The 24-Month Rule for SAP Security Patching
Regular patching is critical for protecting SAP software against security vulnerabilities. Security weaknesses are discovered by SAP through internal testing and testing performed by external researchers. The latter disclose vulnerabilities directly to the SAP Product Security Response Team and through the official SAP bug bounty program.
Once a vulnerability is identified or reported, it is validated and reviewed by SAP. Corrective measures can be automated or manual or a combination of both. Corrections are published as SAP security notes on the second Tuesday of each month. SAP provides several tools for discovering, analyzing and implementing required security notes including the SAP Support Portal, Maintenance Planner, System Recommendations, and Note Assistant.
Security notes are rated by SAP based on the severity of each vulnerability. Hot news notes address the most severe vulnerabilities in SAP solutions. Other severities include high, medium and low. SAP also uses the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) to rate vulnerabilities. CVSS is a widely used standardized model for assessing vulnerabilities across all software solutions. CVSS scores of 9.0-10.0 and 7.0-8.9 are considered critical and high, respectively. Most vulnerabilities are scored by SAP using CVSS version 3.0. The CVSS score is based on a complex calculation that includes an assessment of multiple factors such as attack complexity, dependencies, user interaction, and the impact to data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The values used to rate each factor and determine the score are included in the vector string for each vulnerability.
SAP is a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA). Most security notes are assigned a unique CVE and published by SAP in CVE databases. Therefore, SAP vulnerabilities are publicly disclosed even though SAP security notes can only be accessed through the SAP support portal. Some information in security notes is not publicly available. This includes details of workarounds where customers cannot or choose not to implement automated corrections. However, the majority of security notes do not include workarounds. Many older SAP security notes do not include a CVE. SAP became a CVE Numbering Authority in late 2017 and therefore older SAP vulnerabilities are not publicly disclosed.
