Configuration and Security Analytics with SAP Focused Run
SAP Focused Run supports real-time monitoring for high-volume SAP landscapes and customers with advanced requirements for system management, user and integration monitoring, and vulnerability management. Configuration and Security Analytics (CSA) in SAP Focused Run applies security policies to discover vulnerabilities in SAP systems. The policies read the contents of configuration, software and user-related stores in the Configuration and Change Database (CCDB). The CCDB stores are refreshed daily using the Simple Diagnostics Agent (SDA), installed in SAP systems monitored by Focused Run.
This article explores capabilities in CSA for tuning security checks using exclusions, configuring alerts for critical vulnerabilities, and investigating security-related changes reported by CSA.
Exclusions can be applied to exclude specific checks in security policies. In the example below, we have applied an exclusion to exclude a check that validates the status of the standard DDIC user. The first step is to open to CSA in the Advanced Configuration Monitoring workgroup.

The next step is to select the relevant policy and select Exemption for Policies.
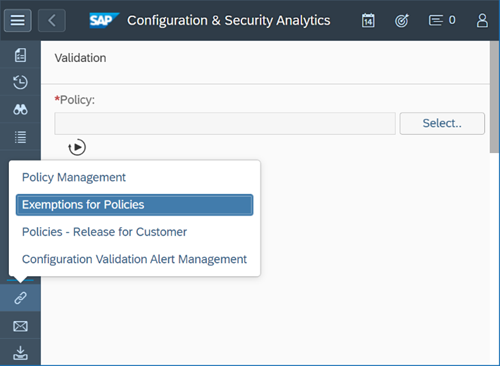
Select Create to add the exemption. Select the Check ID based on the available checks in the policy and add an Exception ID and Description.
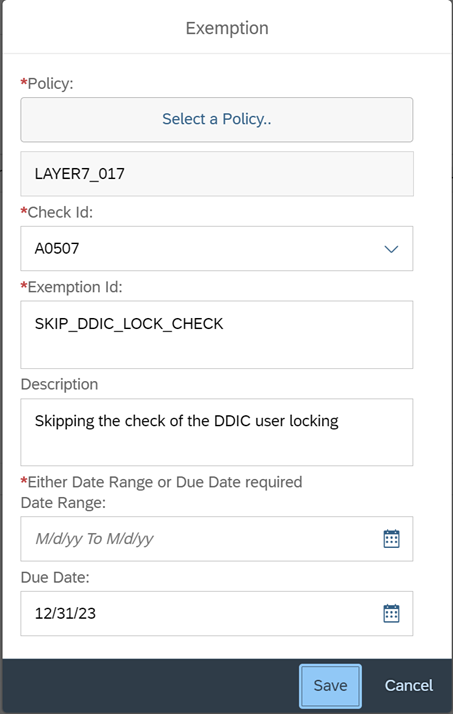
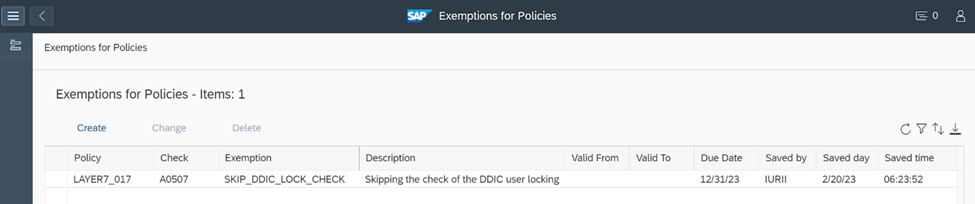
You can add a date range if the exclusion is temporary and should be automatically removed after a target date. Once saved, the check will be excluded from the policy. Exemptions can be maintained and deleted after they are applied.
Alerts for systems that fail checks in security policies can be configured using Configuration Validation Alert Management.
