In response to the dramatic rise of cyber attacks targeting ERP applications, the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) issued a warning earlier this year that encouraged organizations to respond to the risks targeted at their business applications by implementing specific measures to secure, patch and monitor SAP systems. The measures included scanning for vulnerabilities and missing security patches, managing SAP interfaces, and monitoring user behaviour, indicators of compromise, and compliance against security baselines for systems.
This article discusses how you can leverage SAP Solution Manager to comply with the DHS recommendations. Solution Manager is installed and available in most SAP landscapes and includes diagnostics and monitoring applications to support cybersecurity. The specific applications are outlined below against each of the DHS recommendations.
1. Scan systems for all known vulnerabilities, such as missing security patches and dangerous system configurations.
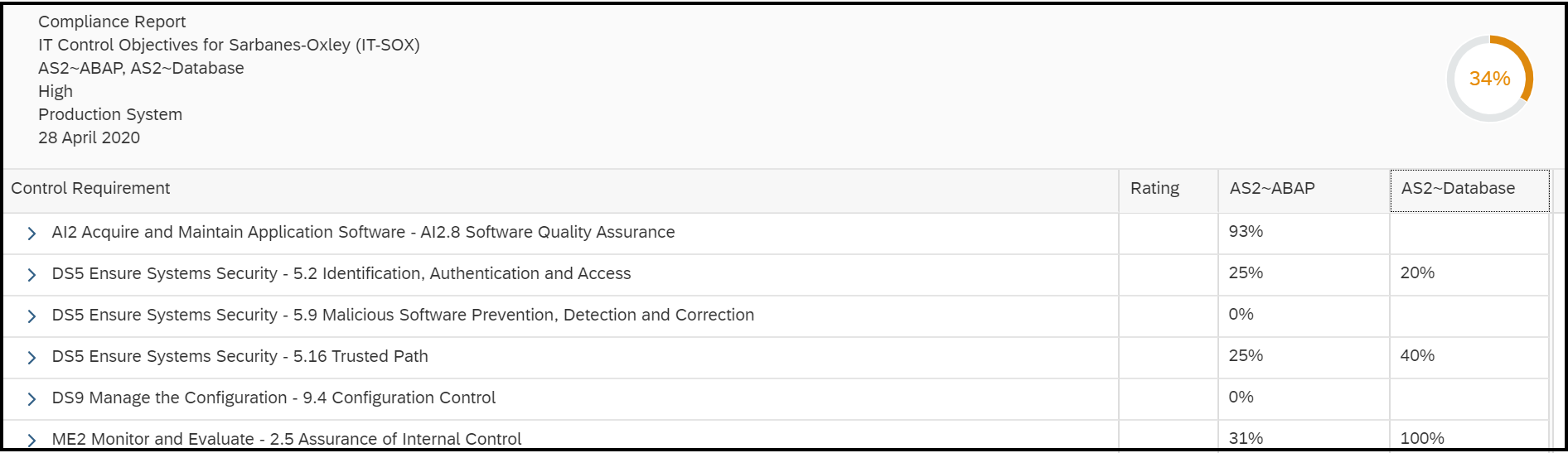
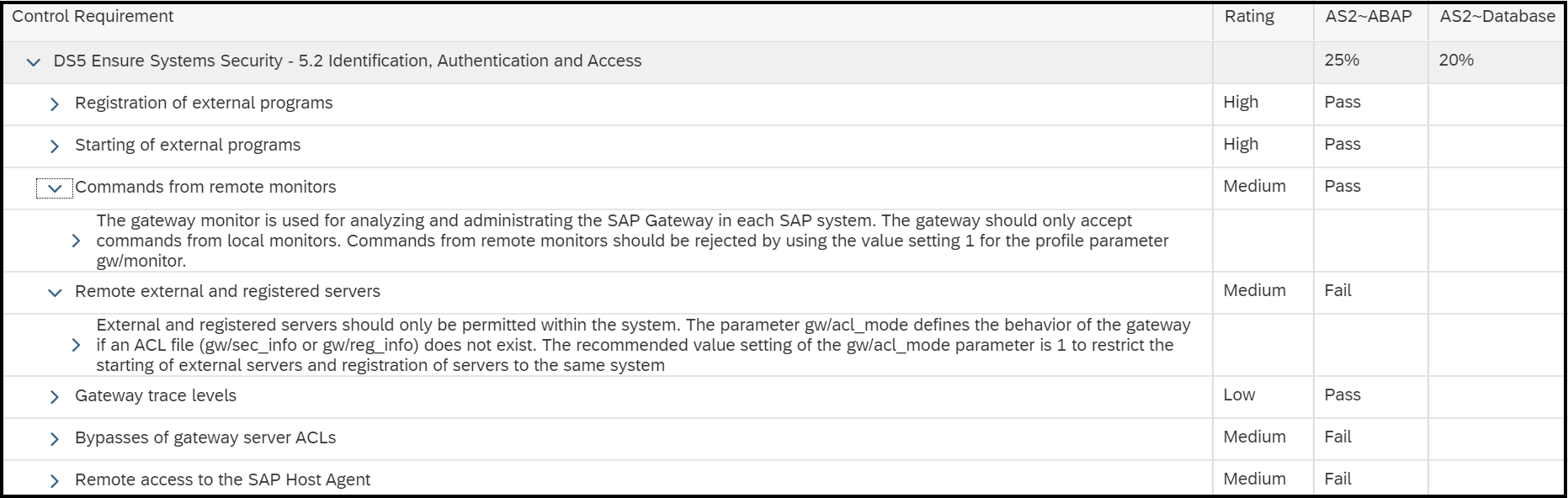
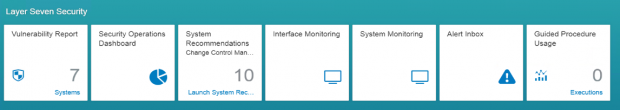
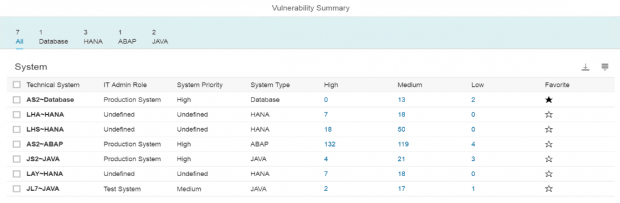
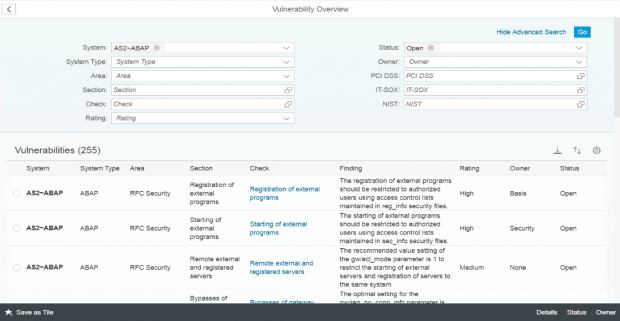
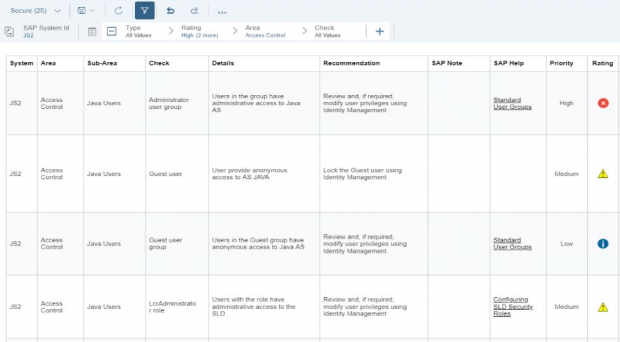
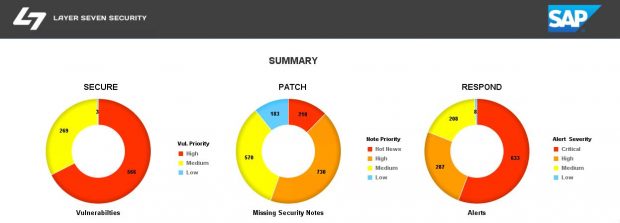
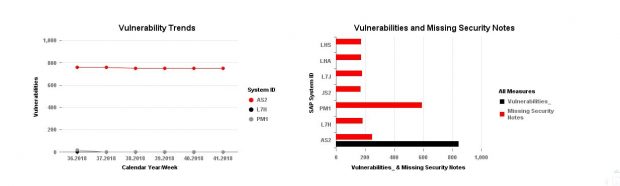
Configuration Validation in Solution Manager can perform automatic daily scans of SAP systems against security benchmarks to identify misconfigurations that could expose systems to cyber threats. The scans are performed against snapshots of systems stored in the Configuration and Change Database (CCDB). The results of the scans are stored in an internal Business Warehouse (BW). Service Level Reports and Security Dashboards connect to BW using BEx queries to read the results of the security scans and report the findings.
