Key Security Findings from the RISE with SAP 2025 Benchmark Report

SAPinsider’s RISE with SAP 2025 benchmark report, co-sponsored by Layer Seven Security, was released in December. Based on a survey of 122 SAPinsider community members conducted between August and November 2025, the study focuses on customer adoption of SAP Cloud ERP Private (formerly referenced in the survey as RISE with SAP) and the factors shaping migration decisions. From a security standpoint, the most material finding is broad customer non-compliance with the shared model of responsibility, and more specifically, failure to implement and sustain SAP’s mandatory security hardening requirements documented in relevant SAP notes for SAP systems operating in SAP’s cloud delivery model.
Broad Non-Compliance with Customer Security Responsibilities
The report identifies a significant gap between SAP’s cloud security expectations and customer execution. While SAP delivers and operates key elements of the cloud platform, customers remain accountable for critical security outcomes, including secure configuration, access controls, and compliance with SAP-defined hardening standards.
Two key findings stand out:
- Less than half (45%) of respondents are aware of and actively following the shared responsibility model for SAP Cloud ERP Private security.
- Approximately one-third are aware of the model but do not follow it rigorously, indicating that a majority of organizations either do not fully understand or are not consistently executing their responsibilities.
This is not a minor administrative gap. The report explicitly warns that failure to follow both the shared responsibility model and SAP’s mandatory hardening requirements leaves systems open to attack. For leadership teams, the implication is straightforward: cloud migration does not transfer accountability for SAP security outcomes to SAP. If required customer-side controls are not implemented and maintained, the organization bears the risk.
Hardening Requirements Are Frequently Missed
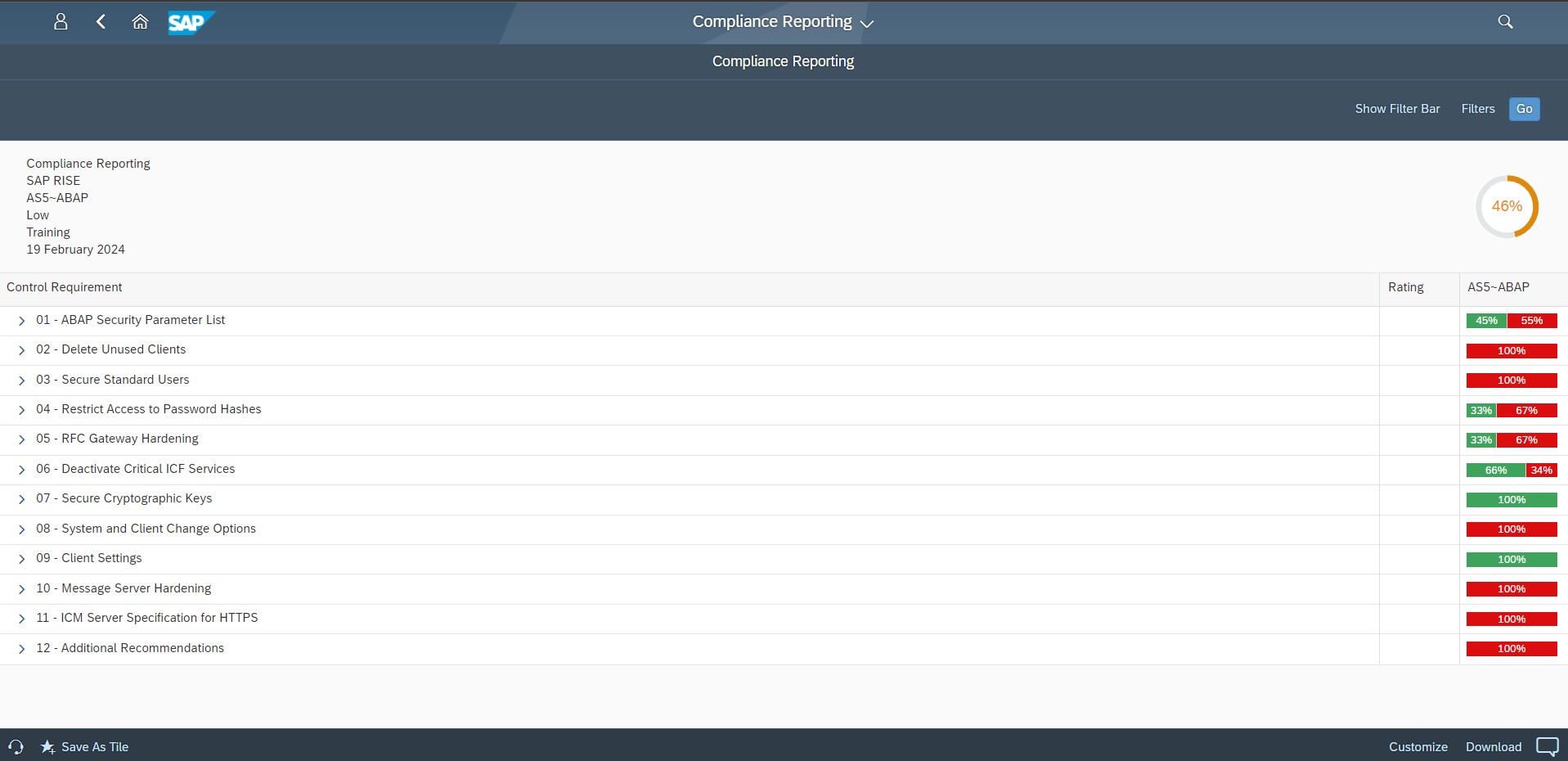
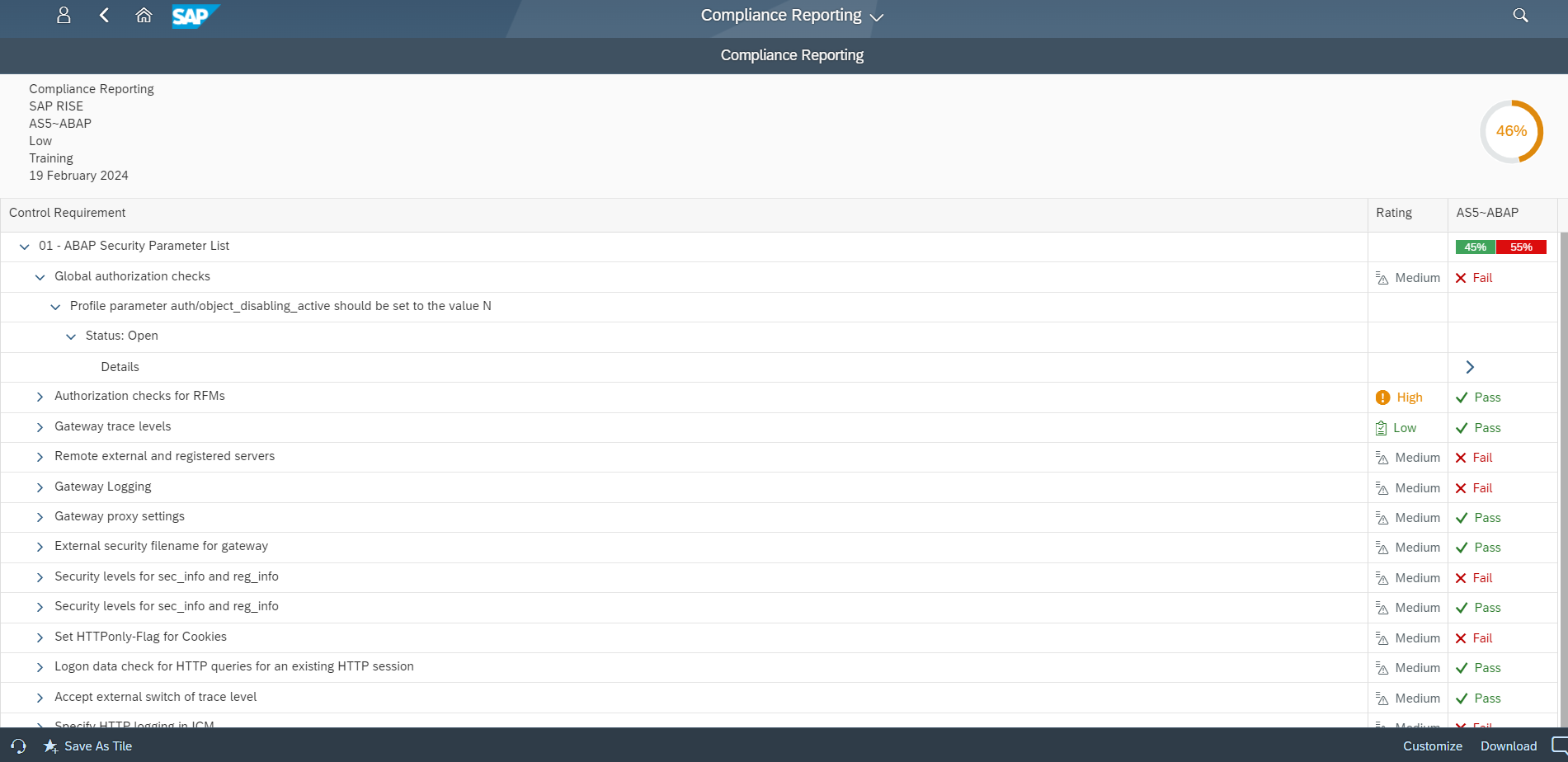
The report goes beyond general security awareness and points to a more specific and operational problem: customers running SAP Cloud ERP Private in SAP’s cloud delivery environment must comply with SAP’s mandatory security parameters and hardening requirements, as documented in relevant SAP notes for ABAP, HANA and Java systems and related components. This includes notes 3250501, 3480723 and 3381209.