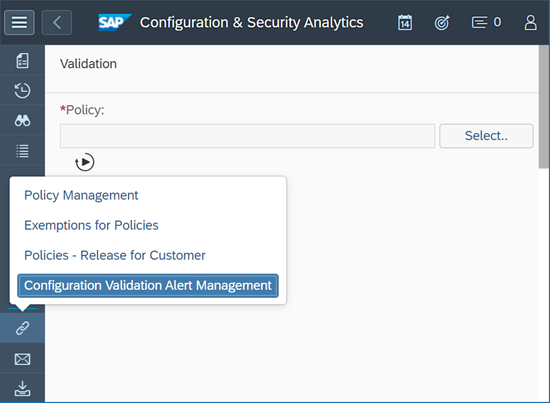
Select Create and add an Alert ID and Description. The Alert Source should be set to Configuration Validation – Policy. Select the Policy and maintain options for Aggregation Level, Scope, Frequency and Severity. Select ON and click on Save to activate the alert.
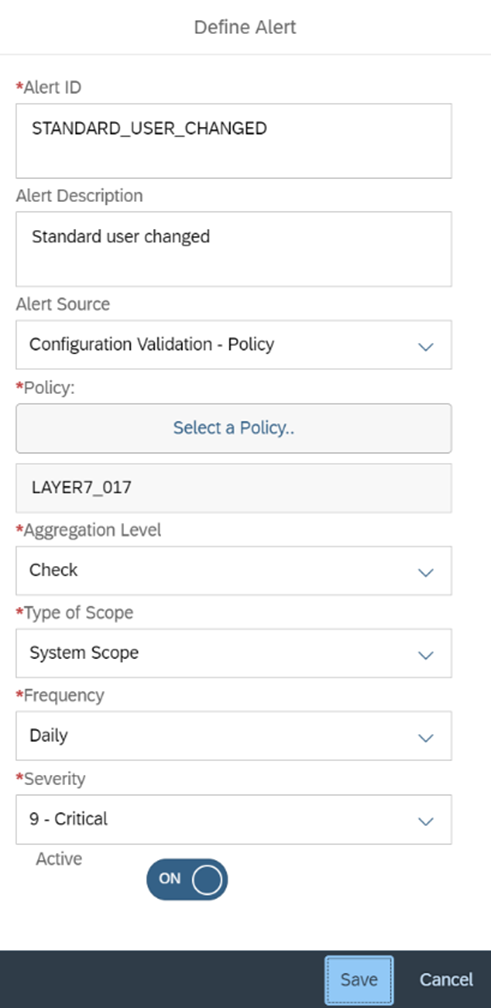
Alerts can be configured for specific systems or groups based on Customer ID, Data Center, IT Admin Role, Lifecyle Status, or Networks.
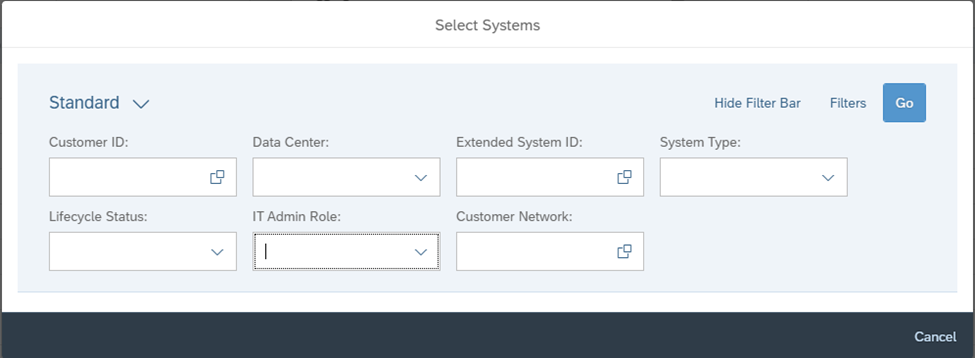
IT Admin Role can be used to apply alerts for systems based on environments.