System Recommendations (SysRec) in Solution Manager connects directly to SAP Support to discover missing security patches. SysRec also connects to each system in an SAP landscape to determine the current patch level. It reads the system information in the Landscape and Management Database (LMDB) to identify installed software components and versions. SysRec also integrates with the ABAP Call Monitor, Usage Procedure Logging, and Solution Documentation to perform change impact analysis for security patches.
2. Identify and analyze the security settings of SAP interfaces between systems and applications to understand risks posed by these trust relationships.
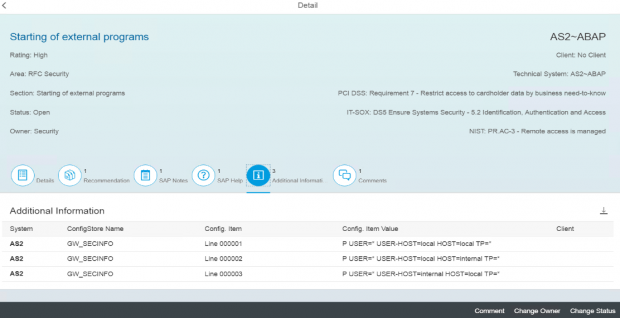
Interface and Connection Monitoring (ICMon) in Solution Manager automatically maps cross-system interfaces including RFC, HTTP, IDOC and Web Services. This includes internal and external connections. It also monitors real-time traffic patterns to detect and alert for malicious actions including dangerous RFM and URL executions.
3. Analyze systems for malicious or excessive user authorizations.
Solution Manager can detect users with administrative privileges in SAP systems. It flags users with privileged authorizations, profiles, roles, transactions, Java permissions, and HANA system and table privileges. Privileges can include standard and custom objects.
4. Monitor systems for indicators of compromise resulting from the exploitation of vulnerabilities.
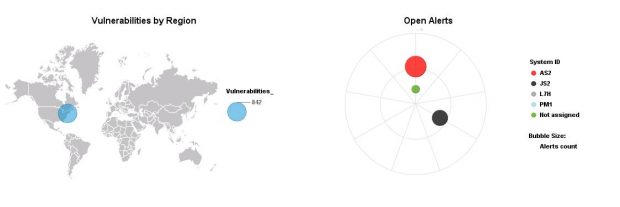
