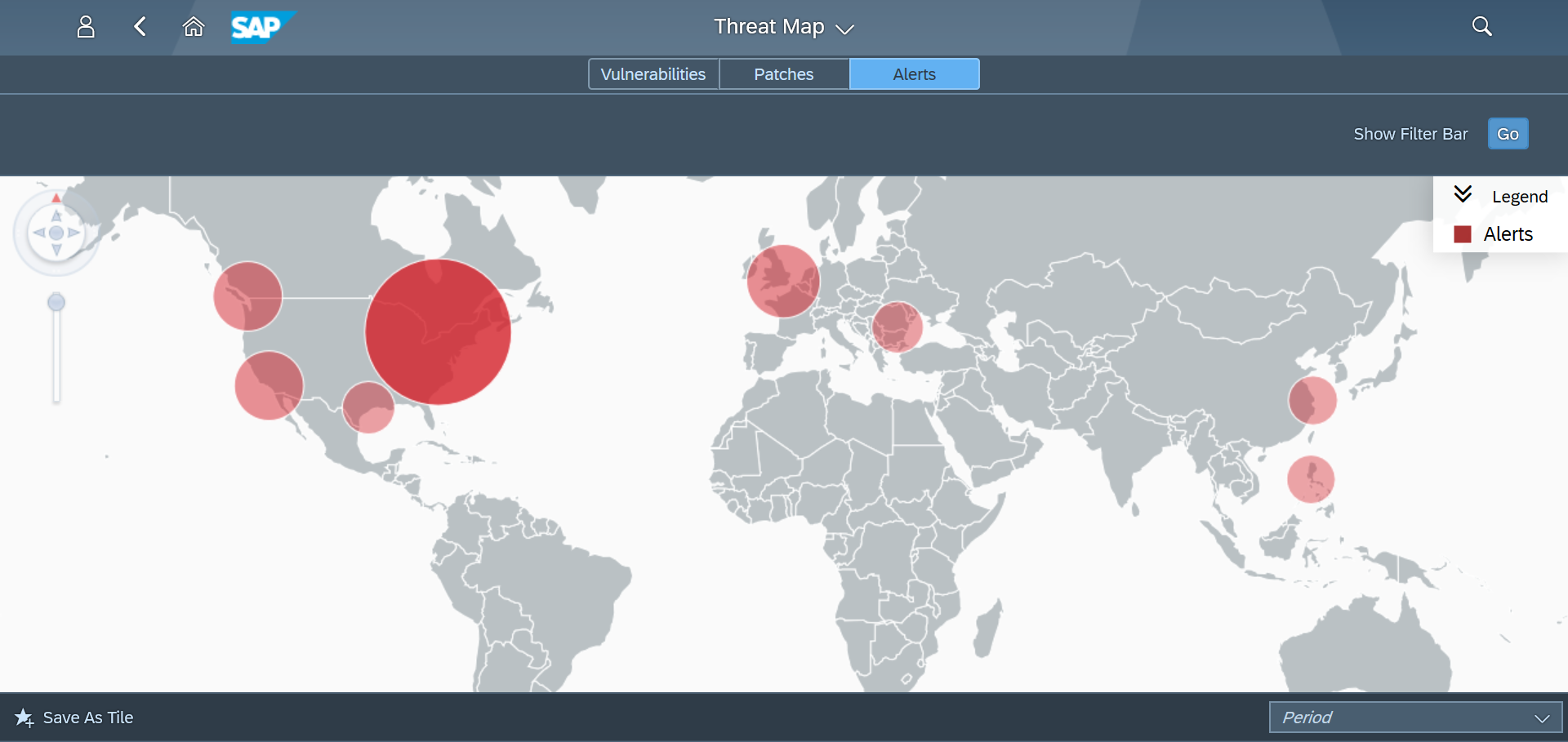
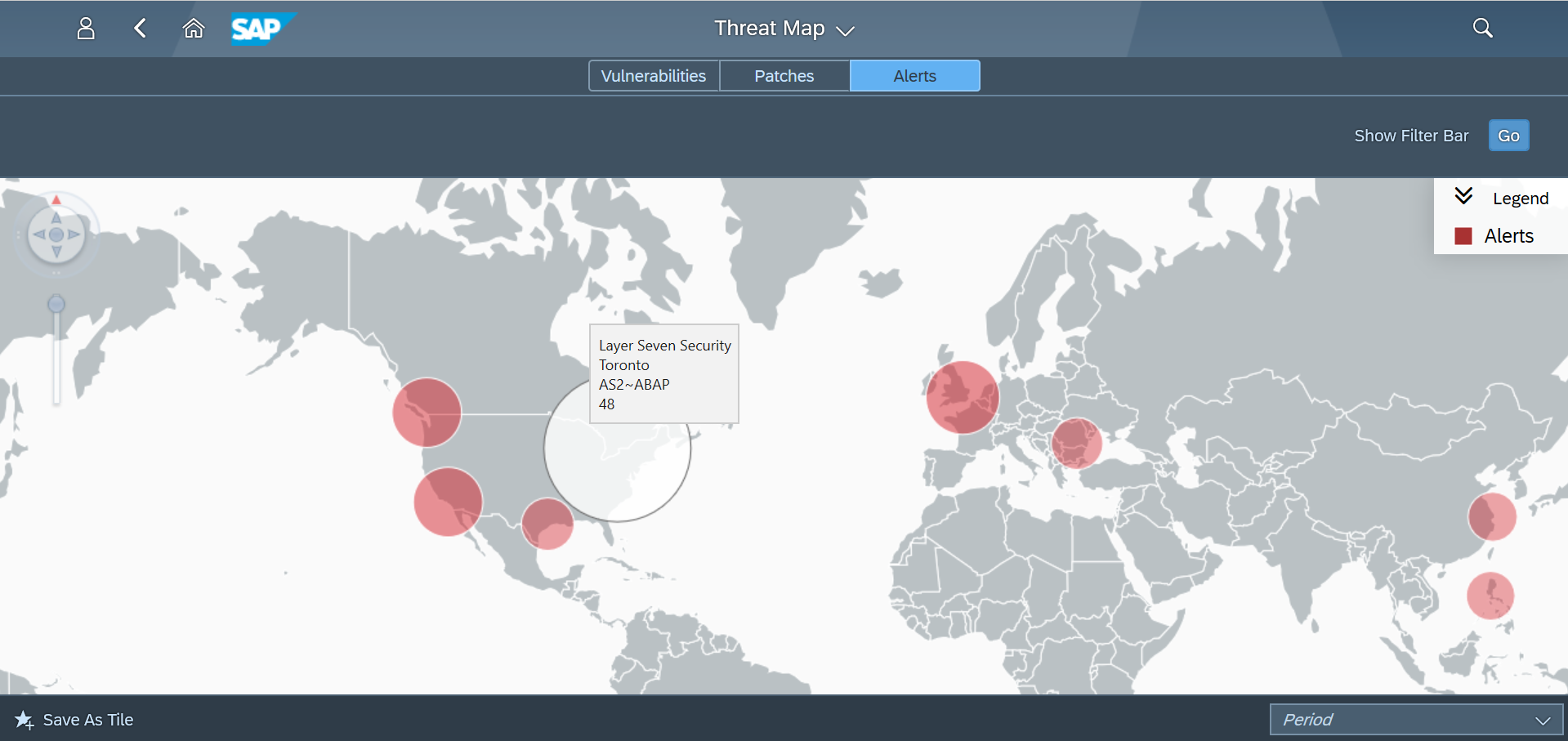
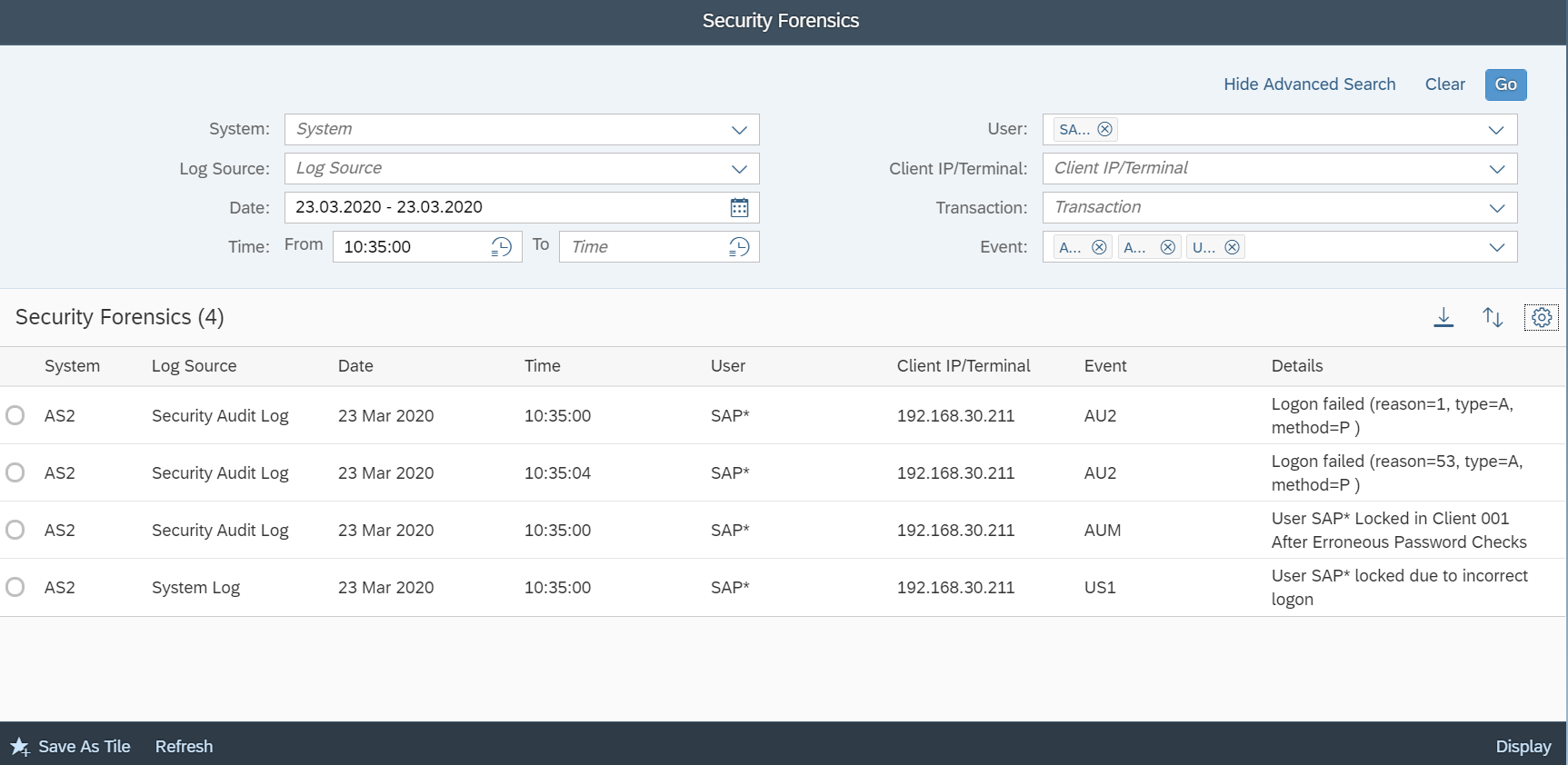
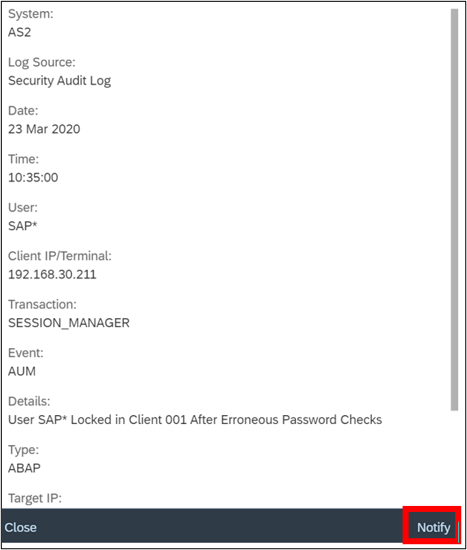
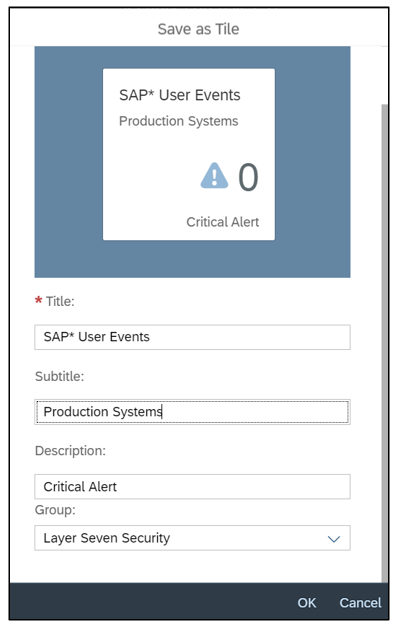
SAP Security Notes, May 2020
Hot News Note 2835979 patches a critical code injection vulnerability in Service Data Download. The vulnerability can be exploited by attackers to inject malicious code into the ST-PI plugin for NetWeaver Application Server ABAP (AS ABAP). This could lead to the complete compromise of ABAP servers. The vulnerability carries a base CVSS score of 9.9/10 and can be exploited over the network.
Hot News Note 2885244 carries a similar CVSS score of 9.8/10 and can be exploited to bypass authentication using REST Webservices (BIPRWS) for Live Data Connect in the SAP Business Intelligence Platform. The fix packaged with the note enables Live Data Connect to logon to the BI Central Management Server (CMS) with a shared key. This prevents logons to the CMS without a password when using trusted authentication. The fix is available for version 2.4 of Live Data Connect. Customers using earlier versions are advised to upgrade to version 2.4.
Notes 2917275 and 2917090 patch critical code injection and information disclosure vulnerabilities in the Backup Server and Cockpit of SAP Adaptive Server Enterprise (ASE), formerly Sybase ASE. ASE is a widely used database platform for SAP systems. Note 2917275 applies input validation checks for DUMP and LOAD commands to prevent the execution of malicious user-provided code. Note 2917090 prevents the disclosure of sensitive system and user data including account credentials. The impacted ASE versions are 16.0 SP02 and SP03.