SolMan-SIEM Integration for Advanced Threat Detection
SAP Solution Manager monitors real-time event information in SAP logs to automatically detect and trigger alerts for specific Indicators of Compromise (IOCs). This includes events written to the security audit log, system log, gateway server log, change document log, HTTP log, transaction log, SAProuter log, Java security log and the HANA audit log. Alerts are managed in the Alert Inbox or the System Monitoring app of SAP Solution Manager and automatic email and SMS notifications are triggered for critical incidents. Alerts are integrated with Guided Procedures to support an end-to-end process for incident detection and response within Solution Manager.
The data collection for event monitoring using Solution Manager is performed using existing RFC connections and Diagnostics Agents installed in managed systems. Since Diagnostics Agents can be installed in both SAP and non-SAP systems and components, Solution Manager can perform many of the functions of a Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) system. SolMan can monitor across the technology stack including database, operating system, and application layers, as well as network components such as routers, switches and firewalls. These areas are often monitored by organizations using existing SIEM platforms. Therefore, SolMan is more commonly used for application-level monitoring.
SIEM platforms support direct monitoring of SAP log files, tables and other data sources. However, there are several drawbacks with this approach. One of the drawbacks is that each data source within every target system must be connected separately to SIEM platforms. This increases deployment times and complexities. Once connected, rules and patterns must be defined in the platforms for every possible event. Also, since SIEM platforms are ingesting raw logs, the cost of monitoring and storing mammoth-sized logs for multiple SAP systems can be prohibitive, especially for large landscapes.
SAP Solution Manager overcomes these drawbacks by parsing log files and tables and filtering events before forwarding alerts to SIEM platforms. This enables the platforms to avoid ingesting raw logs to monitor SAP event information. Since the event data forwarded to SIEM platforms is derived from a single source for all SAP systems in a landscape, deployment is also faster and less complex. Finally, Solution Manager structures and enriches the event data before it reaches SIEM platforms to reduce the need to develop rules and patterns to interpret SAP event information.
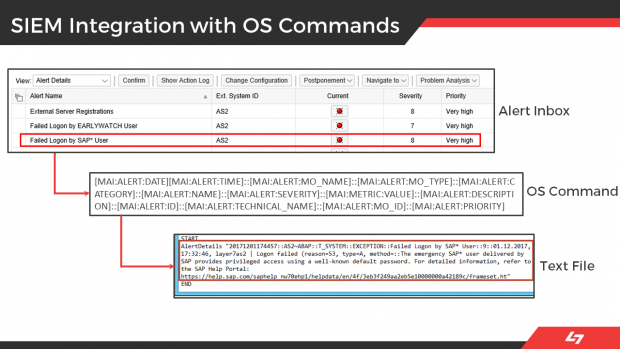
Solution Manager can integrate with SIEM platforms through several ways. The most common is using OS commands that are called by SolMan to write event data to external files that are ingested by SIEM solutions. Alerts are written to external files as soon as they are triggered by SolMan. Alert fields can include the alert name, description, priority, date, time, SAP System ID, and other areas.
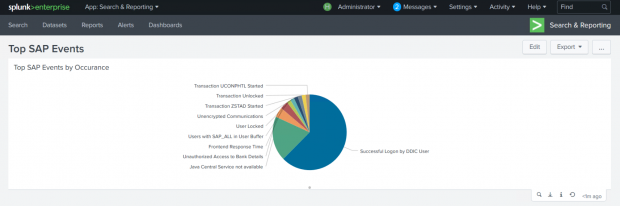
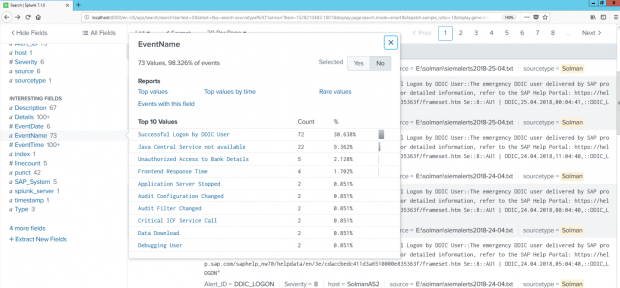
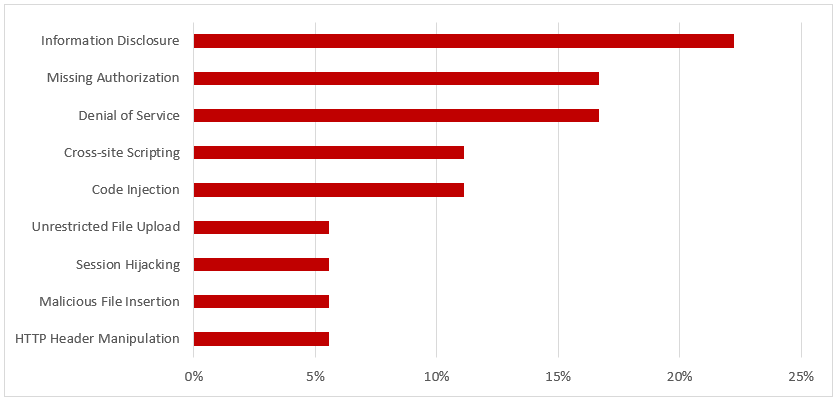
This process integrates alerts for IOCs and other security risks detected by SolMan for SAP applications with SIEM systems for centralized monitoring and cross-platform correlation. The example below is for Splunk Enterprise. Click on the images below to enlarge.