Detecting SAP Cyber Attacks with SAP Solution Manager
Despite the $75 billion spent by organizations on security software in 2015, average times to detection for cyber attacks are an astounding 170 days (DBIR, 2016). Most attacks therefore go undetected for almost six months.
An incident response strategy can address this gap by enabling organizations to proactively discover and contain security incidents that could lead to data breaches if left unchecked. The cornerstone of effective incident response is detection. This involves collecting and analyzing information from a variety of sources to identify signs of abnormal events that could include potential malicious actions. SAP systems capture a variety of security-relevant events across multiple logs. The most significant is the Security Audit Log.
The Security Audit Log should be configured to log successful and unsuccessful logon attempts by privileged and standard users, RFC calls, changes to user records, report and transaction starts, and other critical events. This is performed through filters defined in each system. Log data is stored in local or central files that are read by the Security Monitor of the CCMS. This data is available to Solution Manager for centralized alerting.
Solution Manager should be configured to monitor not just events in the Security Audit Log, but also security-relevant events in logs for the gateway server, message server, SAProuter, Web Dispatcher, system log, UME log and, for HANA systems, syslog servers. This captures critical events such as external programs started through the gateway server, external programs registered with the gateway, HTTP requests from remote or unrecognized IPs, and successful/ unsuccessful connections through application gateways.
