoring for SAP systems. The Extension delivers real-time security intelligence for cloud and on-premise SAP systems including SAP HANA®, ABAP® and J2EE platforms. It supports security monitoring across the SAP system stack including application, database, operating system, and program layers, as well as components such as the SAProuter and SAP Web Dispatcher.

###
SAP and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP SE in Germany and other countries. Please see https://www.sap.com/copyright for additional trademark information and notices. All other product and service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective companies.
Any statements in this release that are not historical facts are forward-looking statements as defined in the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. All forward-looking statements are subject to various risks and uncertainties described in SAP’s filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, including its most recent annual report on Form 20-F, that could cause actual results to differ materially from expectations. SAP cautions readers not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements which SAP has no obligation to update and which speak only as of their dates.