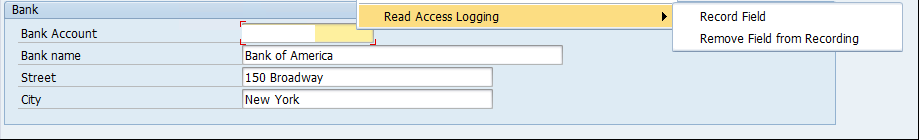
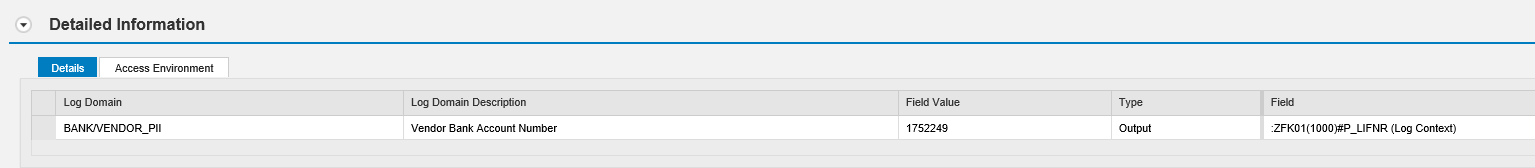
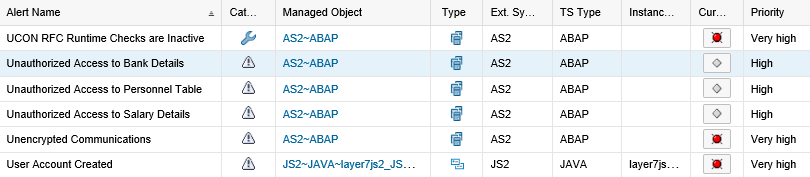
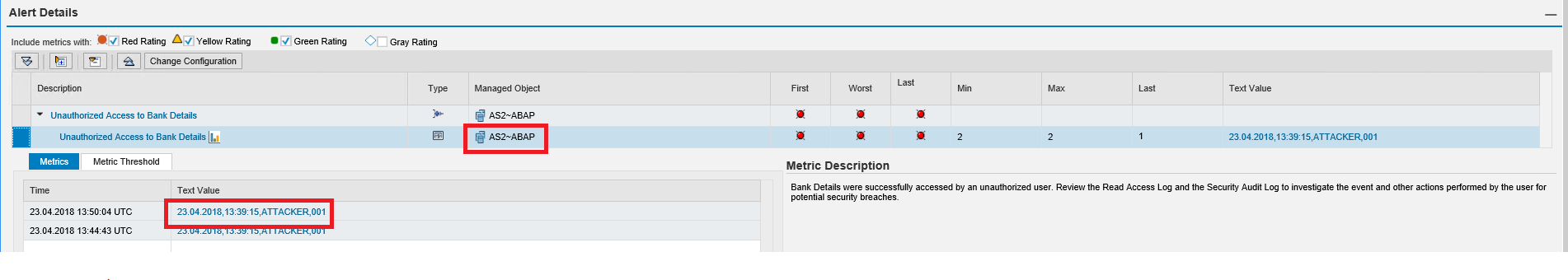
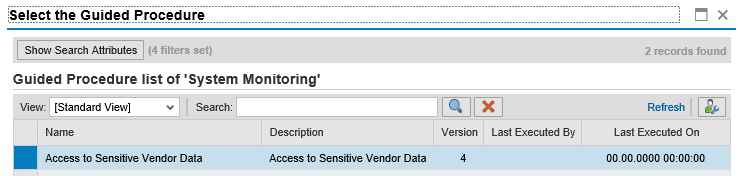
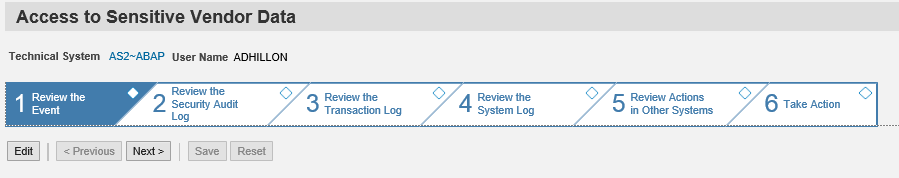
The Monitoring and Alerting Infrastructure (MAI) in Solution Manager can monitor event logs in SAP systems to detect and alert for indicators of compromise (IOCs). This includes log files and tables such as the Security Audit Log, HTTP Log, System Log, Gateway Server Log, Change Document Log, Read Access Log, Java Security Log, HANA Audit Log, and the SAProuter Log. The MAI triggers alerts and email and text notifications for IOCs. Guided procedures provide a framework for incident response and tracking.
5. Monitor systems for suspicious user behavior, including both privileged and non-privileged users.
MAI monitors user logs to detect and alert for suspicious behavior covering both privileged and non-privileged users. This includes unauthorized access, escalation of privileges and actions that could lead to data leakage.
6. Apply threat intelligence on new vulnerabilities to improve the security posture against advanced targeted attacks.
SAP Partners periodically update content for Solution Manager to address new vulnerabilities and attack vectors.
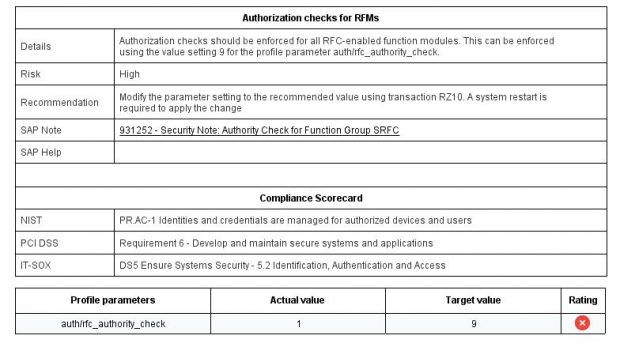
7. Define comprehensive security baselines for systems and continuously monitor for compliance violations and remediate detected deviations.
