What’s New in the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP
The new release of the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP (CES) is scheduled for general availability on April 24. It includes several important enhancements, configuration checks and patterns for threat detection to further protect SAP solutions from advanced cyber threats.
The prior release of the CES provided capabilities for SAP customers to automatically discover and remove false positive security notes calculated by System Recommendations (SysRec) in SAP Solution Manager. This improved the quality and reliability of results in SysRec and reduced the manual effort required by SAP administrators to analyze security patches. The new release of CES extends the enhancements for SysRec by including CVE, CVSS and vector information for calculated security notes.
The new release also includes configuration checks for protection against directory traversal in ABAP systems. The checks review path validation for files with no defined physical paths and the definition of physical file paths for logical paths. Checks are also applied for settings in SAP Virus Scan Interface (VSI) profiles and supported MIME types. SAP VSI integrates with scanning engines to discover and block malware in file uploads and downloads from SAP solutions.
The new release includes extended checks for Unified Connectivity (UCON) including HTTP whitelists for protection against clickjacking attacks and relevant background jobs. It also includes extended checks for Read Access Logging including log domains, groups and fields. In addition, checks for the masking and encryption of payment card data are included in the new release.
There are over 210 checks for critical transactions in S/4HANA included in the release. Future releases will rollout authorization checks for solutions such as S/4HANA, ECC, BW/4HANA, BW, CRM. The checks will enable customers to use the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP to monitor critical access and segregation of duties in lieu of SAP Governance, Risk & Compliance (GRC), given the scheduled end of maintenance of GRC.
