How does Solution Manager detect threats and vulnerabilities in SAP systems? What specific applications in SolMan are used for vulnerability, patch and threat management? What are the requirements for using these areas? How long does it take to configure? What are the differences between monitoring using SolMan 7.1 and 7.2? What are the benefits of using SolMan versus third party tools? Why should you partner with Layer Seven Security to help you leverage the cybersecurity capabilities of SAP Solution Manager?
Discover the answers to these and many other questions in the new Q&A section and learn how you can immediately protect your SAP systems from advanced threats using tools you already own and an approach recommended by SAP.
Remember to bookmark the page since we will be updating the questions and answers periodically. Also, feel free to submit your questions for our experts in the comments below.
Q: What is SAP Solution Manager?
A: Solution Manager is the most widely deployed SAP product after ECC. It’s installed in almost all SAP landscapes and is used for application lifecycle activities such as system patching and upgrades, change management, incident management, and system monitoring.
Q: How is Solution Manager licensed?
A: Usage rights for Solution Manager are bundled with SAP support and maintenance agreements. SAP Enterprise Support customers can manage their whole IT infrastructure with Solution Manager. Customers with Standard Support can manage SAP products within their IT landscapes with Solution Manager. Licensing for SAP HANA is included with the usage rights for SAP Solution Manager 7.2.
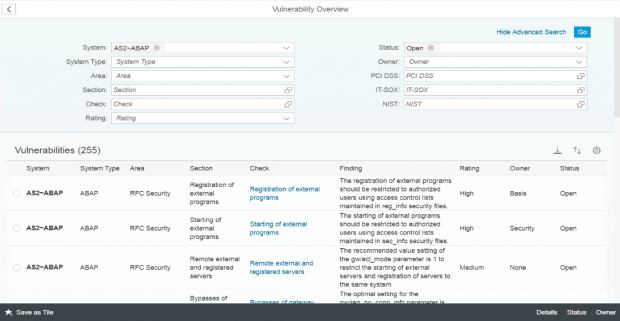
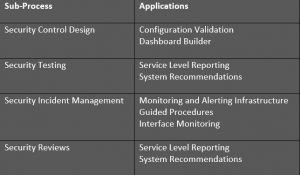
Q: What security tools are available in Solution Manager?
A: There are several applications in Solution Manger that should be used for advanced security monitoring. We recommend Service Level Reporting, Security Dashboards, System Recommendations, Interface Monitoring and Security Alerting.

Q: Why doesn’t Layer Seven Security recommend the EWA and SOS reports?
E: There are drawbacks with both reports. The EarlyWatch Alert (EWA) performs some security checks but is not specifically a security report. Therefore, the range and volume of checks performed by EWA for security is low. The Security Optimization Service (SOS) provides better coverage but is not fully automated. You must submit a service request to run SOS for ABAP systems. Service requests to run SOS for Java systems must be submitted to SAP.
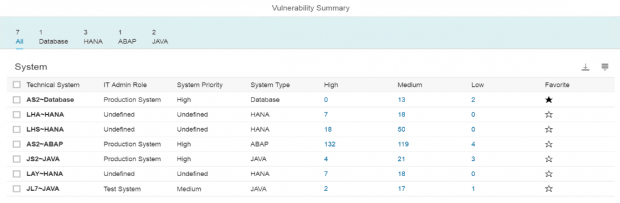
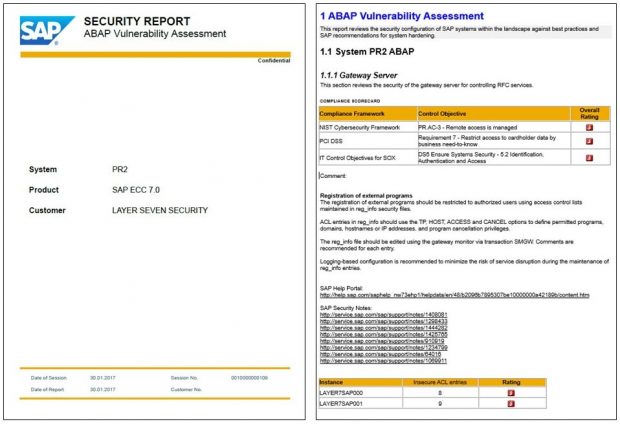
Q: What are Service Level Reports?
A: Service Level Reports (SLR) automate vulnerability reporting for SAP systems. They perform scheduled checks for hundreds of security weaknesses for ABAP, HANA and Java systems and automatically distribute the results via email, SFTP or the Enterprise Portal. SLRs include detailed descriptions for findings, risk ratings, links to relevant SAP Notes and guidance at the SAP Help Portal and compliance scorecards for frameworks such as NIST, PCI DSS and IT-SOX.
Q: How do SLRs work?
