GDPR Compliance with SAP Solution Manager 7.2
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) will be enforceable throughout the European Union in less than a month. The regulation specifies how personal data should be managed and applies to organizations that collect data on EU citizens, regardless of whether or not they are located within the EU. GDPR requirements include data protection measures to secure systems that store or process personal data (privacy by design). They also include breach notification requirements that oblige organizations to notify customers within 72 hours of any compromise of their personal data. Organizations may be fined up to €20 million or 4% of global turnover for non-compliance, whichever is greater. Therefore, GDPR is regarded as the most stringent data security framework to date.
In SAP environments, the requirement for privacy by design can be met by hardening and patching systems using Service Level Reporting, Security Dashboards, and System Recommendations, available in SAP Solution Manager. This will support automated monitoring for security vulnerabilities and missing security patches that could be exploited to target SAP systems and compromise personal data. Interface Monitoring and the Monitoring and Alerting Infrastructure (MAI) in Solution Manager can be used to perform event monitoring to detect potential attacks in near-time.
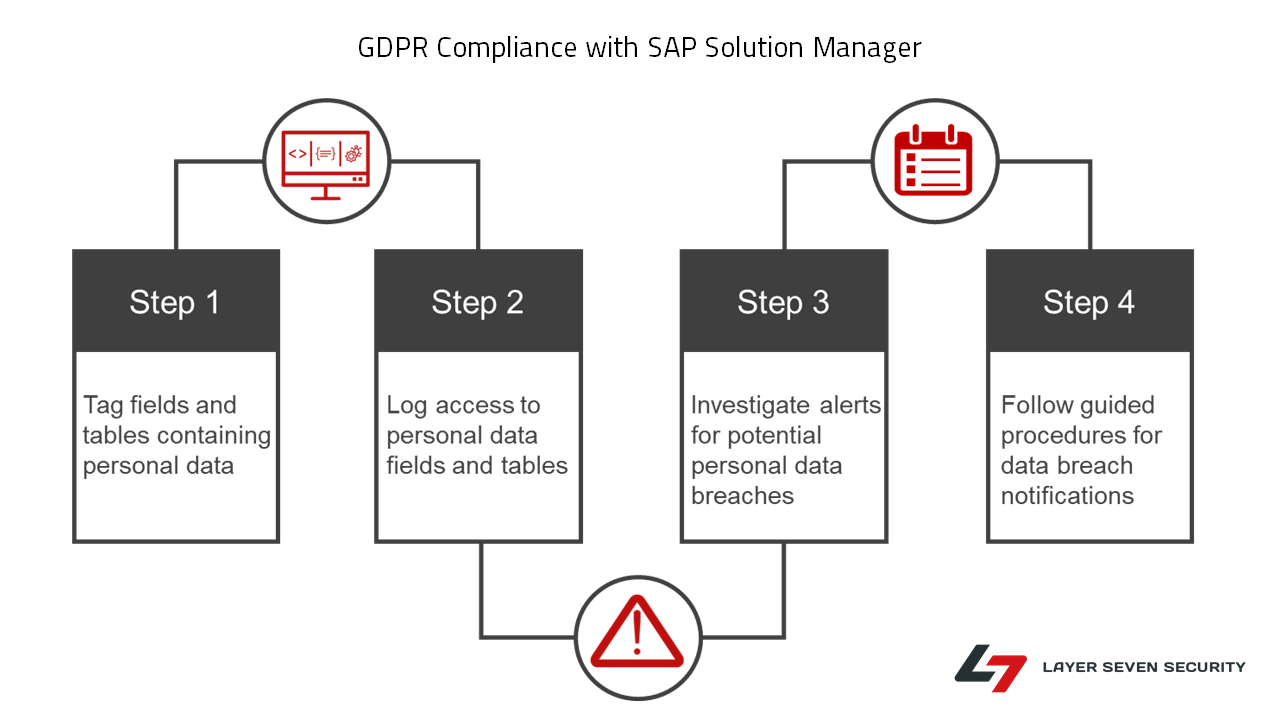
The requirement for breach notification can be met through systematic monitoring of access to personal data, supported by incident response procedures aligned to GDPR disclosure standards. This can also be performed using SAP Solution Manager. The flowchart below summarizes the process for logging access to personal data in SAP systems, automatically monitoring logs for access violations and finally, responding to potential breaches using guided procedures.
