Monitor Dangerous Function Module Calls with SAP Solution Manager
SAP systems operate in highly interconnected landscapes integrated by numerous interfacing technologies. The most common interface technology is the RFC protocol. The RFC protocol enables remote-enabled function modules (RFMs) to be called in remote systems. Some RFMs can be exploited to perform dangerous, administrative commands in target systems. For example, the function module BAPI_USER_CREATE can be used to create or maintain users. RFC_ABAP_INSTALL_AND_RUN can be used to register and execute arbitrary code. External commands including operating system commands can be executed using SXPG_CALL_SYSTEM and SXPG_COMMAND_EXECUTE. Therefore, monitoring for the execution of dangerous RFMs is critical for detecting potential attacks against SAP systems.
This article discusses how SAP Solution Manager detects and triggers alerts for dangerous RFM calls using Interface and Connection Monitoring (ICMon) and the Monitoring and Alerting Infrastructure (MAI). The article also discusses how the Guided Procedure Framework in Solution Manager can be used to create automated workflows for alert handling and forensic investigations.
ICMon provides a centralized platform for monitoring communications between systems within and across SAP landscapes. The application is accessed from the System and Application Monitoring group in the Fiori Launchpad.
Monitoring scenarios must be configured before using ICMon. The scenarios define the target systems and interface channels for monitoring. They also define the direction of the communications traffic. ICMon supports monitoring for both internal and external systems. It also supports several communication protocols including not just synchronous, transactional, queued, and background RFCs but Web Services, Gateway (OData) connections, HTTP, IDoc, CRM, PI and Cloud services.
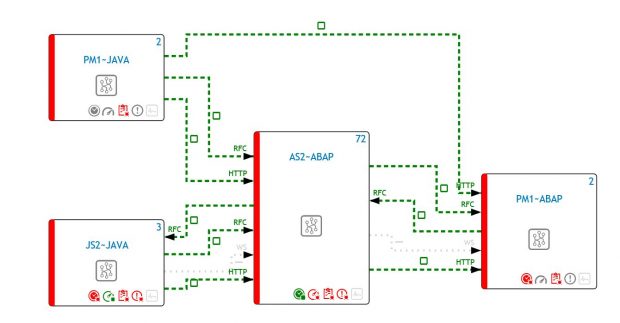
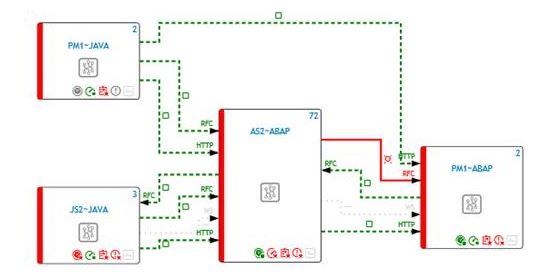
Once configured, Solution Manager starts to collect usage data for each scenario at regular intervals through background jobs. It also generates dynamic topologies for each scenario to visualize connections. Channels are color coded based on performance, availability, and configuration issues or exceptions detected by Solution Manager.
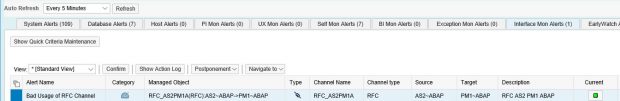
Monitoring for specific function modules can be performed by maintaining blacklisted RFMs for RFC interface channels in each scenario. The Number of RFC Executions metric should then be enabled to automatically trigger alerts for the execution of any of the RFMs.
The channel will be colored red in the topology if a dangerous RFC function module call is performed.
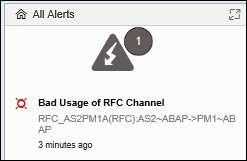
The Alert Ticker displays open alerts in the Overview screen.
Alerts can be managed from the Alert Inbox of the MAI.
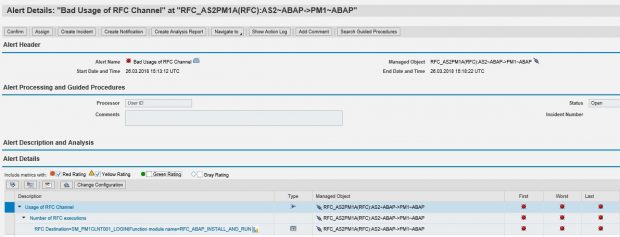
The Alert Details specify the function module and the RFC destination used to call the RFM, as well as details of the calling system, called system, and the timestamp of the event.
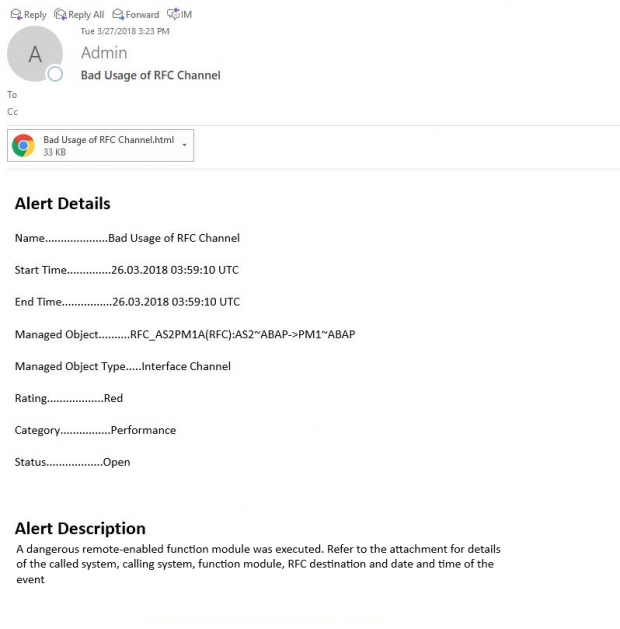
The details are also included in attachments appended to email notifications sent by Solution Manager.
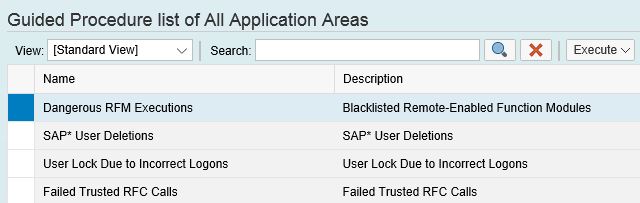
The Guided Procedure Framework (GPF) in Solution Manager can be used to create standard operating procedures for investigating dangerous RFM executions. The procedures can be started by selecting the option to Start Guided Procedure in each alert. Once initiated, the guided procedure will provide investigators with detailed instructions for performing forensic investigations and log the progress of each step in the procedure.