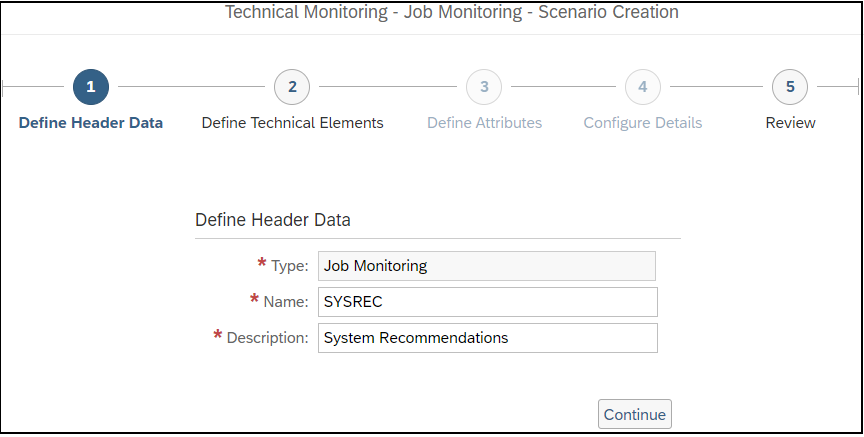
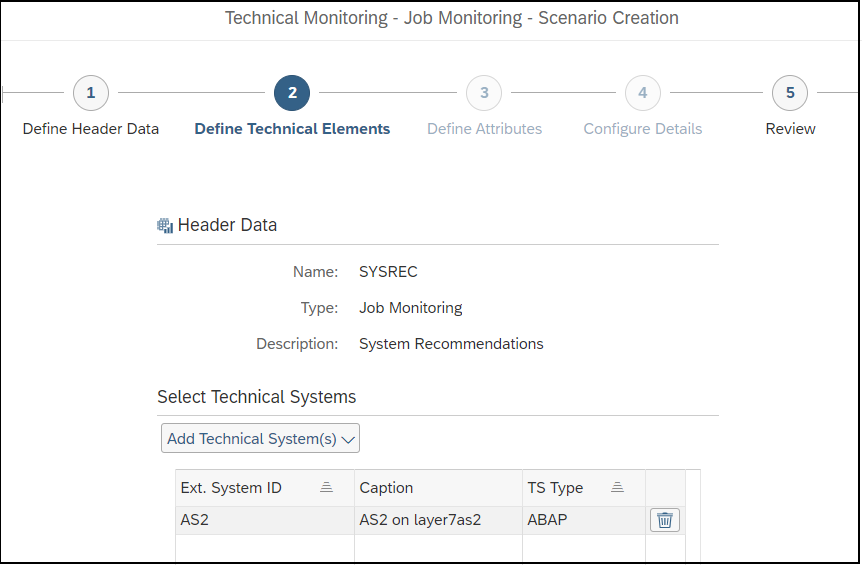
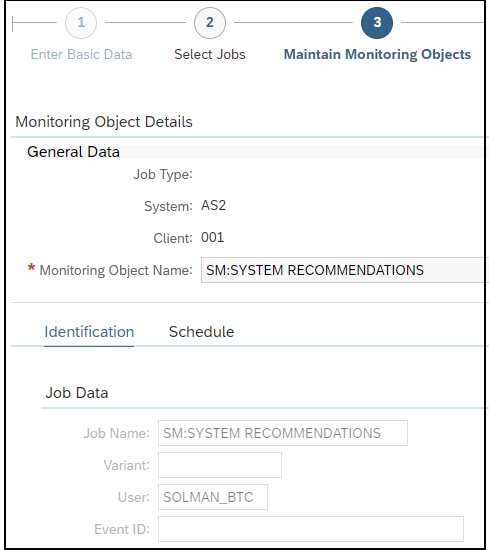
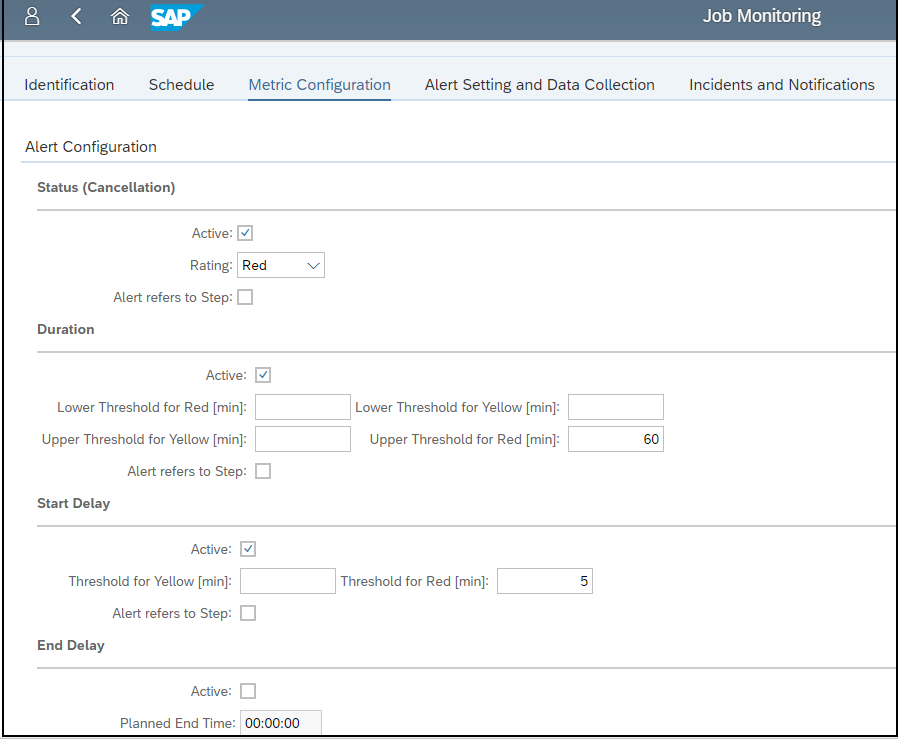
Securing the Web Dispatcher with the Cybersecurity Extension for SAP
The SAP Web Dispatcher is an application gateway that filters Internet based traffic to SAP systems including HTTP requests. As an entry point for Web-based communications in SAP landscapes, the Web Dispatcher can help to secure remote access to SAP systems by enforcing security standards for external connections and filtering connection requests.
