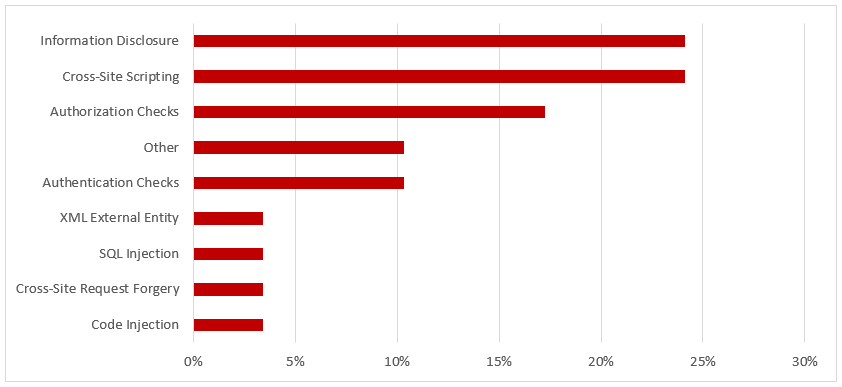
SAP Security Notes, September 2017
Note 2408073 prepares systems to handle digitally signed SAP Notes. Digitally signed Notes will be issued by SAP in the future to protect against the risk of uploading Notes containing malware. Digital signatures will support authentication and the identification of changes performed by attackers to SAP-delivered Notes. SAP recommends only uploading digital signed Notes once they are available.
Note 2518518 should be implemented before Note 2408073 to install new objects required to support Notes with digital signatures. The Notes will update the Note Assistant tool to verify digital signatures using the SAPCAR utility. SAPCAR must version 7.20, patch level 2 or higher. The Note Assistant tool will process ZIP files containing Notes downloaded from the SAP Support Portal and log the results of digital signature checks. Notes that fail the digital signature check will be logged in the Application Log (transaction SLG1) and read by the Notes Assistant using the authorization object S_APPL_LOG. For further information, refer to 2537133 – FAQ – Digitally Signed SAP Notes and the Digital Signature User Guide referenced in Note 2408073.
Note 2520064 provides detailed instructions for removing a missing authentication check in the SAP Point-of-Sale (POS) Retail Xpress Server that was originally reported in July. The vulnerability could be exploited by attackers to modify files, capture sensitive information and perform a denial of service.
Notes 2531241 and 2520772 provide corrections for patching SAP Landscape Management (LVM) to prevent the storage of sensitive information including administrative passwords in plaintext within logs that can be read in database tables. The patches released with the Notes prevent LVM from persisting passwords in plaintext but do not remove sensitive information already stored in the logs. Therefore, the solution section includes instructions for changing passwords and discovering and removing sensitive log entries.
Finally, Note 2278931 removes a high-risk code injection vulnerability in Document Management Services. The vulnerability could be exploited by attackers to create backdoors or escalate privileges.