Security Advisory for Critical SAP ICMAD Vulnerabilities

International threat intelligence agencies including the U.S Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and the Computer Emergency Response Team for the EU (CERT-EU) issued security advisories last week for critical vulnerabilities in the SAP Internet Communication Manager (ICM). The ICM supports inbound and outbound communication with SAP systems using the HTTP(S) protocol. It is a standard component of the NetWeaver Application Server ABAP and Java and the SAP Web Dispatcher.
The advisories relate to CVE-2022-22536, CVE-2022-22532 and CVE-2022-22533, labelled ICMAD (Internet Communication Manager Advanced Desync). The most critical is CVE-2022-22536: a memory corruption vulnerability that can be exploited through a single HTTP request to fully compromise SAP systems, remotely and without authentication. This impacts AS ABAP and the Web Dispatcher when they are accessed through an HTTP gateway. For AS ABAP, the gateway could be the Web Dispatcher. The vulnerability does not impact direct access to SAP application servers. CVE-2022-22532 impacts AS Java only. This vulnerability has a lower CVSS than CVE-2022-22536 due to a higher attack complexity, but ranks high in terms of impact to Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. CVE-2022-22533 is for a lower priority denial of service vulnerability in AS Java triggered by requests that exhaust Memory Pipes (MPI) used for communicating between the ICM and work processes in application servers.
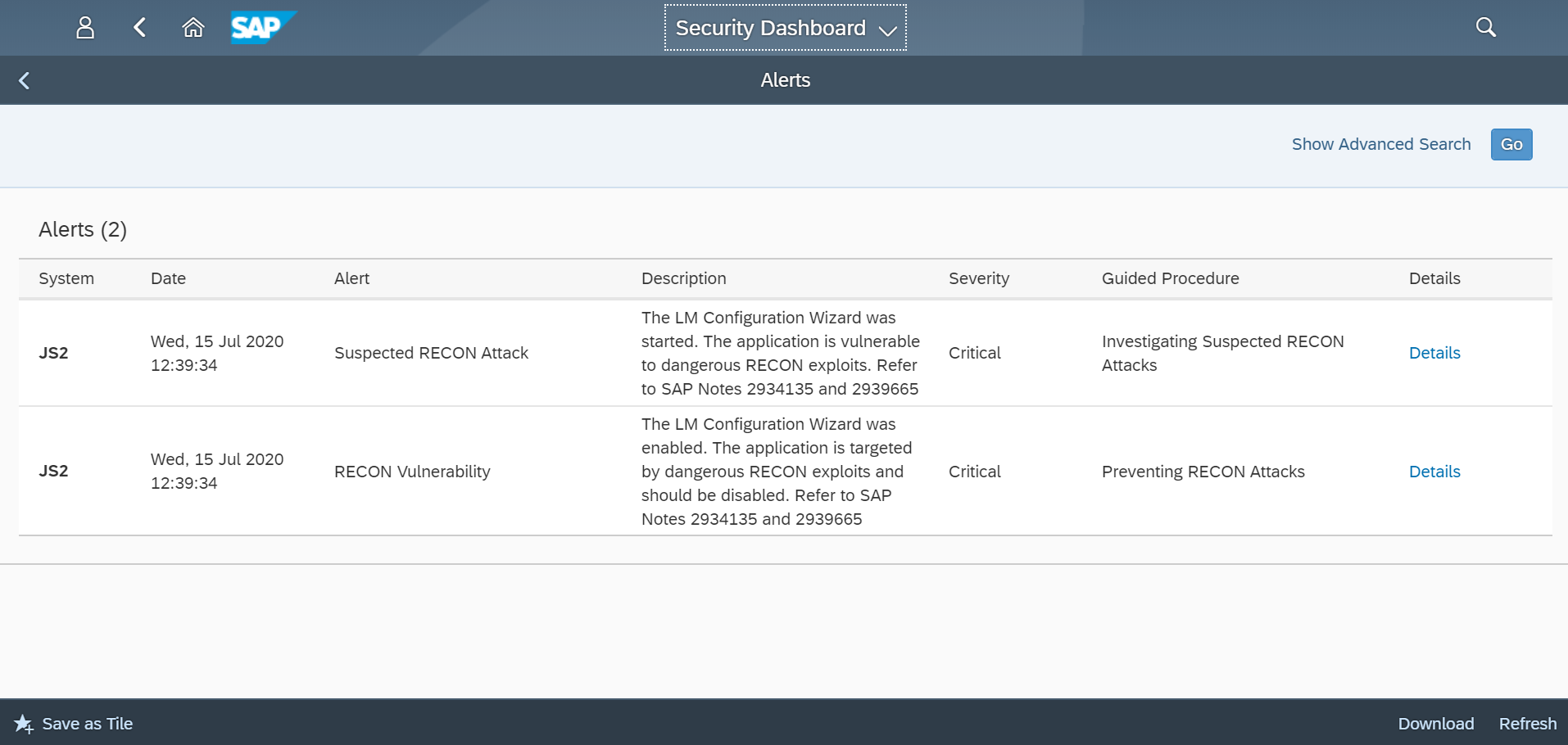
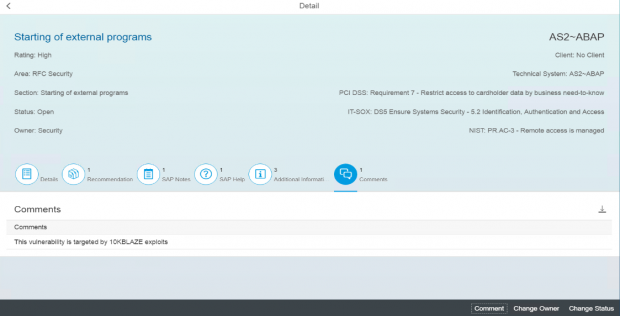
There is evidence of active scanning for ICMAD. SAP systems exposed to the Internet are especially vulnerable. External-facing Web Dispatchers are equally vulnerable. Consequently, it is critical to apply the relevant security notes to patch SAP systems against ICMAD.
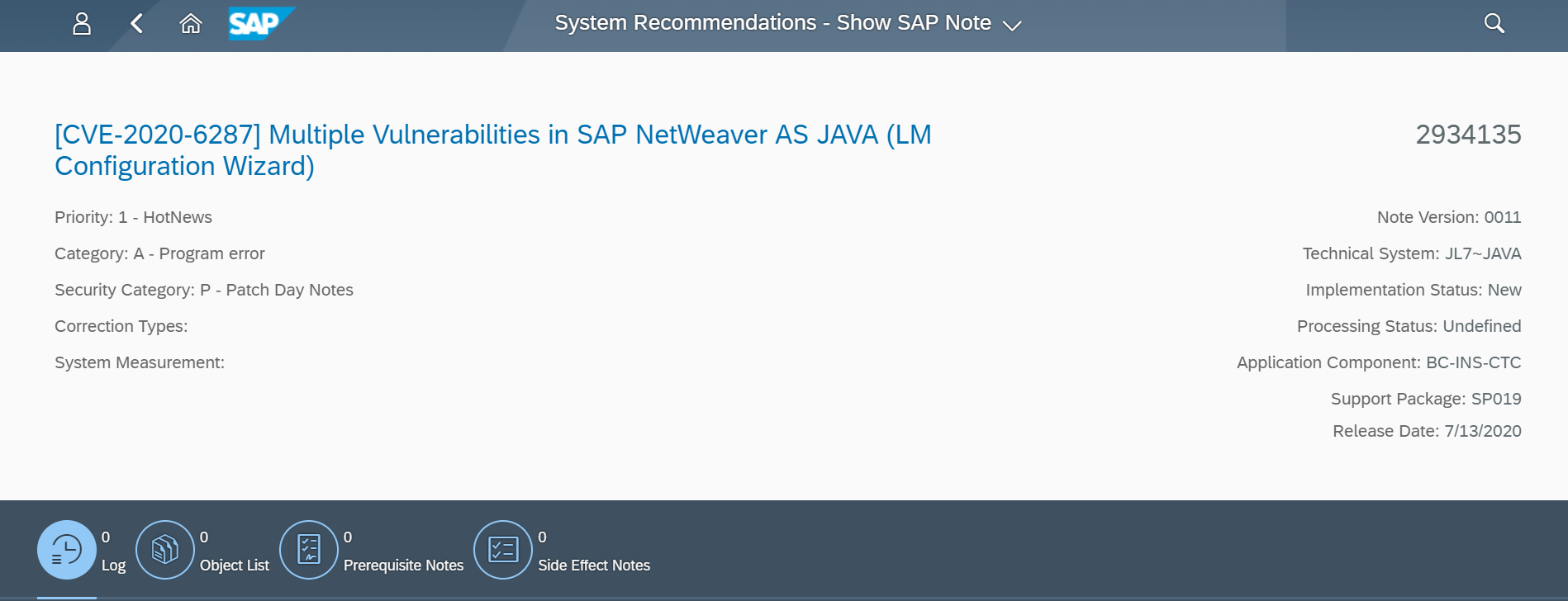
Note 3123396 patches AS ABAP and the Web Dispatcher for CVE-2022-22536. SAP Kernels and Web Dispatchers should be updated to the minimum patch levels detailed in the note. The workaround detailed in note 3137885 can be applied as a stop-gap measure if the patches cannot be implemented at short notice. For access through the Web Dispatcher, refer to 3137885 to ensure that Web Dispatcher installations meet the minimum patch level. To apply the workaround, the profile parameter wdisp/additional_conn_close should be set to TRUE. For more details, refer to note 3138881.