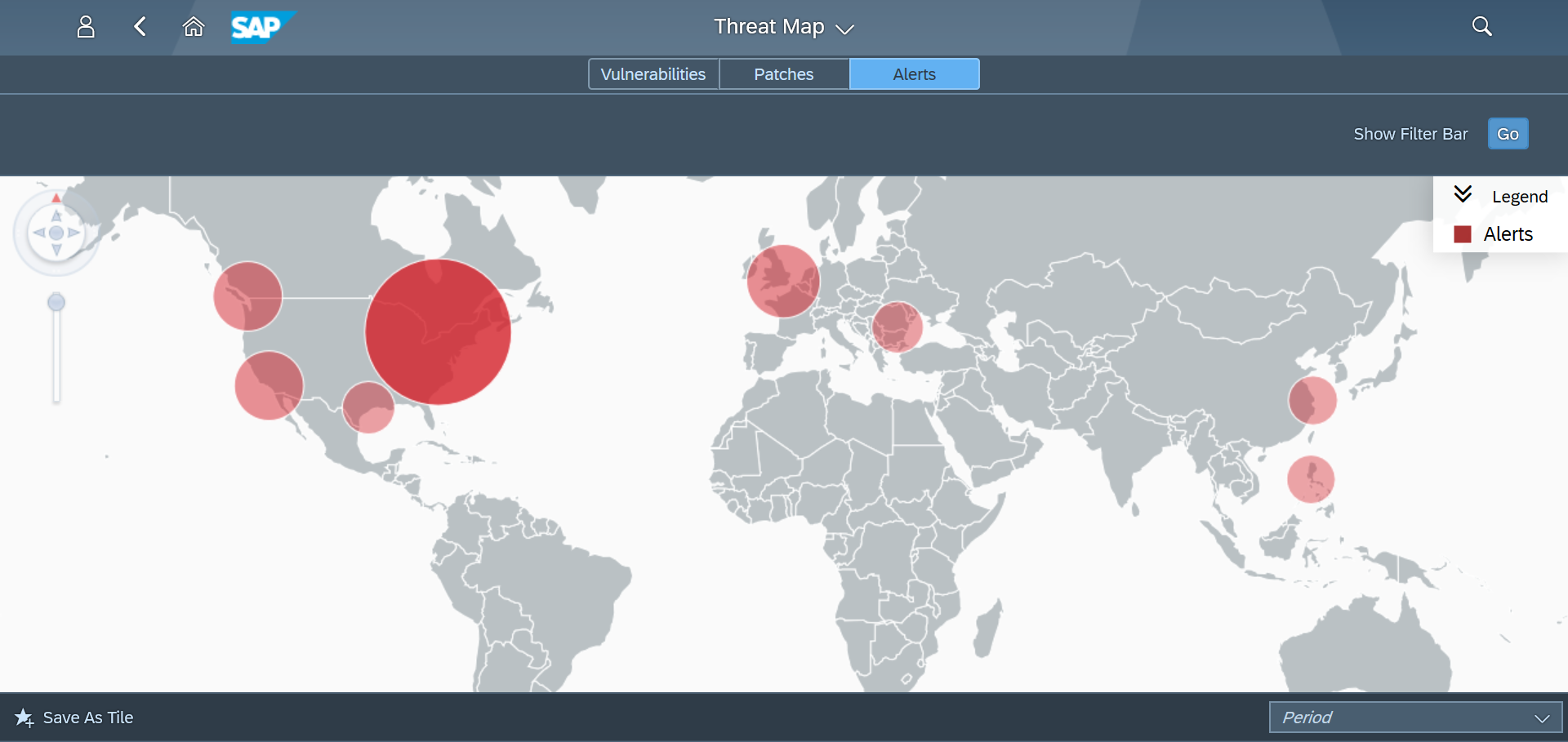
However, the Web Dispatcher can also be the focal point for attackers looking for an externally reachable pathway to SAP systems. Therefore, it is critical to secure the Web Dispatcher against misuse and prevent attackers from compromising SAP landscapes through poorly configured gateways.
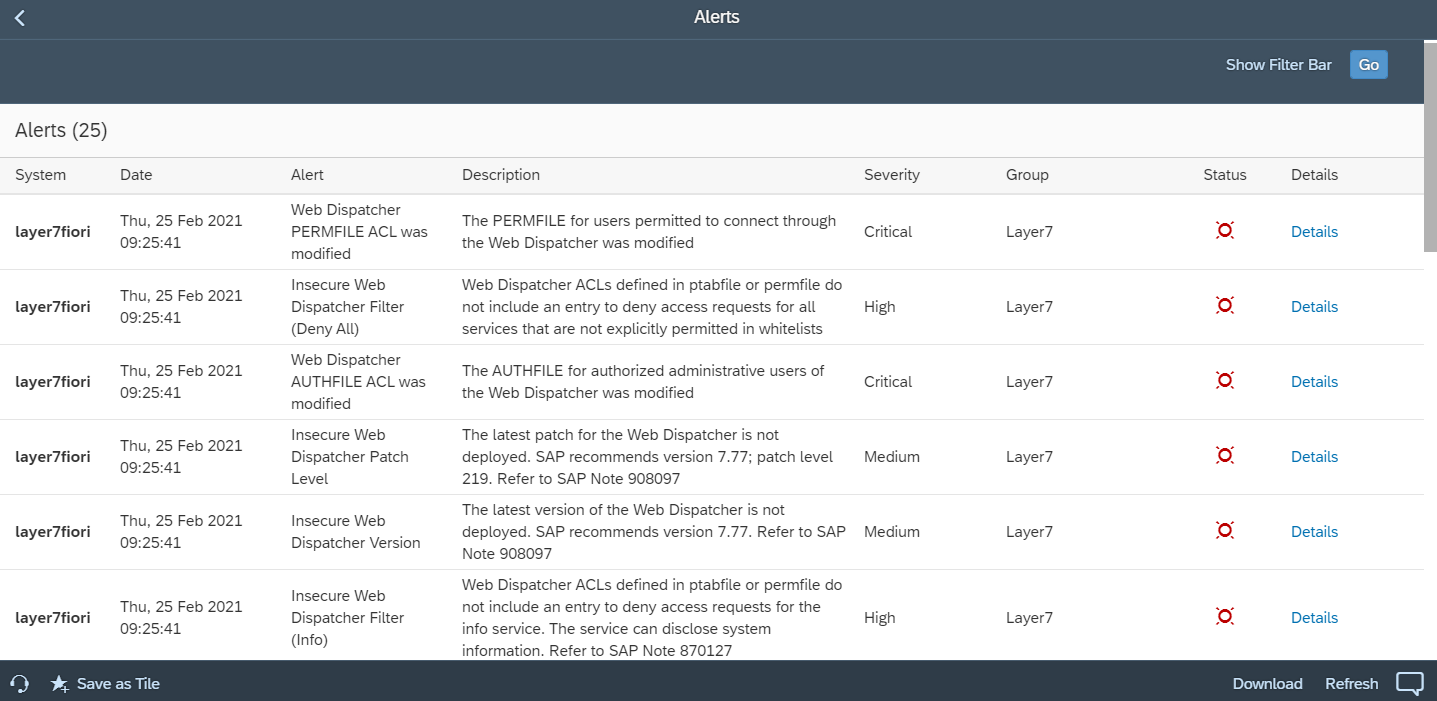
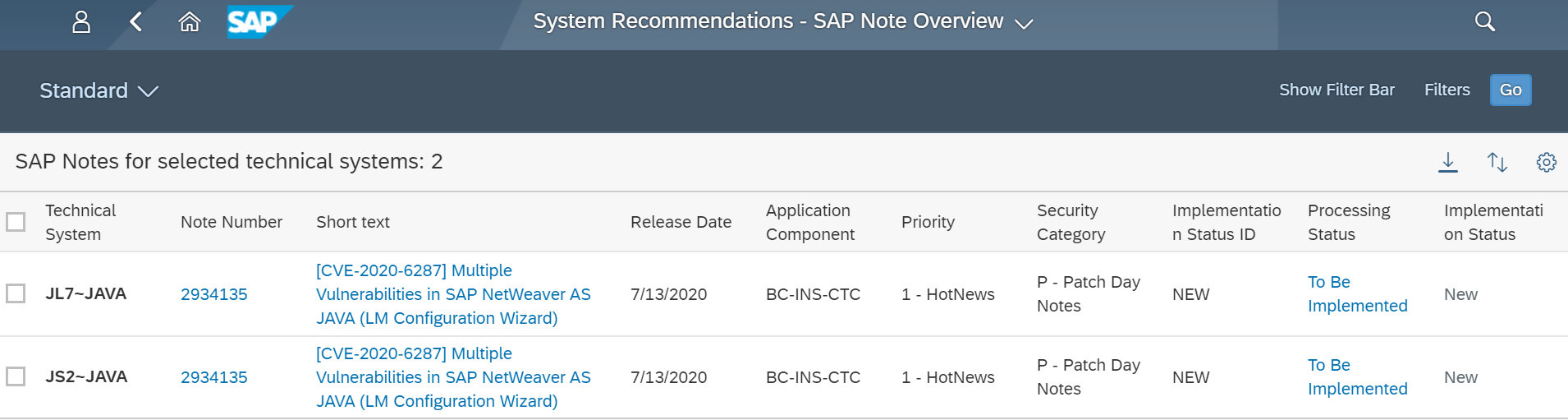
