Prevent and Detect Ransomware Attacks with SAP Solution Manager
Ransomware attacks accounted for one third of malware-based cyber attacks in the first quarter of 2020. Successful attacks encrypt and block access to files in compromised systems. Decryption keys for recovery of the files are typically only released after ransom demands are paid, usually in the form of untraceable cryptocurrencies. The impact of ransomware includes not only ransoms but also recovery costs. The cost of the ransomware attack experienced by Demant in 2019 is estimated at $95M. Costs at Norsk Hydro are expected to reach $70M.
Based on an analysis of telemetry records, there are several early indicators of ransomware operations performed by threat actors. Attackers often use legitimate administrative tools to prepare ransomware attacks. This includes network scanners to identify vulnerable targets and software removal tools to disable antivirus software. Threat actors also often install tools for credential theft on compromised systems.
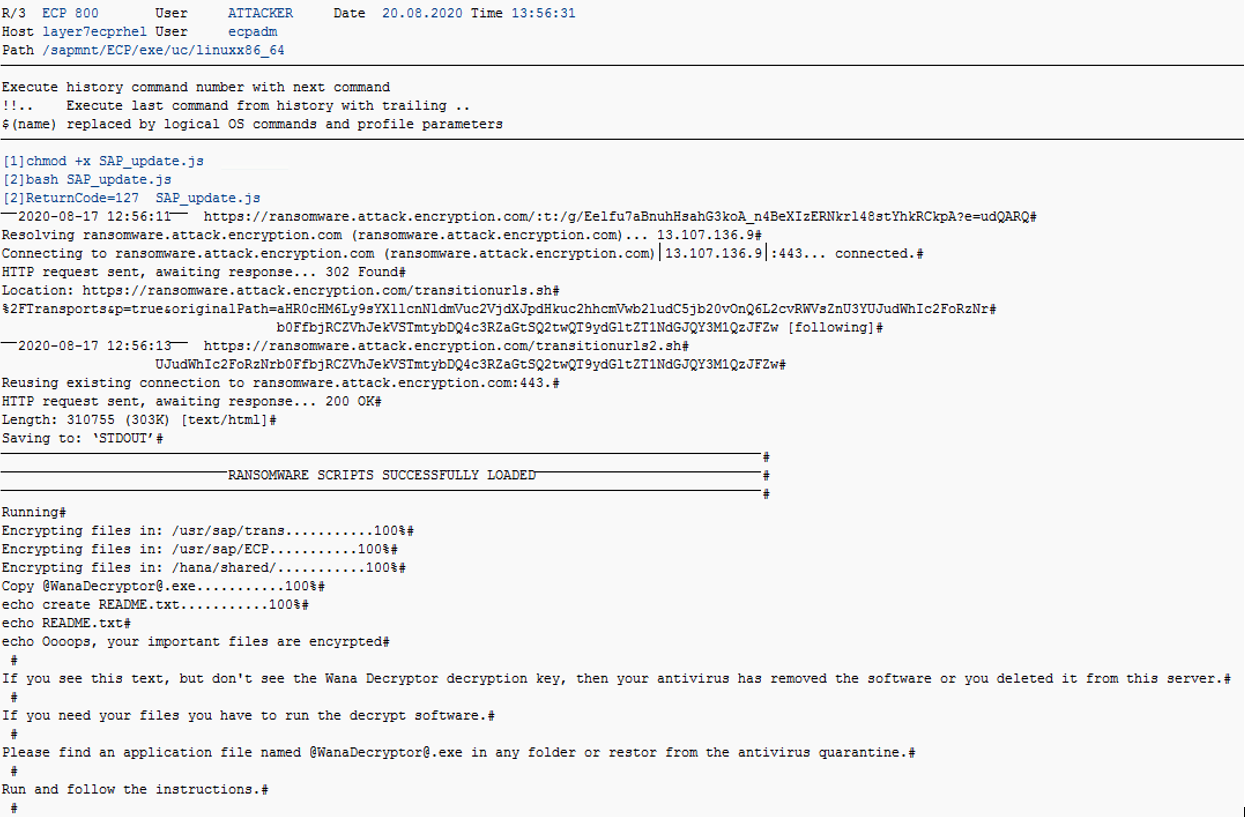
Ransomware is usually packaged in zip files distributed through emails, trojans, and infected web sites. The ransomware WastedLocker, for example, is often disguised as zip files for legitimate software updates. WastedLocker infected digital infrastructure at Garmin in July, leading to a $10M ransom. Ransomware payloads can also be delivered through compromised SAP systems. Attackers can target remote code execution vulnerabilities in SAP GUI for client-side attacks. Ransomware can be installed directly in SAP servers using external operating system commands. OS commands performed by SAP users are executed by the operating system user <SID>ADM. The user has full administrative privileges for local SAP resources.