A: SLRs read the results of automated daily vulnerability scans performed by Solution Manager for SAP systems. The results are checked against security KPIs during runtime. SLRs are typically scheduled to run on a weekly or monthly schedule.
Q: Are SLRs available in multiple languages?
A: Yes, SLRs can be run in any language including French, German, Spanish, Arabic, Japanese, and Mandarin.
Q: Are SLRs customizable?
A: Yes, you can customize every aspect of service level reports including the design, layout, security checks, and KPI metrics and thresholds.
Q: Can you provide a sample Service Level Report?
A: Yes, submit your request here.
Q: What is System Recommendations?
A: System Recommendations is an application in Solution Manger that performs automated patch management for SAP systems. It connects directly to SAP Support to download required security notes and monitor the status of notes implemented in systems through regular background jobs.
Q: Does System Recommendations also download and apply corrections?
A: Yes, System Recommendations downloads corrections from SAP Support to target systems. The user is automatically directed to SNOTE in the target systems once the corrections are downloaded.
Q: Does System Recommendations identify the impact of security patches?
A: Yes, System Recommendations integrates with applications in Solution Manager to perform change impact analysis and discover programs, function modules, transactions, reports and business processes effected by notes.
Q: Does System Recommendations integrate with Change Request Management (ChaRM)?
A: Yes, System Recommendations includes the option to automatically generate a change request for required notes.
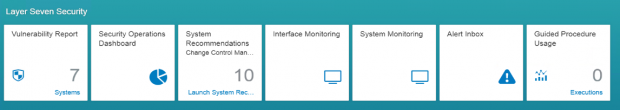
Q: What are Security Dashboards?
A: Security Dashboards monitor critical key performance indicators to track vulnerabilities and threats across SAP landscapes in real-time.
Q: What type of metrics are monitored by Security Dashboards?
A: The Dashboards connect to data stores in Solution Manager for event-driven alerts and system and user level vulnerabilities. Users can drilldown from aggregated results to detailed values.
Q: What type of data visualizations are available in the Security Dashboards?
Users can select from column, line, pie, scatter and other charts and Fiori tiles and tables.
Q: What is Interface Monitoring?
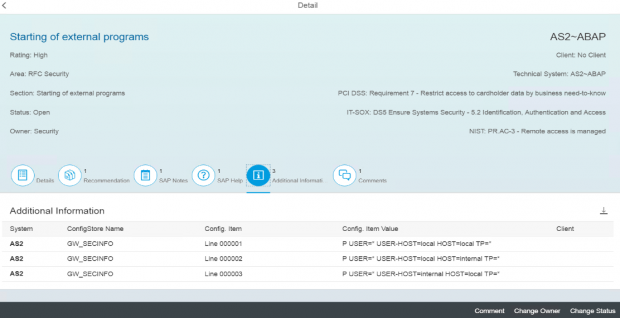
A: Interface Monitoring is used to map and track system interfaces in SAP landscapes including RFC, HTTP, IDoc and Web Service connections. It automatically creates a topology of system interfaces and monitors the usage of the interfaces in real-time. Alerts can be generated for channel metrics including availability, configuration and performance.
Q: What is Security Alerting?
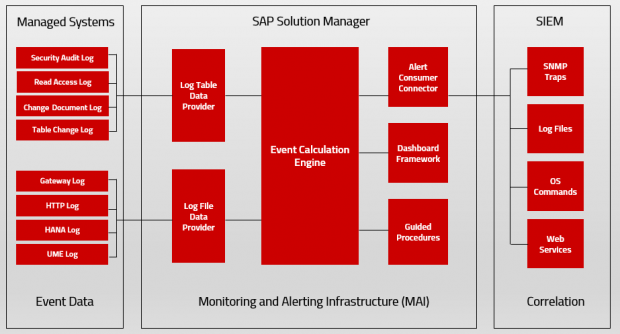
A: Security Alerting is based on the Monitoring and Alerting Infrastructure (MAI) of Solution Manager. MAI connects to data providers including event logs to monitor for security vulnerabilities and incidents. MAI generates automatic notifications for security incidents including emails and text messages.
Q: What type of security vulnerabilities and events are monitored by MAI?
A: MAI monitors system-level vulnerabilities such as the enabling of the invoker servlet in Java systems, insecure entries in access control lists for gateway servers, vulnerable RFC destinations, missing security notes, and many other areas. It also monitors KPIs for user-level security including users with dangerous profiles such as SAP_ALL and unlocked standard users.
Q: Can you perform threat detection using MAI in Solution Manager?
A: Yes, MAI includes file and database connectors for real-time monitoring of event data captured in SAP logs. This includes the security audit log, HANA log, UME log, HTTP log, gateway server log, and the Read Access Log.

Q: Can you integrate MAI alerts with Security Information Event Management (SIEM) and incident management systems?
A: Yes, MAI alerts can be automatically forwarded to SIEM systems such as Splunk, ArcSight, and QRadar for event correlation and forensic analysis. Alerts can also be forwarded to incident management systems such as BMC Remedy and ServiceNow.