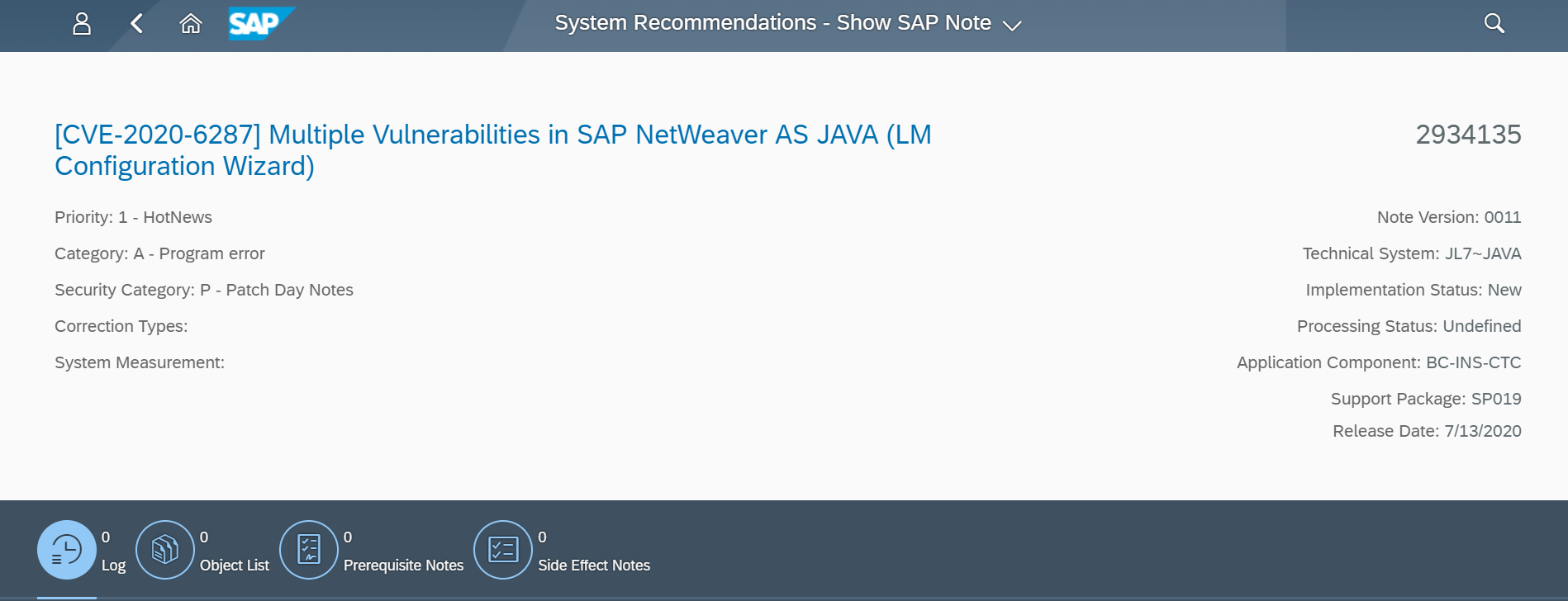
The Web Dispatcher should be regularly patched and updated to prevent attackers from exploiting known program-level vulnerabilities. You should monitor composite note 538405 to stay up-to-date with the latest Web Dispatcher versions.
Default error messages that disclose sensitive information to attackers should be blocked and replaced with custom messages.