There are several new checks for code vulnerabilities in custom SAP programs. This includes checks for XSRF protection and the forceEncode attribute.
New patterns for detecting Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) in SAP solutions include successful and unsuccessful program installations, uninstallations and changes in Microsoft Server platforms for SAP. Similar patterns were included in earlier versions of CES for Linux platforms to support the detection of potential ransomware attacks.
IOCs are also included for the detection of changes to specific security-relevant parameters in SAP ABAP and HANA systems.
A new security framework has been added to CES for S/4HANA. The framework will enable customers to automatically check the compliance of S/4HANA systems with SAP requirements in the Security Guide for S/4HANA.
The new release of CES deprecates custom infocubes and process chains used in earlier versions. This dramatically improves the stability and performance of CES and the ability of the solution to rapidly process large data sets with minimal resources.
Security alerts for multiple hosts can be mapped to specific SAP System IDs in the new release. Also, filters for security alerts include a new field to support searching of security alerts based on time ranges using the format HH:MM:SS for start and end times.
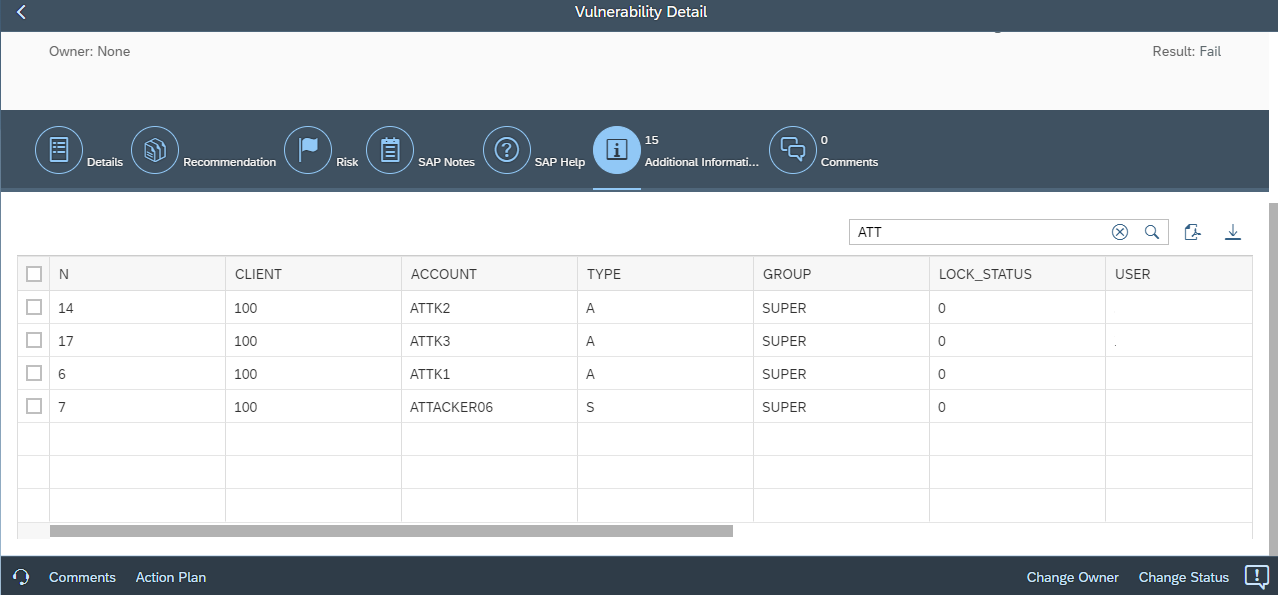
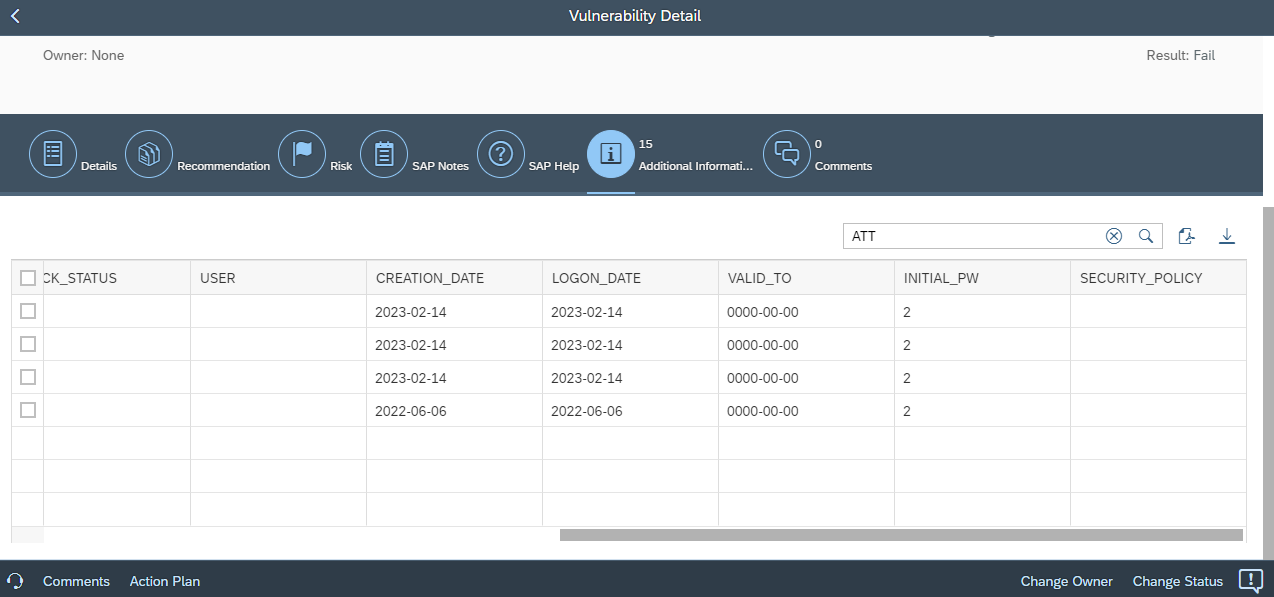
Finally, vulnerability details now include tables containing the complete fields and values from source CCDB stores. The tables support data filtering and export.
The next release of the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP is scheduled for June 2023 and will include support for detecting IOCs in logs for SAP ASE databases, vulnerability and event correlation, and trend analysis for tracking changes in vulnerabilities, patches and alerts for periods covering up to two years.