The Event Calculation Engine (ECE) within Solution Manager continuously monitors event data recorded in such logs to identify potential attacks based on metrics configured for each log source. This is performed using existing data providers such as Diagnostics Agents and sapstartsrv. Both are automatically installed with SAP systems. The monitoring interval for log sources can be customized but the recommended interval is 60 seconds. The ECE can be configured to perform event correlation for sophisticated pattern analysis.
Alerts are triggered by ECE for events that match a defined pattern or exceed thresholds for specific metrics. The alerts are displayed in the Alert Monitor for Solution Manager. Priority levels can be set for each alert based on a High-Medium-Low scale. Alert data also be transferred to Business Warehouse for detailed reporting and analysis using real-time dashboards.
Solution Manager also channels notifications for alerts to designated Incident Responders through email and text message. Notifications can be grouped to avoid alert flooding. Each notification provides a URL to the relevant alert or alert group within Solution Manager. Incident Responders can add comments to the alert in the Alert Monitor, follow guided procedures for handling alerts, and create and assign tickets for incident management within Solution Manager.
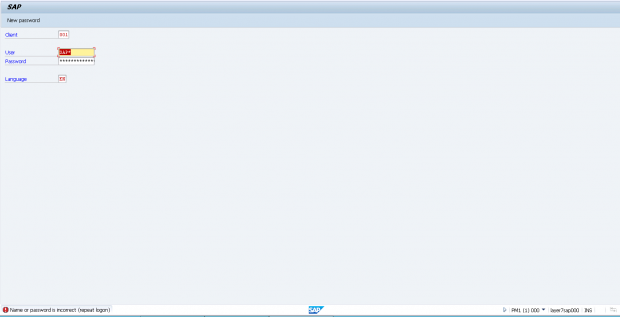
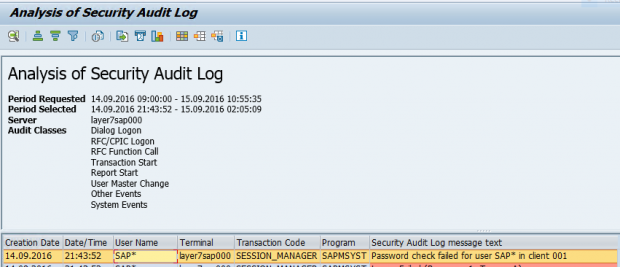
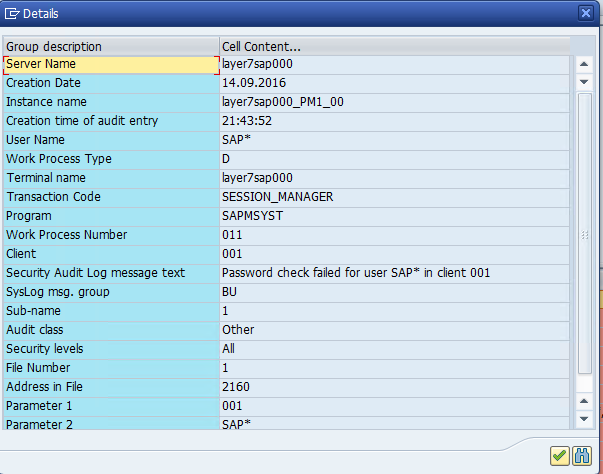
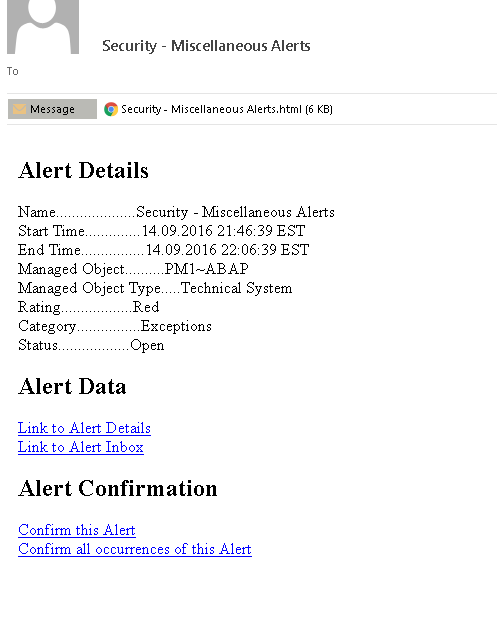
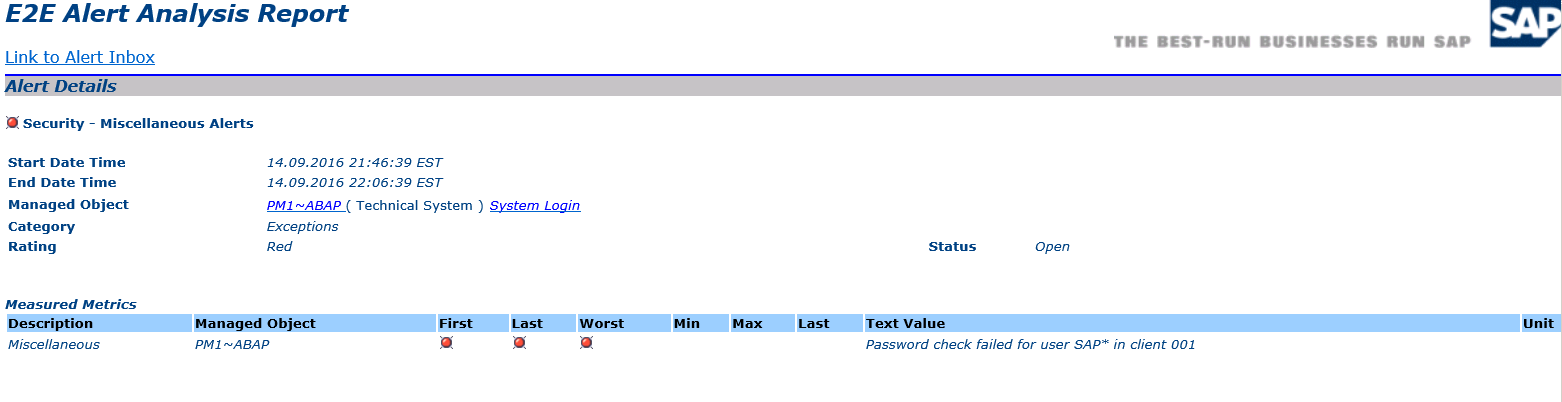
The example below displays the alert details and notifications generated by Solution Manager for a failed logon by the standard SAP* user in a monitored system.
