Code Vulnerability Management with SAP Solution Manager
Custom Code Management (CCM) in SAP Solution Manager can enable you to take control of custom developments by providing transparency into custom objects in your SAP systems and analyzing the usage of custom code. It can also provide insights into security vulnerabilities in custom objects and packages.
CCM provides an overview of the custom developments in systems and identifies unused or redundant code based on usage statistics from Usage and Procedure Logging (UPL). Decommissioning entire programs or specific lines of code within programs if they are unused or redundant can minimize the attack surface and ensure that time and effort is not wasted managing code-level vulnerabilities in custom developments that are not serving a business need.
Decommissioning in CCM is complemented by tools such as the SAP Clone Finder which identifies custom code that is cloned from SAP standard and supports reverting back to standard code, wherever possible.
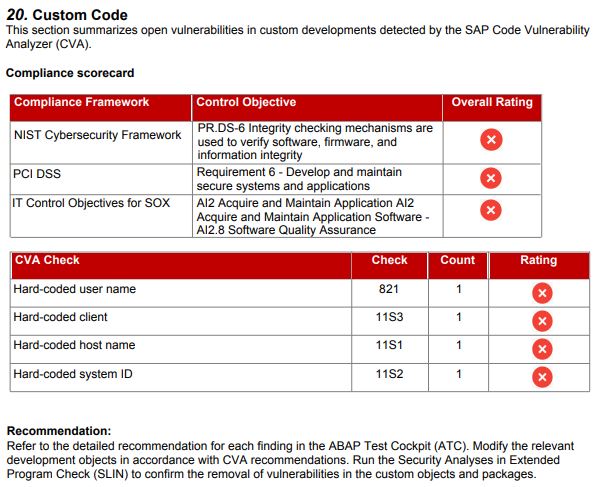
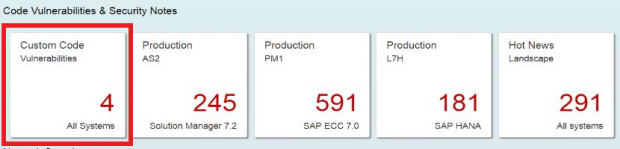
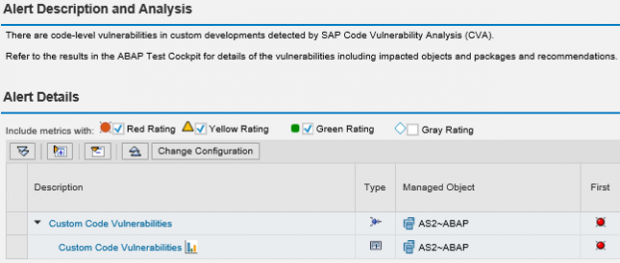
CCM displays the results of code checks performed using the ABAP Test Cockpit (ATC). This includes findings from SAP Code Vulnerability Analysis (CVA). CVA performs static application security testing for custom ABAP developments. The tool is used by SAP to scan and secure SAP-delivered code. Therefore, it enables SAP customers to enforce equivalent standards for the security of custom code as enforced by SAP for standard code. Note 1921820 provides details of the security checks performed by CVA. The details are also available in the SAP Community Network.
Enabling CCM is a prerequisite for monitoring the results of CVA checks in SAP Solution Manager. However, CCM is only available to Enterprise support customers and therefore is not available for customers on Standard support. Details of usage rights for Solution Manager are available at the SAP Support Portal.
Licensing restrictions prevent all SAP customers from integrating CVA results with Solution Manager to support holistic cybersecurity monitoring that includes managing risks at the system, user, event and code level.
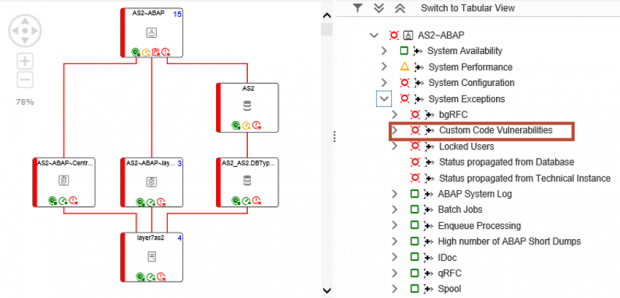
Layer Seven Security’s custom data connector for CVA resolves this issue by integrating CVA findings directly with the Configuration and Change Database (CCDB) in Solution Manager. This avoids the dependency on CCM and Enterprise support. The data is extracted by the connector from each target system to Solution Manager and automatically updated on a daily schedule. The extracted data is integrated with security reports, dashboards and alerts in Solution Manager to support centralized monitoring for cyber risks in SAP systems including vulnerabilities in custom code. The CVA connector is bundled with the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP Solution Manager.
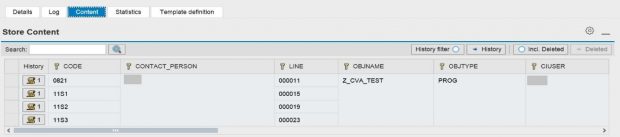
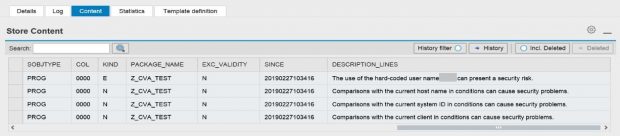
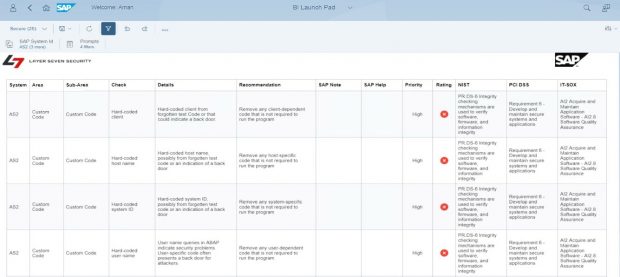
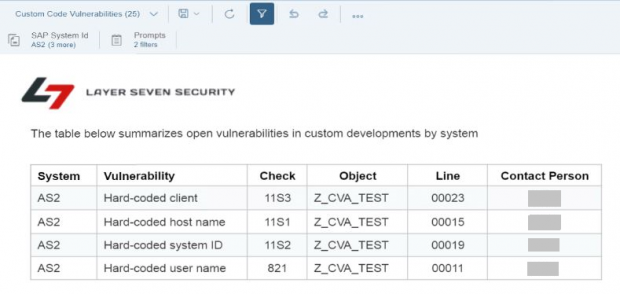
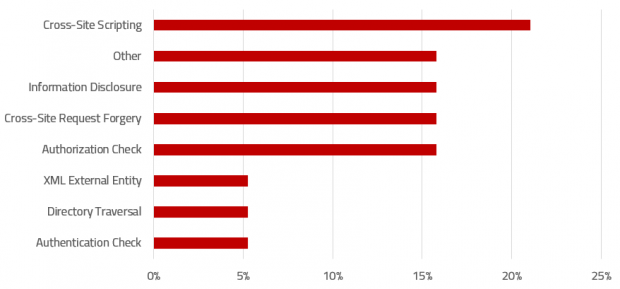
The raw data for CVA results can be viewed in the custom CCDB store ATC_RESULTS. Results include the check ID, object name, package name, developer name, impacted lines, and a description of each finding.
The findings are mapped to service level reports, web-based reports, and security dashboards in Solution Manager.
CVA results are also integrated with security alerts and email/ SMS notifications generated by SAP Solution Manager.