The admin port for the Web Dispatcher should not be accessible from external networks. Administration should be restricted to internal hosts. Public monitoring information in the Web admin interface should be blocked.
SSL should be enforced for connections including communications between the Web Dispatcher and back-end systems and metadata exchange with message servers and application servers.
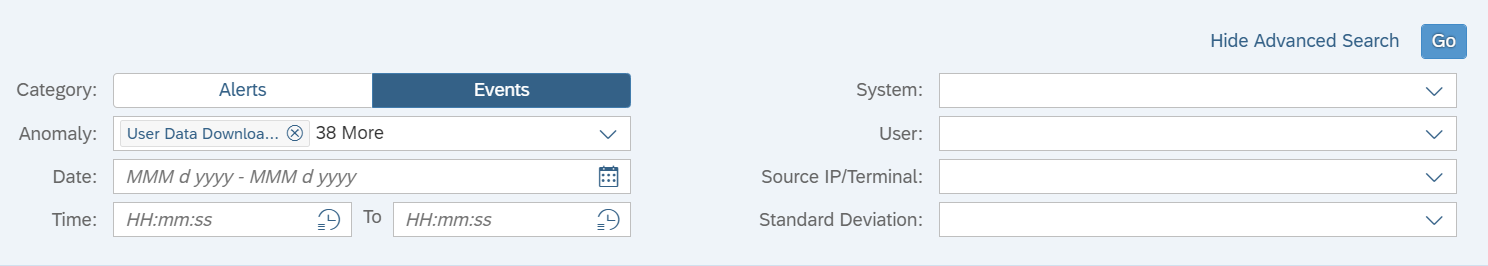
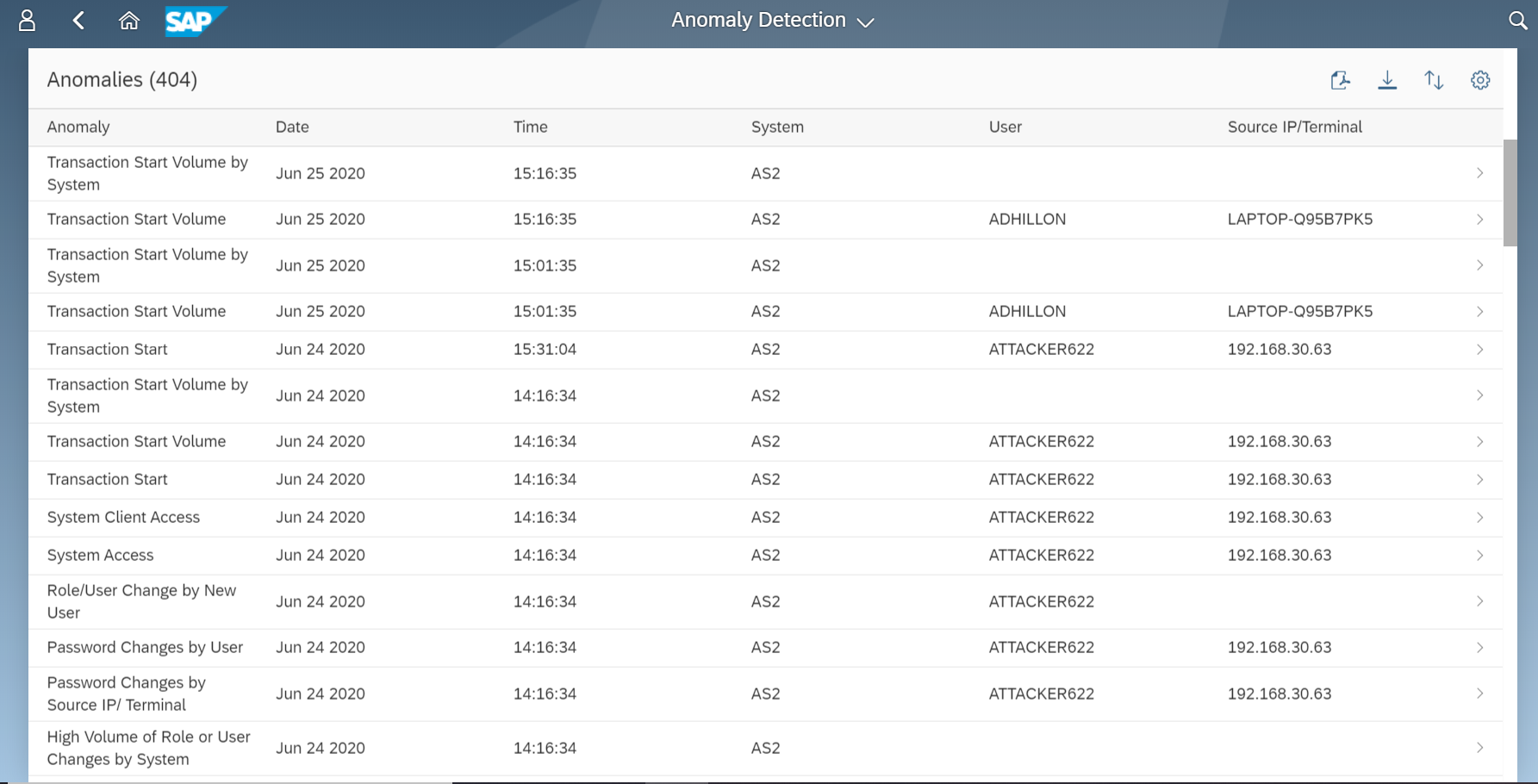
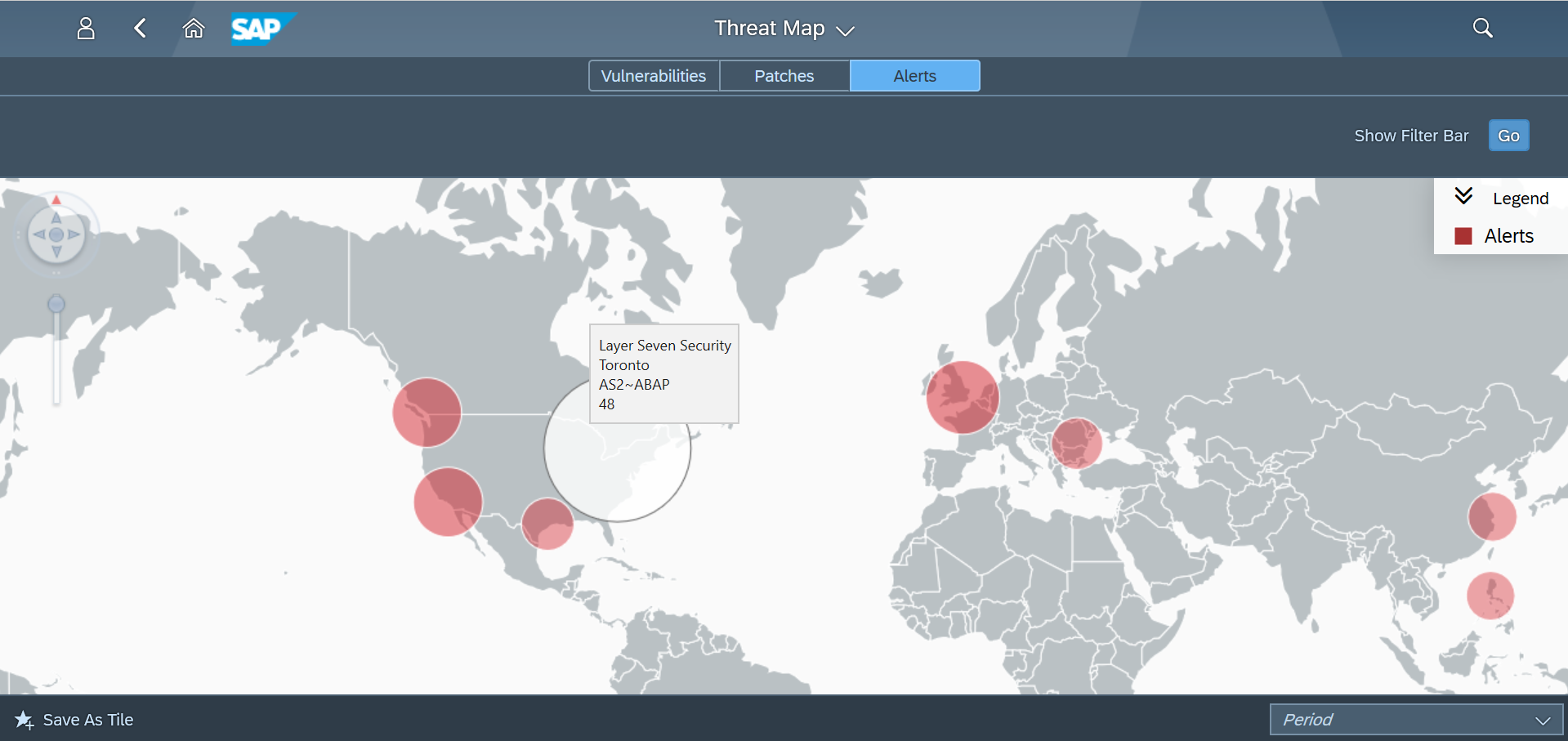
Finally, filtering should be enabled to enforce positive or negative lists for access requests. The Web Dispatcher supports multiple filtering mechanisms including ACL files and authentication handlers. ACL files can be used if access should