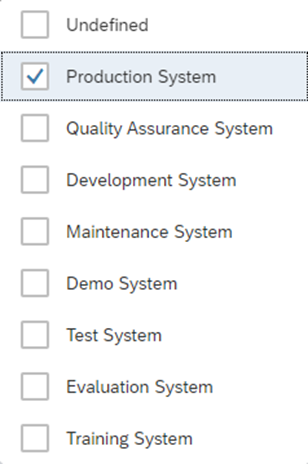
Email and SMS options for alert notifications can be maintained using Outbound Variants.
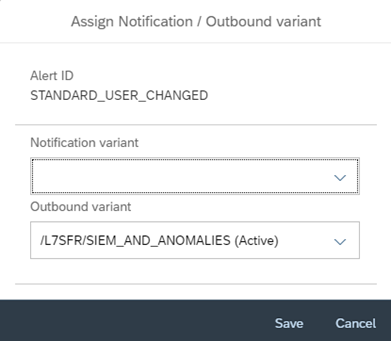
Alerts can be investigated and managed using Alert Management. In the example below, we can see the alert configured in CSA for changes to standard users. Alerts in Alert Management be integrated with SIEM and service desk solutions. For detailed information, refer to the SAP Help Portal.
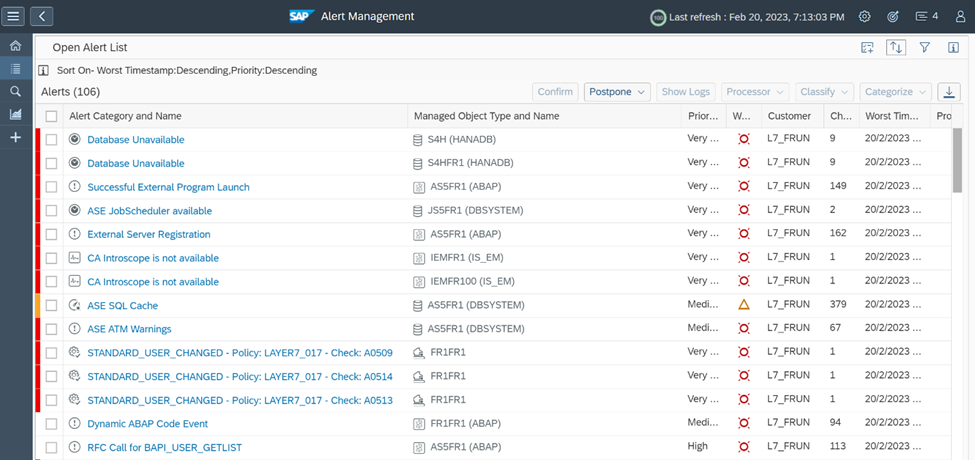
Changes in SAP systems are captured and logged in CSA. This includes areas such as parameter settings, RFC destinations, ICF services, and user authorizations, profiles, roles, and transactions. The details of the changes can be viewed using the option to display change of configuration items. Select a time frame for changes using Time Frame Selection.
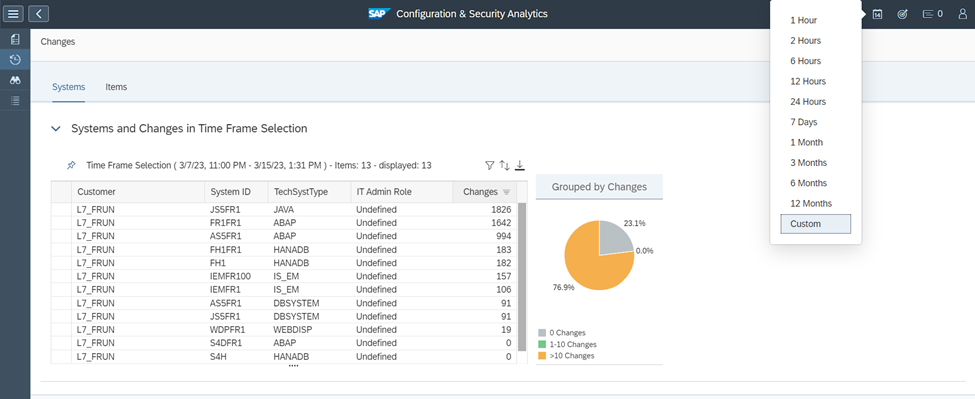
You can also maintain a custom time frame.