The report underscores that non-compliance with these requirements materially increases exposure. In business terms, required hardening defines baseline expectations for how SAP systems must be configured to reduce preventable attack paths. Failure to apply those settings—consistently and over time—creates vulnerabilities that can persist in SAP solutions.
Compliance Is a Moving Target
A key challenge highlighted in the report is that SAP security compliance is not static. SAP regularly updates mandatory parameters and hardening guidance in response to new threats, vulnerabilities, platform changes, and evolving best practices. As a result, a system that was compliant at go-live may drift out of compliance over time even without major architectural change.
This creates a practical operational risk: compliance must be managed as an ongoing discipline, not a one-time implementation deliverable. Organizations need repeatable processes to track new and updated SAP security guidance, assess its applicability, validate their current posture, and remediate gaps across their SAP landscapes.
Business Risk of Non-Compliance: Support, Liability, and Exposure
The consequences of non-compliance extend beyond technical risk and into contractual and legal exposure:
- Support risk: When hardening requirements and mandatory parameters are not implemented, incident response becomes more complicated. In high-severity security situations, customers may face delays and friction in diagnosis and remediation, and their position with SAP support can be weakened if the environment is not aligned with required security standards.
- Legal and regulatory risk: In the event of a data breach, organizations are often required to demonstrate that they followed vendor-prescribed security requirements and reasonable security practices. If an organization cannot demonstrate compliance with SAP’s documented security hardening guidance, it can weaken the company’s defensibility, increase regulatory scrutiny, and raise the likelihood of fines, penalties, litigation, and reputational harm. Ultimately, under a shared responsibility model, the customer retains accountability—and therefore liability—for customer-controlled security controls.
Additional Survey Indicators Relevant to Security Posture
Although the report is broader than security, several survey results reinforce the importance of establishing a robust cloud security operating model:
- 80% of respondents identify comprehensive monitoring to ensure system health and security as a key requirement for their ERP transformation and innovation initiatives.
- 79% indicate the need for best-practice compliance checks that avoid outages, underscoring that organizations see compliance and stability as tightly linked.
These findings align with the report’s security message: maintaining control effectiveness requires continuous monitoring and governance, not periodic reviews.
How the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP from Layer Seven Security Addresses These Challenges
The report’s core security finding—customer non-compliance with evolving security requirements—directly aligns with the capabilities of Layer Seven Security’s Cybersecurity Extension for SAP. The solution is designed to help organizations operationalize their security responsibilities in SAP RISE / Cloud ERP environments where configuration, compliance, and threat conditions change over time.
At a business level, it supports three outcomes:
- Continuous monitoring against current hardening requirements: Automated checks against SAP security baselines help identify non-compliance as SAP standards evolve, rather than relying on periodic manual reviews.
- Reduced risk from compliance drift: Ongoing visibility into configuration posture helps prevent gradual degradation of security controls due to system change, integration expansion, or operational turnover.
- Improved audit and support readiness: Continuous evidence of compliance strengthens governance, improves audit defensibility, and supports more effective engagement during incidents and escalations.
This approach acknowledges the operational reality emphasized by the report: compliance is a moving target, and organizations need a sustainable mechanism to remain aligned to SAP’s required security standards.
Key Takeaways
The most significant security issue identified in the SAPinsider RISE with SAP 2025 report is customer non-compliance. A majority of organizations are not fully executing their responsibilities under the shared security model, and the most consequential example is failure to comply with SAP’s mandatory hardening requirements documented in SAP notes. Because these requirements evolve over time, compliance must be treated as an ongoing operational discipline—supported by clear accountability, continuous monitoring, and repeatable remediation processes—to reduce operational, legal, and reputational risk in SAP Cloud ERP Private environments.
The full benchmark findings will be presented by Robert Holland, Vice President and Research Director at SAPinsider, on Tuesday, January 13, 2026. You can register for the webinar at SAPinsider.