be filtered based on client IP address or IP range. Authentication handlers should be used if requests need to be filtered for specific URLs. Both approaches support logging of successful and unsuccessful requests. Access to the following URLs should be blocked or restricted:
/sap/public/icman/*
/sap/public/ping
/sap/public/icf_info/*
/sap/wdisp/info
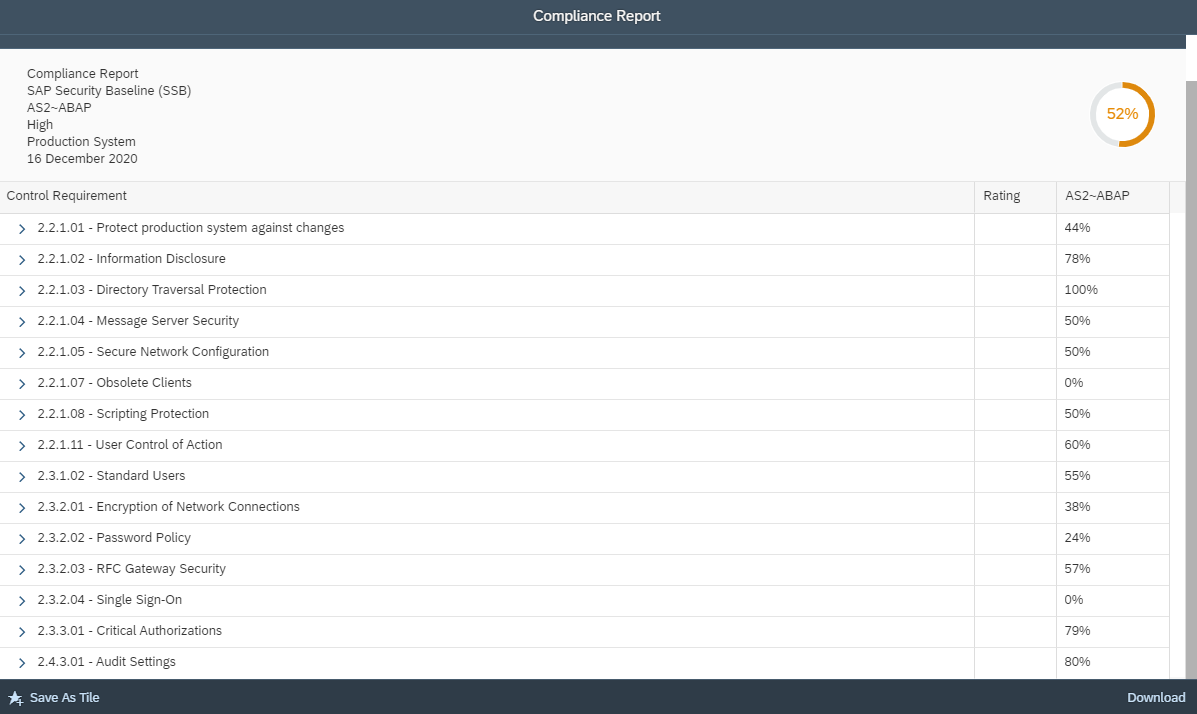