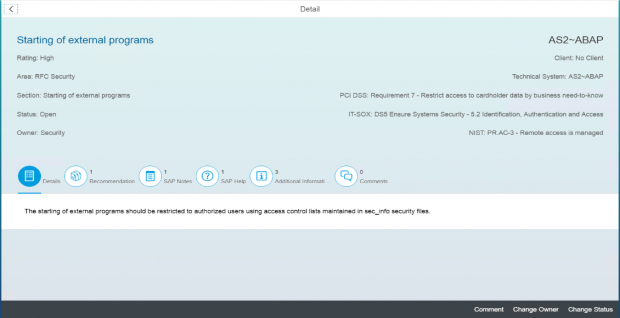
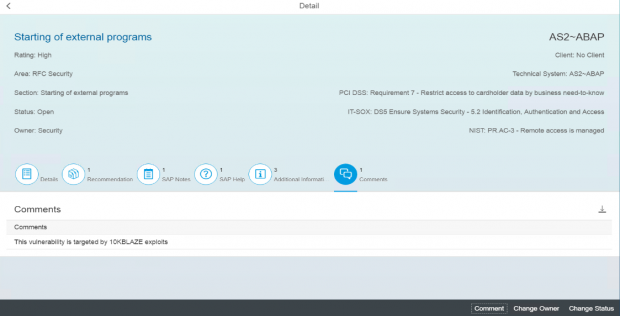
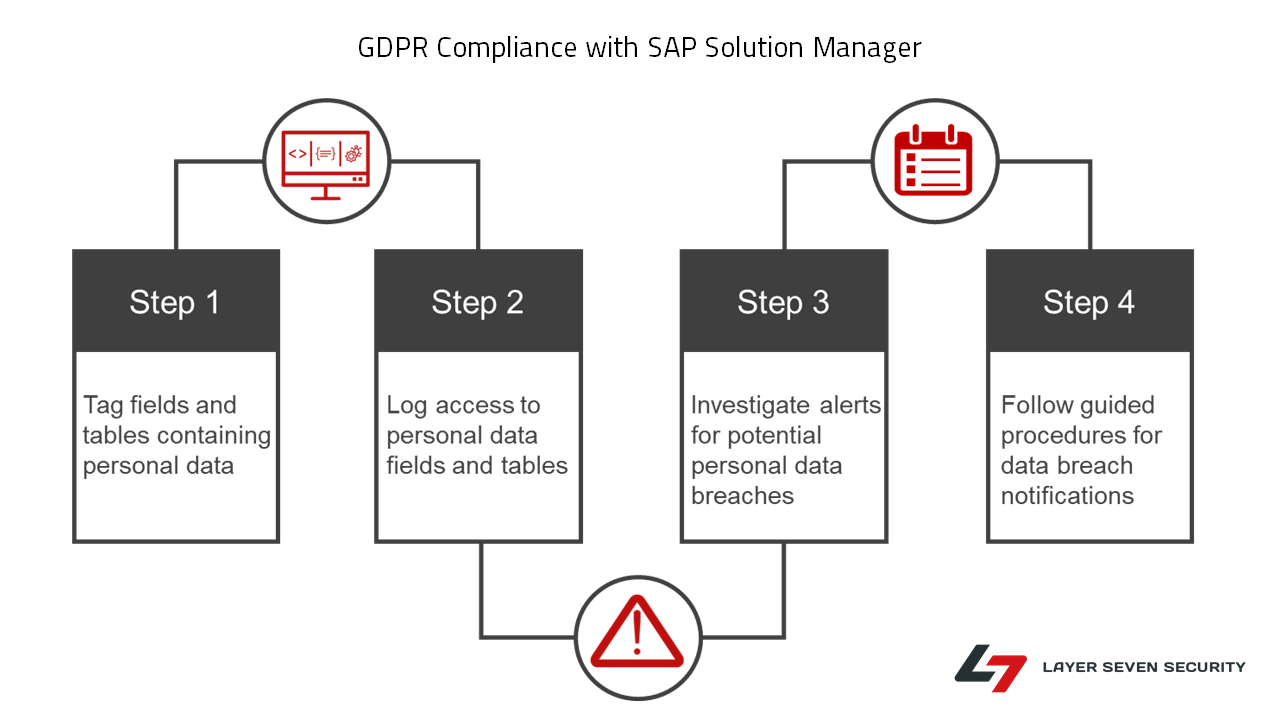
Solution Manager continuously monitors for policy violations against security baselines and compliance frameworks such as GDPR, IT-SOX, NIST and PCI-DSS. Service Level Reports and Dashboards provide directions for implementing and tracking remedial actions taken to patch and secure systems. Guided procedures document incident investigation steps performed by responders. The results are archived in Solution Manager.
To learn more about how Solution Manager can help you comply with the DHS recommendations for securing SAP systems, contact Layer Seven Security.