1. Attempted logon using SAP* user in client 001 of system PM1.
2. Event summary in the Security Audit log.
3. Event details in the Security Audit Log.
4. Email notification of event.
5. The email attachment for the alert notification.
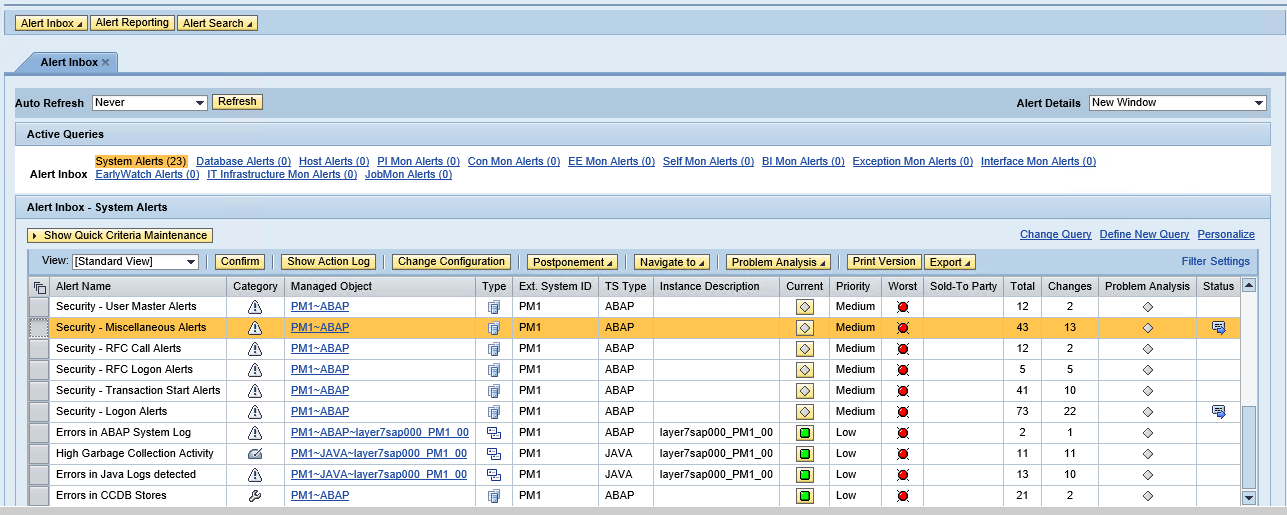
6. The Alert Inbox in SAP Solution Manager
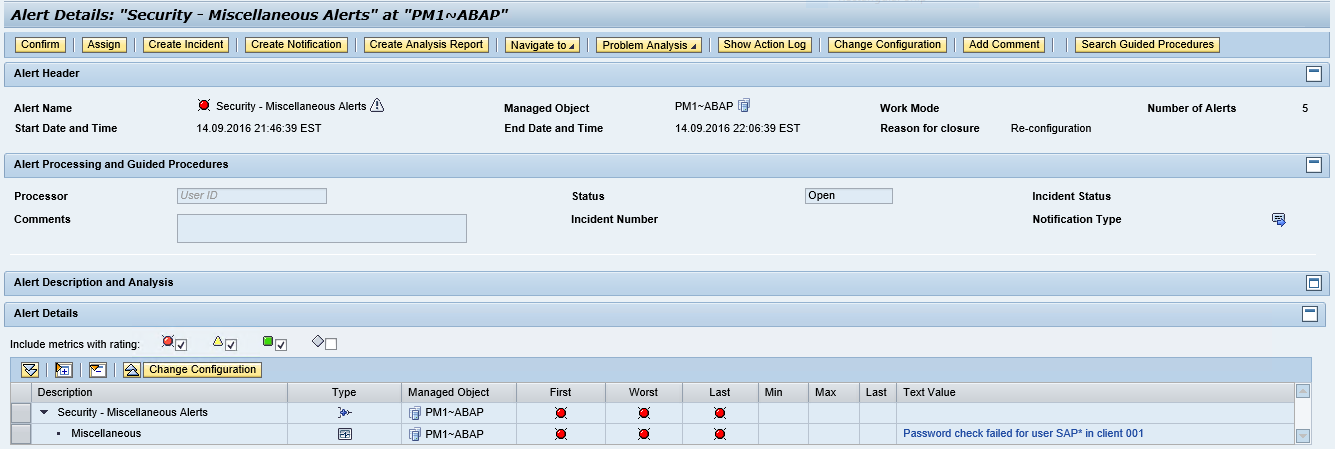
7. The details of the alert in the Alert Monitor