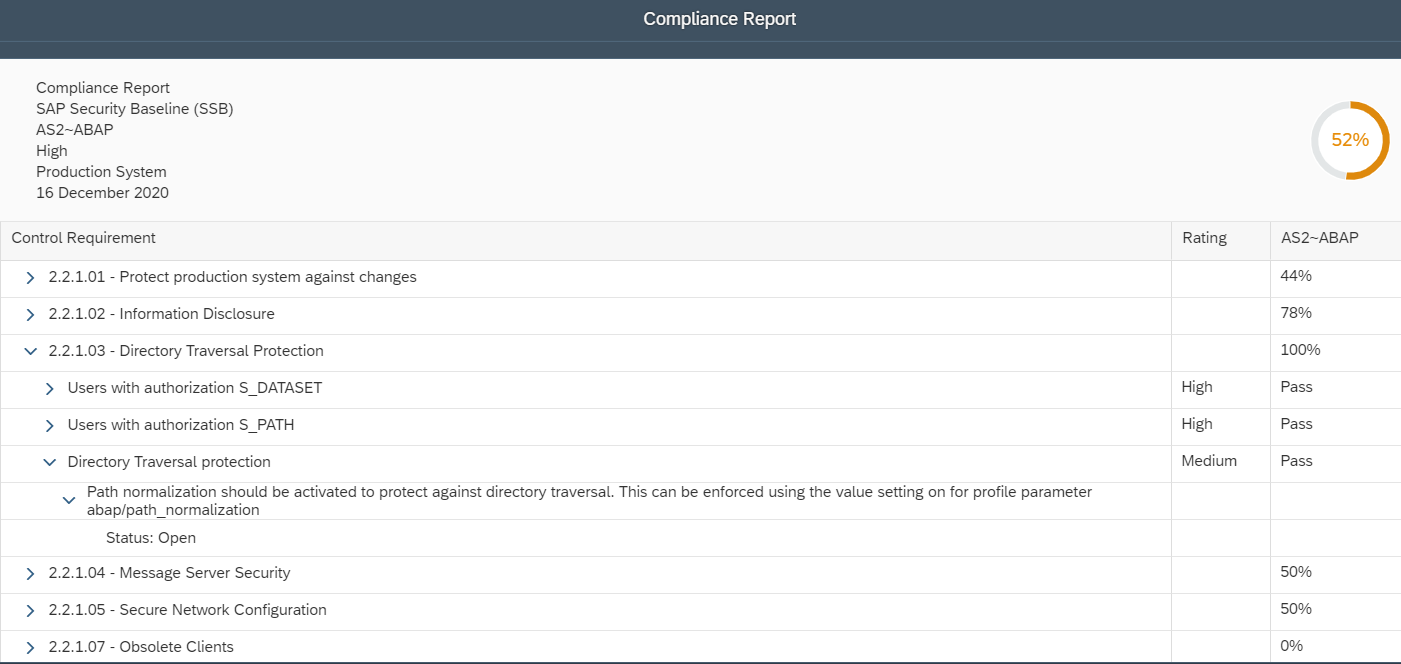
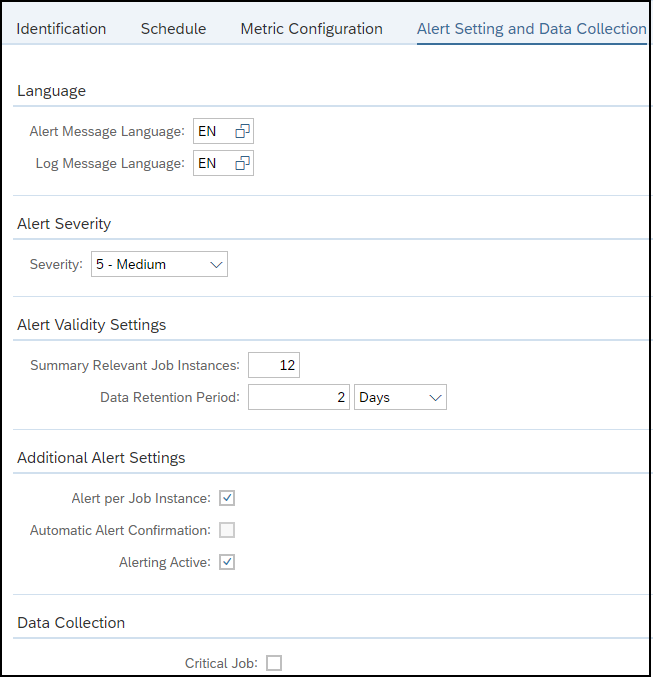
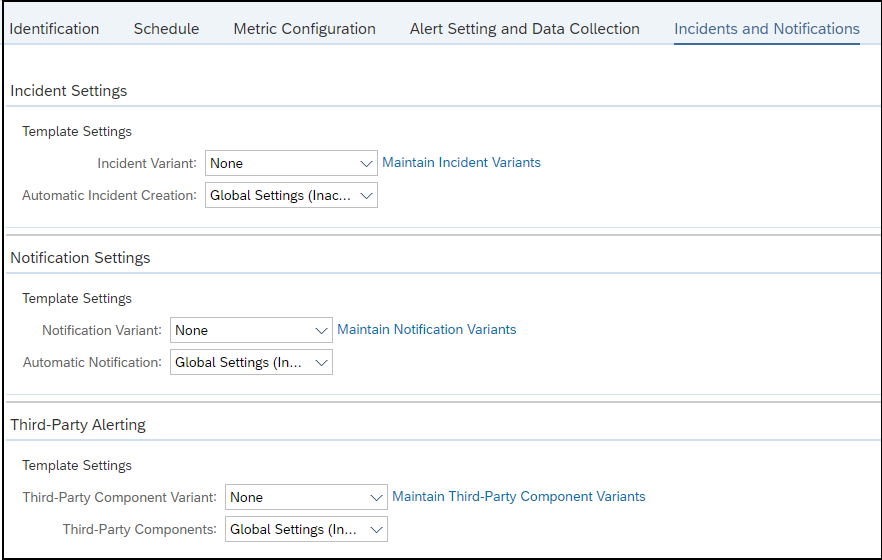
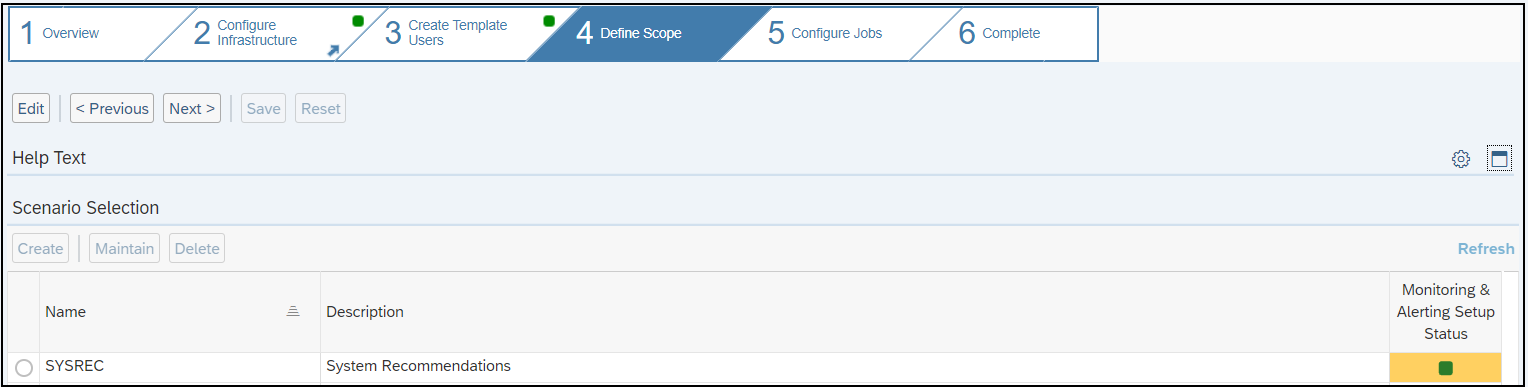
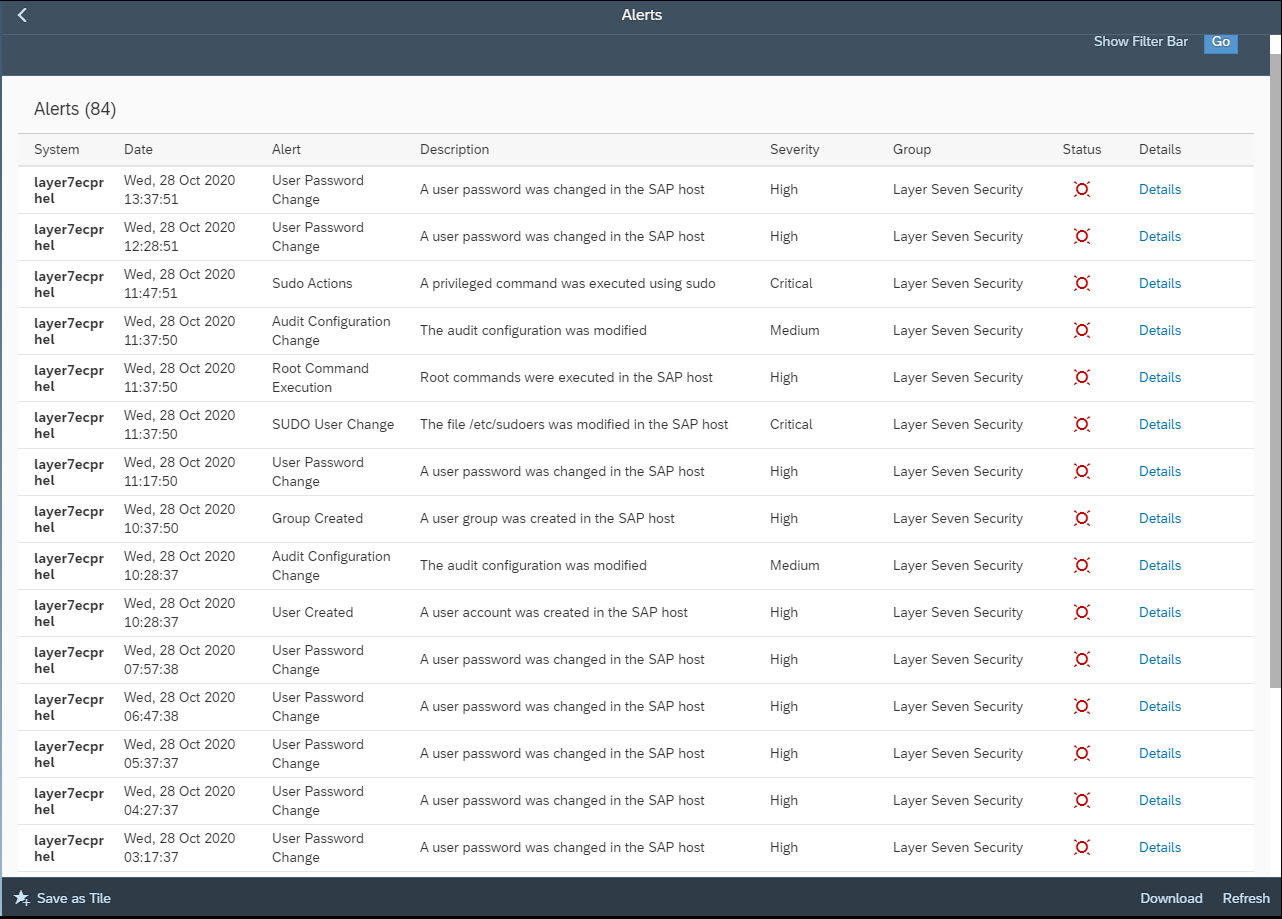
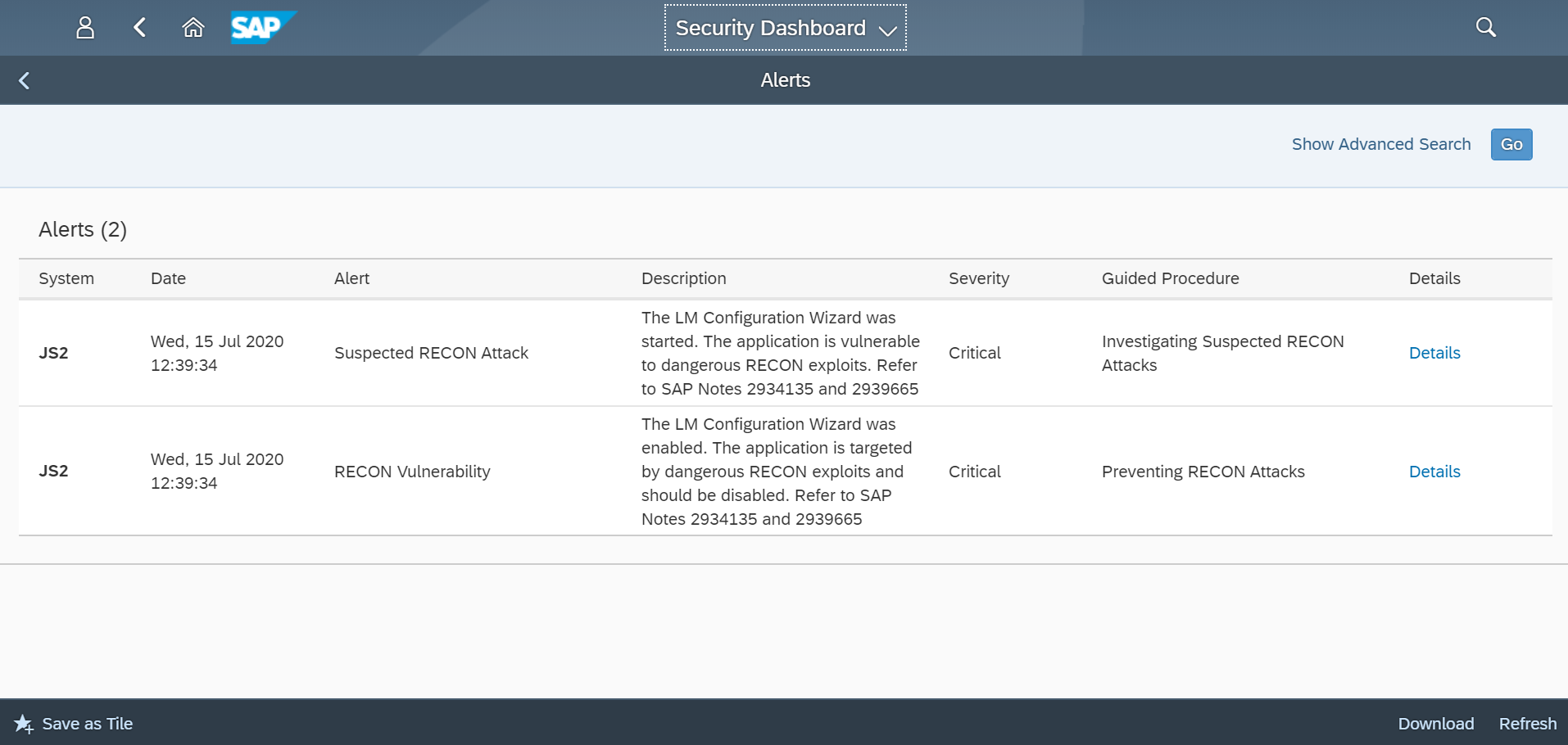
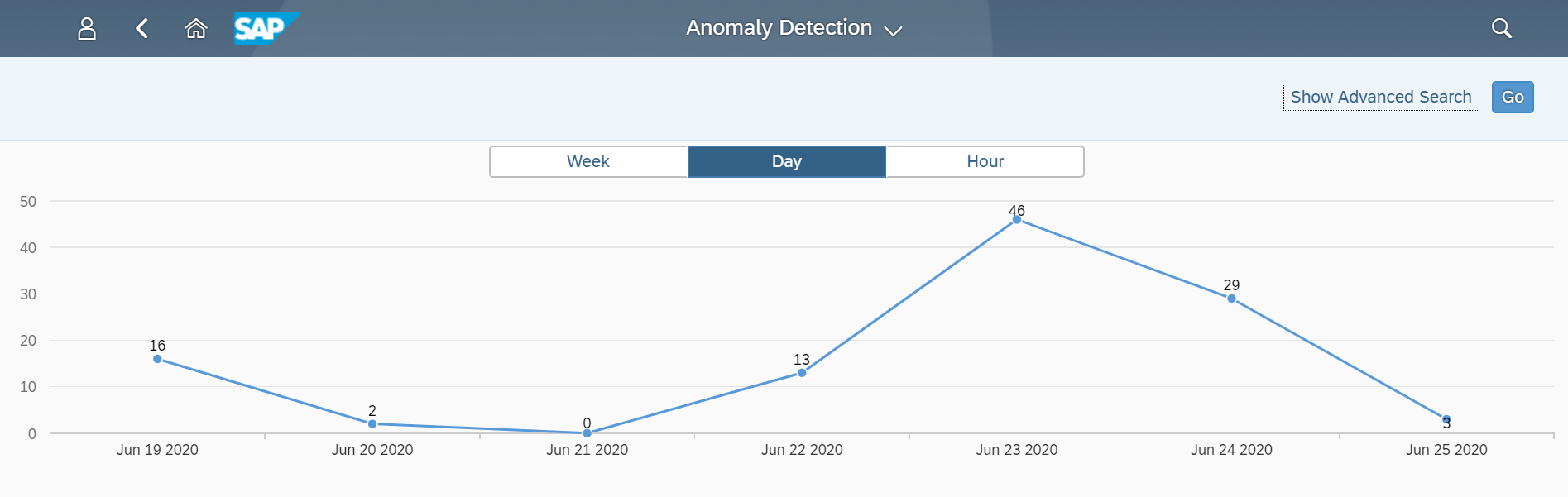
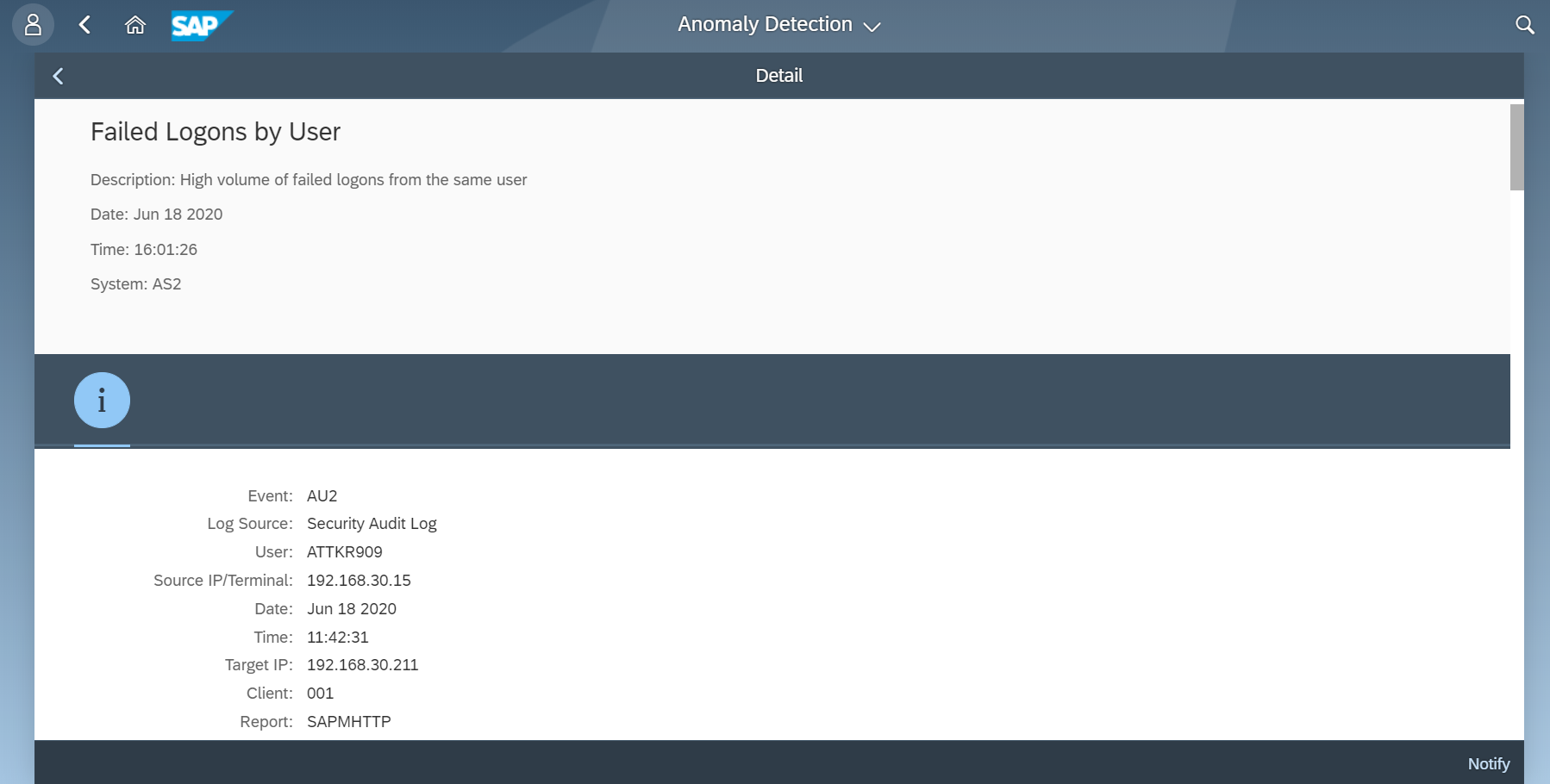
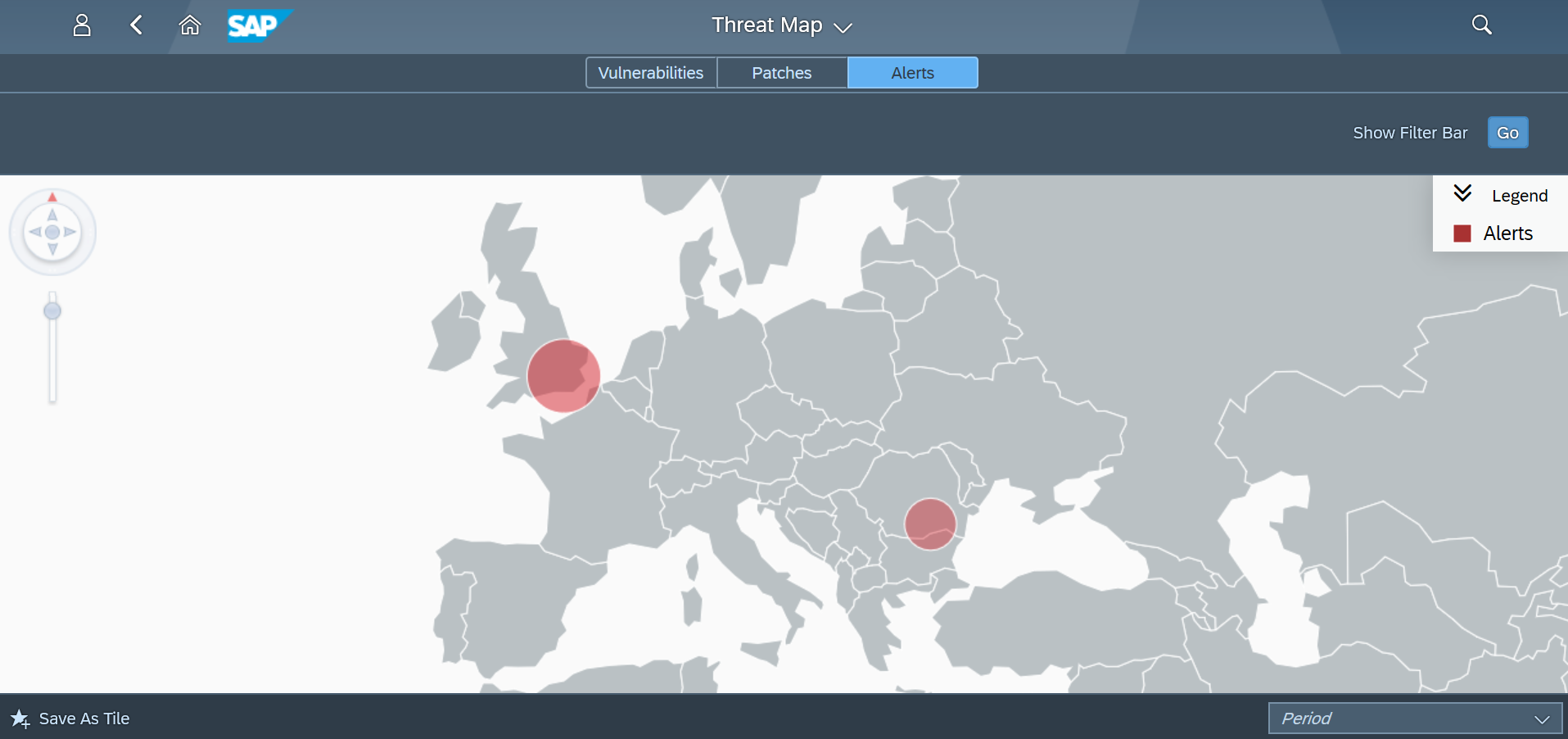
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP monitors the security of the Web Dispatcher using the SAP Solution Manager platform. The SAP-certified addon detects vulnerable Web Dispatcher versions and patch levels, improper error handling that could lead to information disclosure, the use of insecure Web Dispatcher settings, protocols, and filters, and calls to critical URLs captured in Web Dispatcher logs.