Select a system to view to view a summary of the changes.
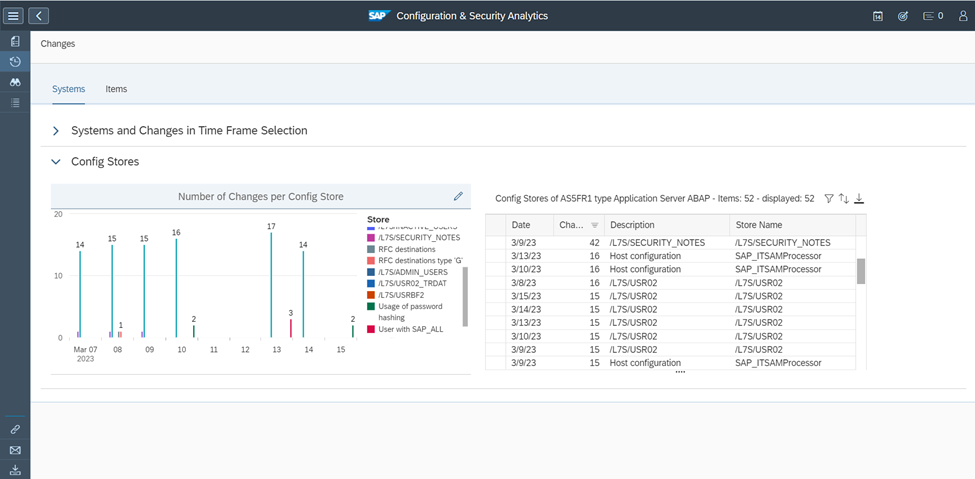
Select a store to view the details of changes. In the example below, we can see the details of users that were assigned the SAP_ALL profile in a system over the last three months.
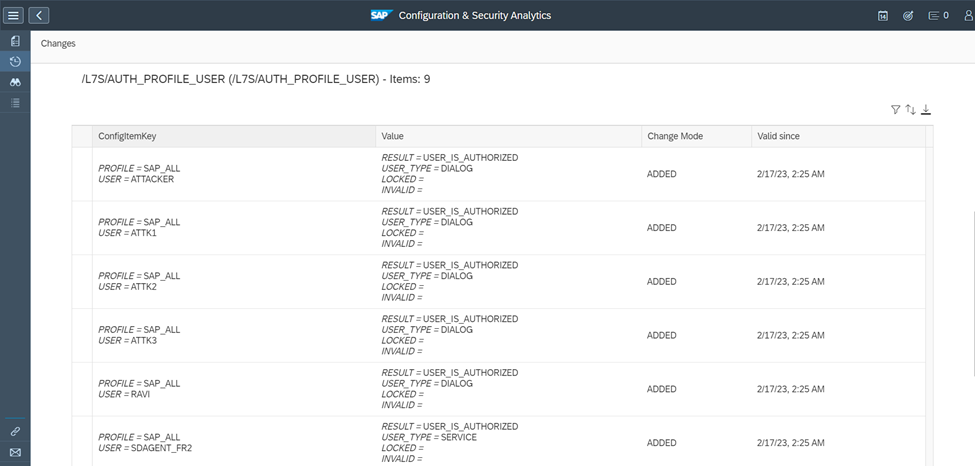
The details can be filtered, sorted and exported to Excel.
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP integrates with CSA in Focused Run to apply thousands of security checks for known vulnerabilities in SAP solutions. It also integrates with System Monitoring in Focused Run to detect and alert for more than 600 indicators of compromise in SAP event logs. To learn how you can protect your SAP systems from cyber threats using the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP, contact Layer Seven Security.