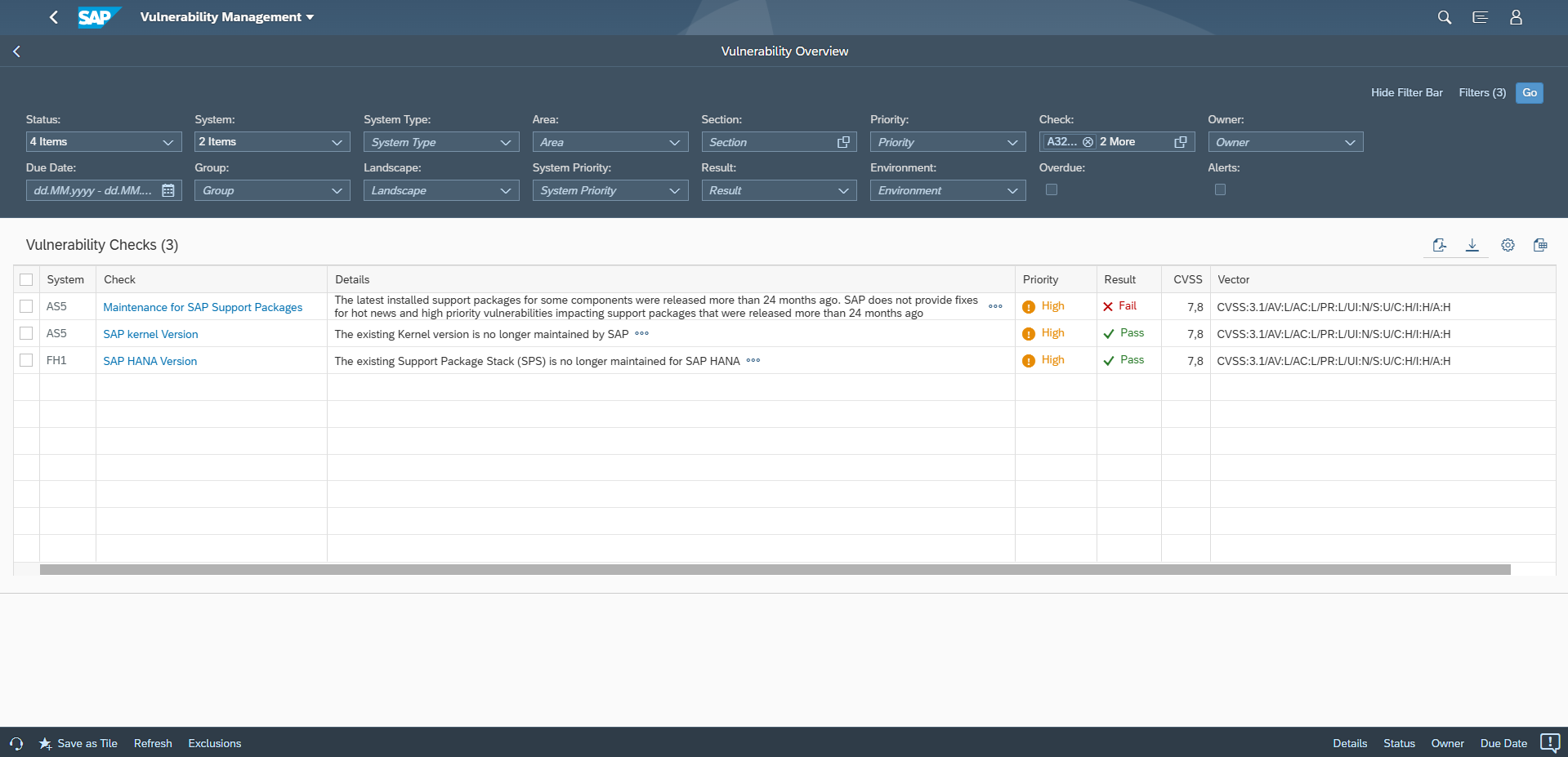
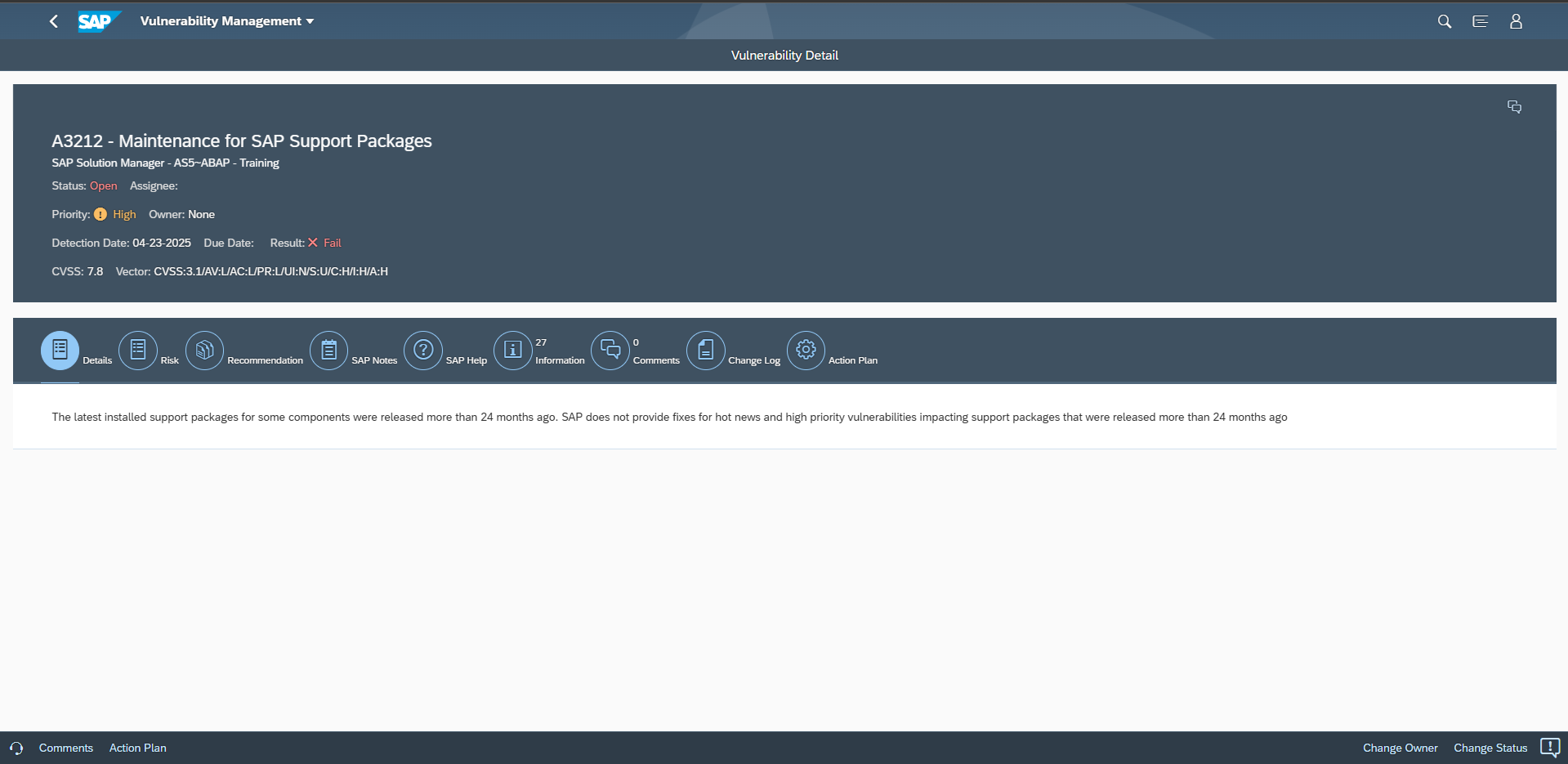
There are two types of security notes, patch day notes and support package notes. Patch day notes address all vulnerabilities reported by external researchers, regardless of severity, and hot news vulnerabilities discovered internally by SAP with a very high (9.0+) CVSS rating. Support package notes address high, medium and low severity vulnerabilities discovered by SAP. Support package notes are implemented via SP fixes or upgrades. In accordance with the general SAP maintenance strategy, SAP only delivers support package notes for support packages shipped within the last 24 months. This is referred to as the 24-month rule. The rule took effect on June 11 2019 and extended the previous coverage period for support packages from 18 months. The impact of the rule is that software components patched up to SP levels where the support packages were released more than 24 months ago are not provided with SP fixes to remove low, medium and high severity vulnerabilities discovered internally by SAP. The vulnerabilities can only be addressed by performing an SP upgrade to a support package that is within the 24-month rule.
There are some exceptions to the 24-month rule. Some SAP products adhere to a product-specific maintenance strategy rather than the general strategy. This includes products such as SAP HANA, BW/4HANA, and SAP Kernel. The maintenance strategy for each product is documented in specific SAP notes. For example, note 2378962 includes the revision and maintenance strategy for SAP HANA version 2.0. HANA Support Package Stacks (SPS) that are out of maintenance are detailed in the note.
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP automatically discovers software components with SP levels outside the 24-month rule. It enables customers to track the lifecycle of support packages to ensure software components are patched up to SP levels that are within the SAP maintenance window. Customers are therefore able to apply fixes for all available SAP security notes.
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP also monitors SAP HANA to identify systems using Support Package Stacks that are out of maintenance, as well as SAP Kernels using outdated Kernel versions.