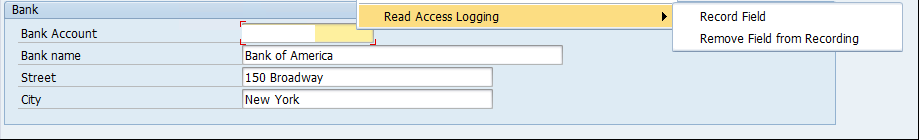
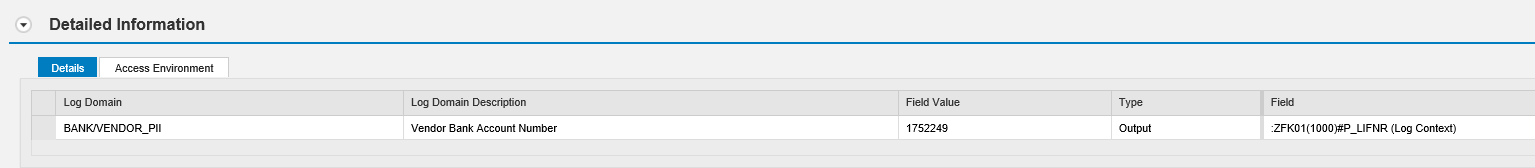
The logging for access to personal data is performed using SAP Read Access Logging (RAL). RAL supports logging for access and changes to sensitive data fields in SAP systems, including custom fields. It can also be used to log access to SAP tables containing bulk records of sensitive data. Data fields and tables are tagged for logging using RAL scenarios. Once configured, RAL configurations can be transported across systems within a landscape. User exclusion lists can be maintained to exclude authorized users from logging. The RAL recording below captures access to banking information accessed through vendor maintenance in SAP ERP.
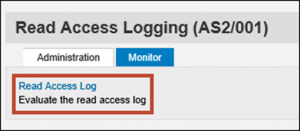
Access violations are logged in RAL tables. The raw log can be viewed using SRALMONITOR. In the example below, RAL has logged access to banking data belonging to vendor number 1752249 by the user ATTACKER on April 24, 2018 at 1.39 PM. Click on each image to enlarge.
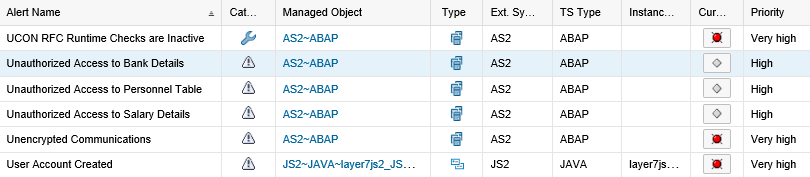
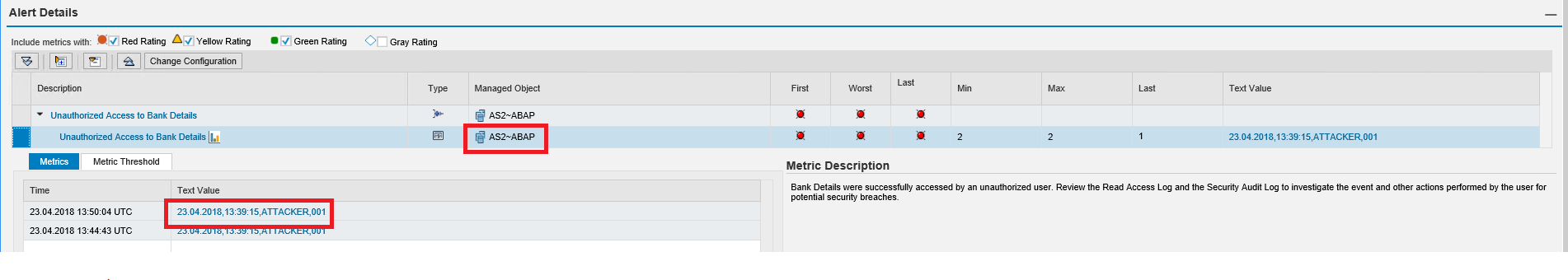
The next step involves automated monitoring of RAL logs and triggering alerts and notifications for suspected breaches to personal data. This is performed using the MAI in SAP Solution Manager. MAI continuously monitors the contents of RAL tables as often as every minute. The MAI Event Calculation Engine alerts for each incident recorded in RAL tables and triggers email notifications to security analysts.
The alert details include the date and time of the event, the impacted system and client, and the name of the user that accessed the personal data.
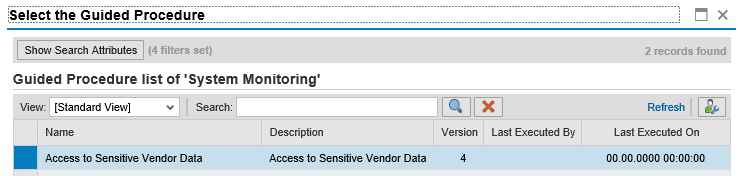
The final step involves incident response. Analysts can execute guided procedures to investigate suspected breaches of personal data directly from each alert. Once executed, guided procedures provide standard operating procedures including automated steps for security investigations.
Guided procedures provide a framework for ensuring incident response procedures are aligned with GDPR requirements including disclosures to impacted customers, employees or other parties within the reporting window mandated by the regulation. Completed guided procedures are archived to provide an audit trail for compliance purposes.
The comprehensive coverage provided by SAP Solution Manager for the privacy by design and monitoring and disclosure requirements of GDPR presents a powerful alternative to third party software platforms. Contact Layer Seven Security to discuss how Solution Manager can help your organization become and stay GDPR-compliant.