Note 3123427 patches AS Java for CVE-2022-22532 and CVE-2022-22533. The workaround recommended in the note can be applied using the parameter setting icm/handle_http_pipeline_requests=FALSE if support for HTTP pipeline requests is not required.
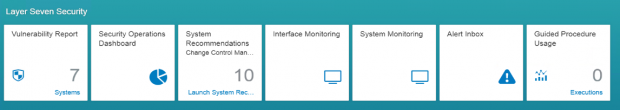
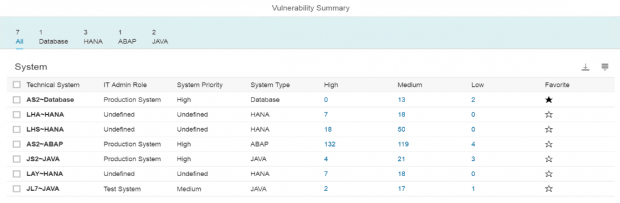
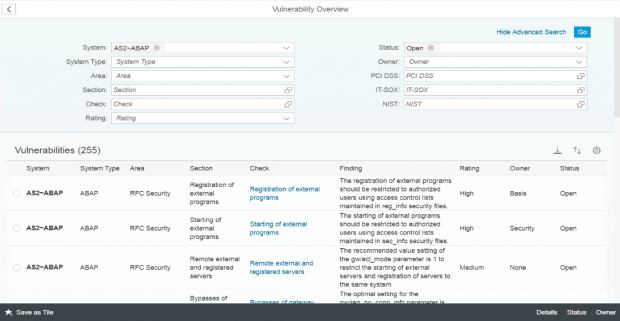
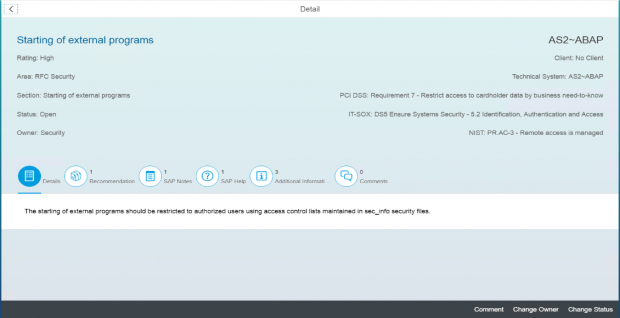
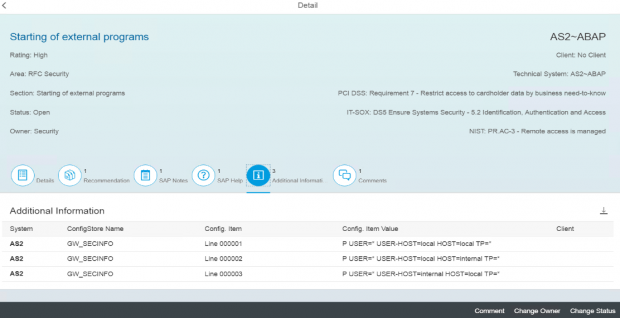
The Cybersecurity Extension for SAP discovers vulnerable ABAP, Java and Web Dispatcher installations that have not been successfully patched for ICMAD. It also identifies missing or incorrectly applied workarounds if the corrections in notes 3123396 and 3123427 have not been applied. The SAP-certified solution performs over 1800 checks for known vulnerabilities in SAP applications and components and supporting databases and operating systems.