The wget command can be used to download ransomware from remote hosts to a target directory in the SAP host. Ransomware payloads can also be loaded directly in servers using transactions CG3Z or CACS_FILE_COPY. Once loaded, the payloads can be extracted and then executed using bash commands in Linux systems. This method for delivering, installing and executing ransomware will encrypt files in folders accessible by the <SID>ADM user and crash SAP applications and services. It may also impact other files and services in the host if the ransomware successfully elevates privileges.
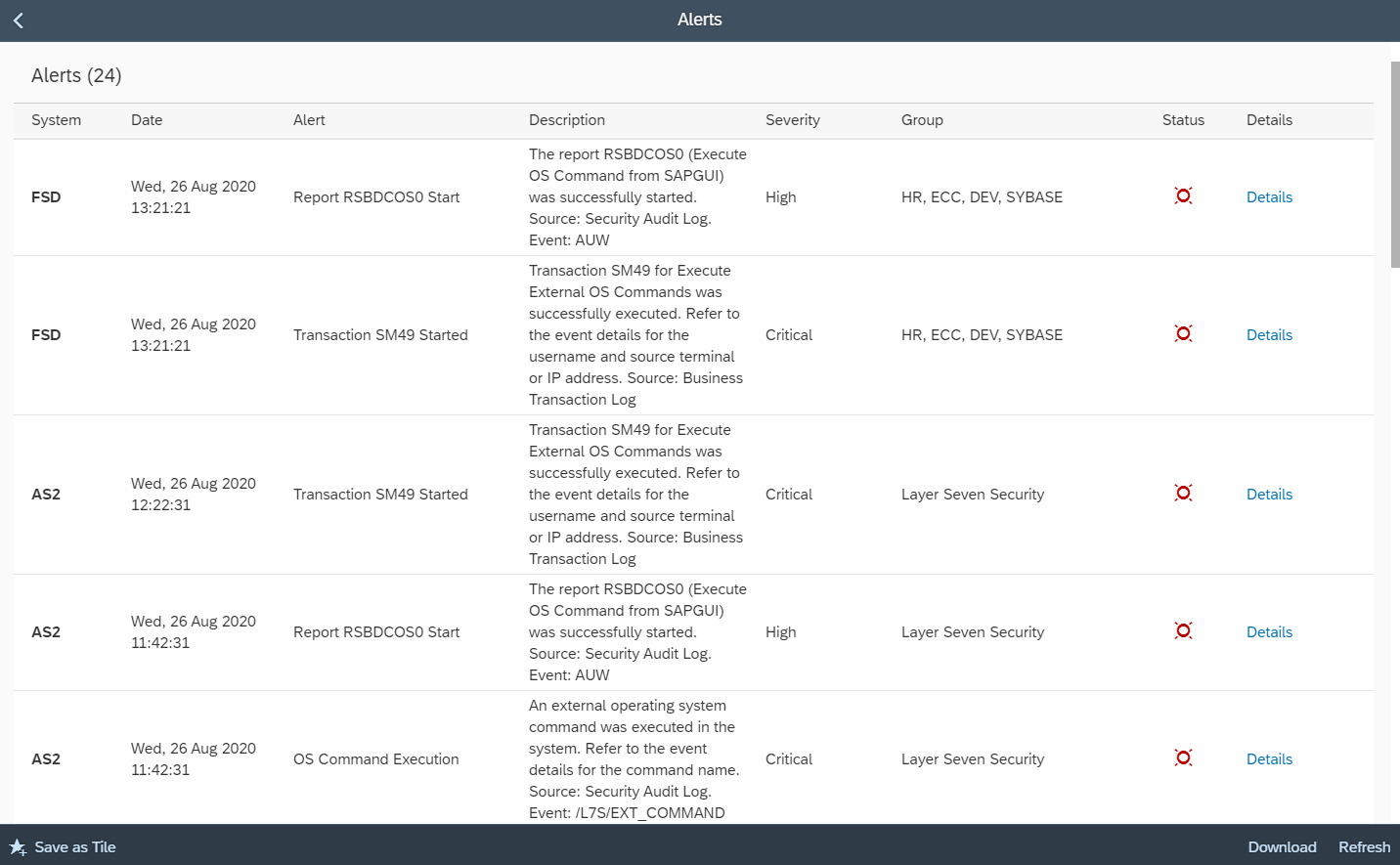
Such exploits can be mitigated or detected in several ways. Access to perform OS commands should be restricted. This includes authorization object S_LOG_COM, transactions SM49 and SM69, program RSBDCOS0, and function modules such as SXPG_COMMAND_EXECUTE. Successful execution of the transactions, programs and function modules should also be monitored, as well as OS commands and changes to custom commands. Refer to SAP Note 1612730 for enabling detailed logging for external commands.
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP Solution Manager performs automated scans to detect users with OS command privileges. It also monitors SAP logs to alert for the execution of OS commands, new custom commands, and changes to existing commands. The extension also detects and alerts for the execution of transactions SM49, SM69, CG3Z and CACS_FILE_COPY, program RSBDCOS0, and relevant function modules. Alerts are automatically forwarded to SIEM systems with event details. To learn more, contact Layer Seven Security