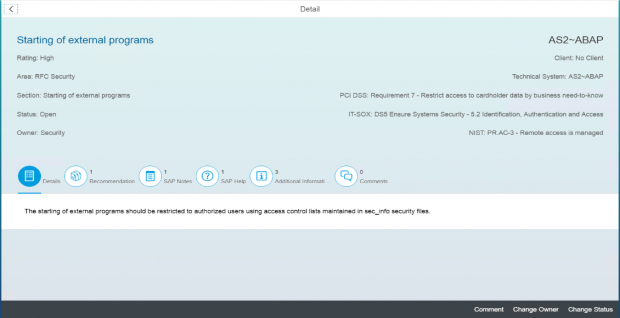
Q: Does Solution Manager provide best practices for alert handling?
A: Yes, the Guided Procedure (GP) Framework in Solution Manager provides best practices and standard operating procedures for investigating and resolving security alerts. This standardizes and improves incident management procedures and reduces response times. The guided procedures include automated steps to further improve incident handling.
Q: What are the main differences between SAP Enterprise Threat Detection (ETD) and threat detection using SAP Solution Manager?
A: SAP ETD provides more advanced capabilities for event correlation and forensic analysis. However, Solution Manager can forward event data to SIEM systems that can correlate and analyze data on a wider scale than ETD by combining data from SAP and non-SAP sources. Also, ETD does not monitor for system-level vulnerabilities or provide guided procedures for alert handling.
Q: What are the requirements for using the security applications in Solution Manager?
A: The security applications are available in any SP level of Solution Manager versions 7.1 and 7.2. The only requirements are the completion of the SOLMAN_SETUP procedures for the relevant version.
Q: What are the differences between Solution Manager 7.1 ad 7.2 for security monitoring?
A: The main difference is the user-experience. Solution Manager 7.2 provides the improved Fiori interface including a launchpad for direct access to applications. Some functions such as automatic download of SAP corrections in System Recommendations are only available in Solution Manager 7.2. Also, the dashboarding and interface monitoring capabilities are more advanced in the latest version of Solution Manager.
Q: How many environments and systems can you monitor with Solution Manager?
A: There are no limits on the number of environments or systems that can be monitored by Solution Manager. However, Solution Manager must be appropriately sized to monitor large landscapes.
Q: How long does it take to configure the security applications?
A: Typical implementation timeframes are between 2-4 weeks for mid-sized landscapes.
Q: If security applications are available in standard installations of Solution Manager, why do we need to work with SAP Partners such as Layer Seven Security to configure these components?
A: Solution Manager provides the framework and the tools to perform advanced security monitoring. However, the standard installation of Solution Manager does not provide sufficient content for security monitoring. The content is developed, maintained and supported by Layer Seven Security. This includes patent-pending custom security policies, BW infoproviders, service level reports, monitoring objects and guided procedures. The content is licensed by SAP customers from Layer Seven Security and imported or transported into Solution Manager.
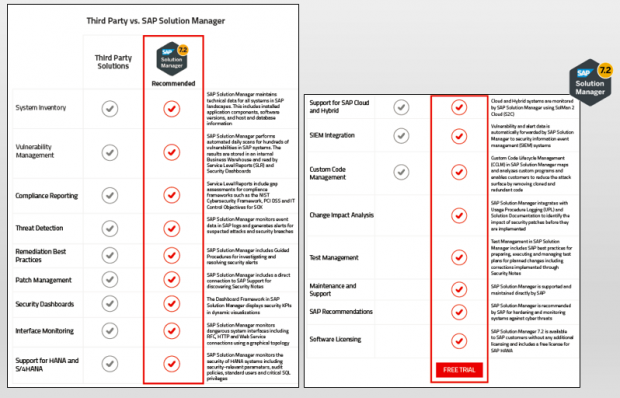
Q: What are the benefits of using Solution Manager for security monitoring versus third party tools ?
A: There are many advantages for using Solution Manager over third party tools. The most significant is lower cost: licensing and importing content for Solution Manager is less expensive than licensing entire platforms and solutions for SAP security monitoring. Solution Manager is also more flexible and customizable. It’s also recommended by SAP and supported and maintained directly by SAP. For further information, download the comparison chart.

Q: Does Layer Seven Security provide online demos for security monitoring using Solution Manager?
A: Yes, you can request a demo here.
Q: Does Layer Seven Security provide free readiness checks and trials for security monitoring using Solution Manager?
A: Yes, we offer free readiness checks to discover and remove any configuration gaps in Solution Manager to support security monitoring. We also provide free trials for Layer Seven’s custom security content. The trials can be performed remotely or on-site for up to 5 systems.
Q: Who shall I contact for further information?
A: Please call Layer Seven Security at 1-647-964-7370 or email info@layersevensecurity.com