FBI and CISA Issue Alert for Threat Actors Actively Exploiting SQL Injection Vulnerabilities
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) issued an alert this week to urge organizations to urgently address SQL injection vulnerabilities in software. The alert is based on recent exploits performed by the CL0P cybercrime group, also known as TA505. The Russian group has exploited SQL injection vulnerabilities to propagate ransomware that has extorted an estimated $100M from organizations.
TA505 provides Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) to other threat actors, sells access to compromised corporate networks as an initial access broker, and operates botnets specializing in financial fraud. The group is actively exploiting SQL injection vulnerabilities to install web shells in compromised servers. The web shells are used to execute operating system commands, install malicious ransomware programs, and exfiltrate data. TA505 is believed to have breached 130 organizations in just 10 days.
SQL injection vulnerabilities arise when user inputs are included in SQL commands to execute database queries. The processing of database queries containing malicious commands can enable threat actors to access and modify sensitive data, change programs and system configurations, and install and execute programs such as ransomware.
The risk of SQL injection can be mitigated using a combination of input validation and output encoding, escaping and quoting. Input validation reviews user-provided data before it is included in database queries and rejects data that does not conform with expected specifications such as character types, length, and syntax. Output encoding, escaping, and quoting can be more effective than input validation since programs often need to support free-form text containing arbitrary characters.
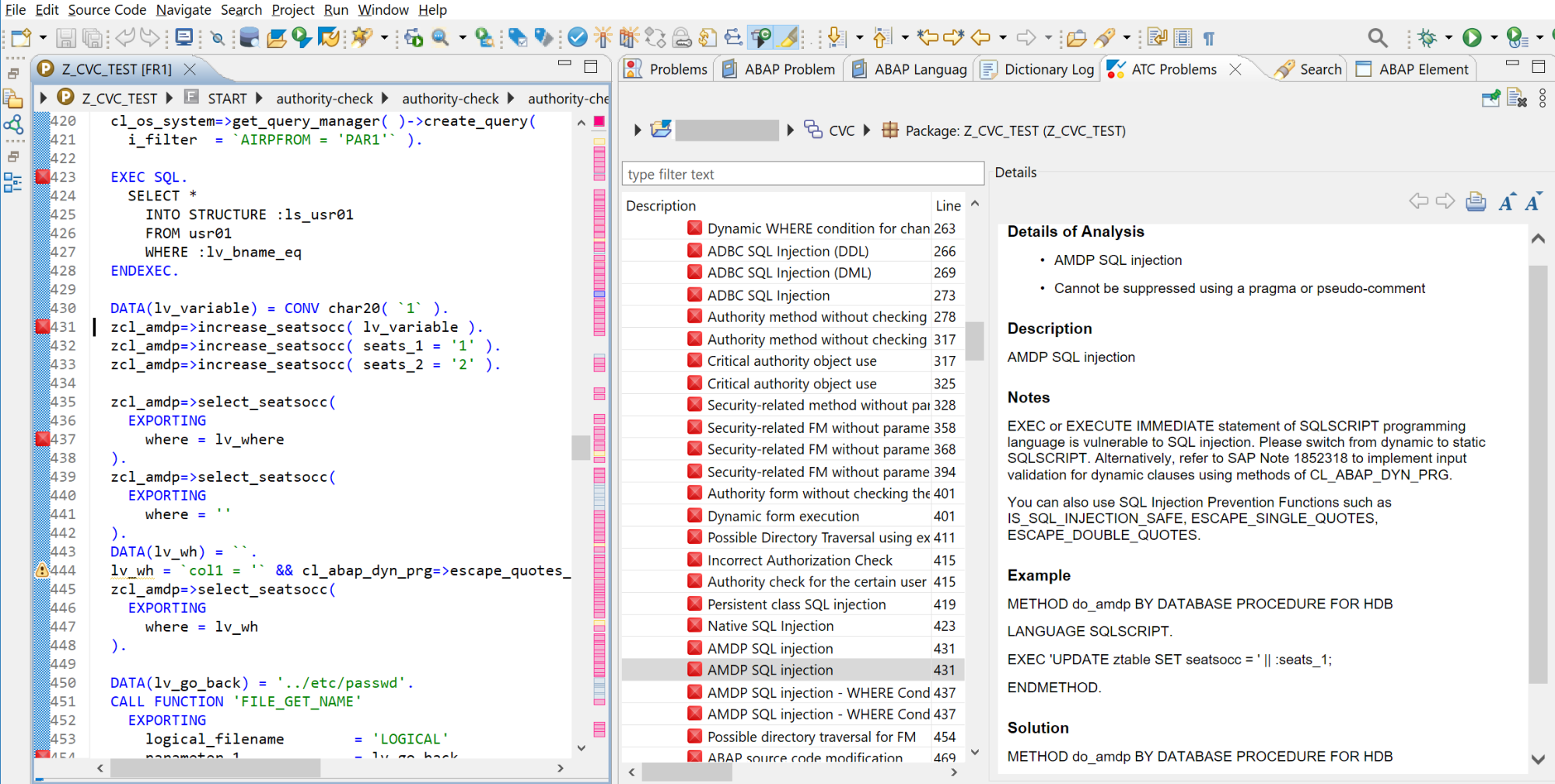
SAP software is subjected to static code analysis and other forms of security testing to detect and remove potential SQL injection vulnerabilities. However, SAP is not responsible for securing custom programs and applications deployed to SAP systems. Securing custom programs is the responsibility of each SAP customer. The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP is an SAP-certified addon that automatically detects SQL injection vulnerabilities in custom SAP ABAP programs and SAP UI5 applications. This includes SQL injection vulnerabilities in SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, MODIFY, DELETE and other statements, as well as GROUP, JOIN, SET, WHERE, and other conditions and clauses. It also detects SQL injection issues in ADBC, DDL, DML and other statements executed by APIs in SAP systems.
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP integrates with the ABAP Test Cockpit (ATC) and SAP Code Inspector (SCI). It also integrates with the Transport Management System (TMS) to automatically scan and block requests containing SQL injection and other security vulnerabilities.