How to Protect Sensitive Data in Your SAP Systems with Read Access Logging
The need to monitor access to classified data in SAP systems has never been greater. End users are increasingly working with SAP data from outside the borders of corporate networks. Corporate information is also increasingly under threat from cyber criminals, hacktivists, cyber spies and terrorists that seek to exploit classified information for financial gain or to further ideological or national interests.
Read Access Logging (RAL) empowers organizations to combat these threats by providing the ability to detect and contain information leaks before they escalate into large-scale data breaches. This is performed by logging and monitoring access to sensitive data in SAP systems. RAL can also be used to identify malicious changes by tracking old and new values for classified data.
This article will explain how you can enable RAL in your SAP systems. The use-case illustrated in the article is sensitive employee data including social security numbers (SSN), salary and banking information. However, RAL can support any use case including health records, payment data, pricing information, etc. It can also be used to monitor access to custom data fields in your SAP systems.
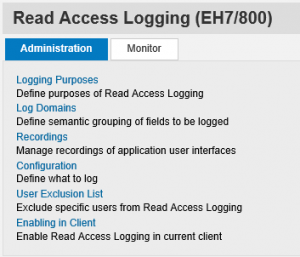
RAL is accessed using the SRALMANAGER transaction. The screen below displays the options available in the Administration tab of the control panel. You will need the templates roles SAP_BC_RAL_ADMIN_BIZ, SAP_BC_RAL_ADMIN_TEC and/ or SAP_BC_RAL_CONFIGURATOR to administrator RAL.
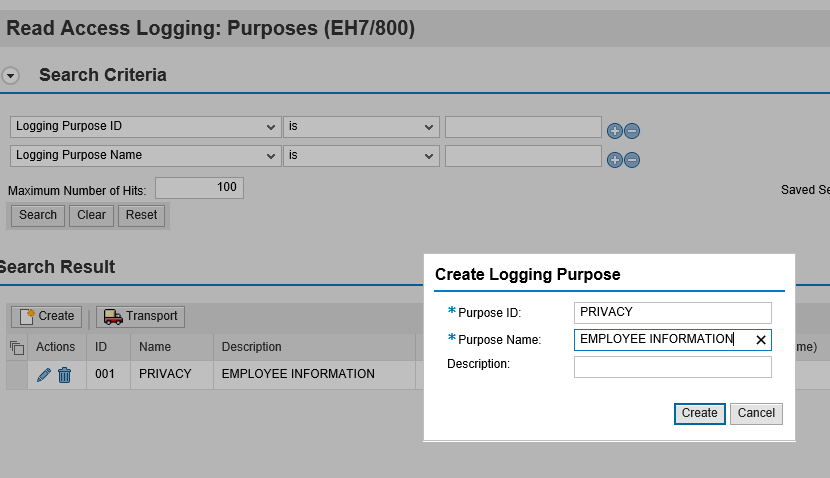
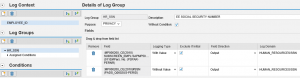
The options in the Administration tab are organized in line with the sequence of activities performed to configure RAL. The first step is the definition of Logging Purposes. A log purpose is the specific use-case for the log groups you will create in later steps. In the example below, we have created a use-case to group sensitive employee-related data.
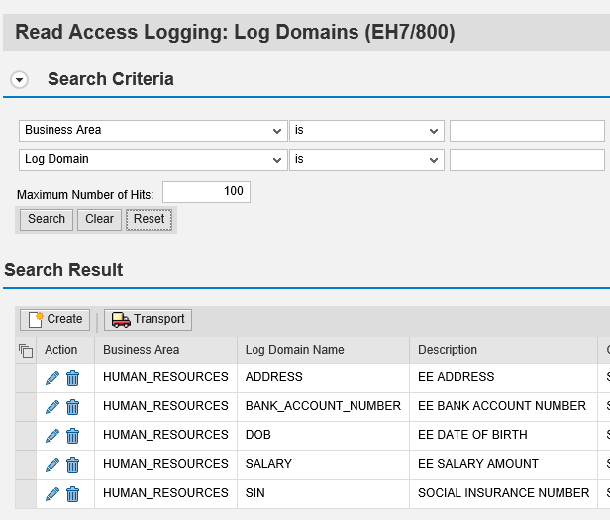
Next we must create Log Domains. These are assigned to data fields to support log analysis since many fields are unintelligible when relying on just system identifiers. The screen below captures the log domains we have created for employee data including banking information, salary and SSN.
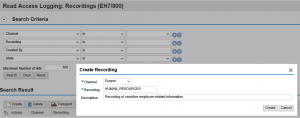
Once we have defined our log domains, we must configure recordings to capture the data fields that we will assign to the domains. Recordings can be used for SAP GUI (Dynpro) and Web GUI (Web Dynpro) sessions. Below we have created a recording to capture specific types of employee information using SAP GUI. Click on the image to enlarge.
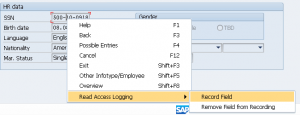
We can choose the data fields to log by selecting the Record Field option in the context menu. The screen below shows that we have selected to record the SSN field during a recording session in an IDES system with mock data using SAP GUI.
The fields captured in RAL during the recording sessions are assigned to log domains during the configuration step. In the example below, we have assigned the SSN field to the SSN log domain. You can choose to record field values in log entries during this step and to include/ exclude initial values. You can also specify whether the trigger for logging should be data entry performed by the end user or data displayed to the user or both. Specific users can be excluded from RAL using the User Exclusion List. Therefore, we can ensure HR and other users that require access to employee information for their role are not included in log results.
The final step is enabling RAL by maintaining the profile parameter sec/ral_enabled_for_rfc in each application server. RAL configuration settings can be transported within your SAP landscape using transaction SRAL_TRANS.
Log analysis is performed using the options in the Monitor tab. This can be performed using the role SAP_BC_RAL_ANALYZER.
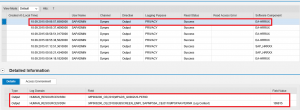
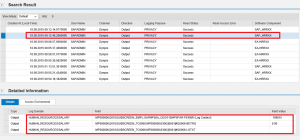
The entries for all log domains are displayed below. The first entry in the log reveals that the user SAPADMIN successfully read the SSN of employee ID 109815 at 9.06AM on September 18, 2015.
Other log entries reveal that the user also accessed the bank details and salary information of the employee on the same day. See below.
Changes performed by SAPADMIN for data fields logged by RAL would be displayed as separate log entries if we had selected the option to record field inputs with values.
RAL is available in NetWeaver 7.40 but SAP intends to make it available for earlier releases. For further information including professional services to enable Read Access Logging in your SAP systems, contact Layer Seven Security.
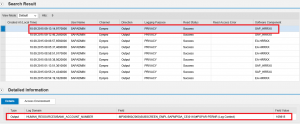
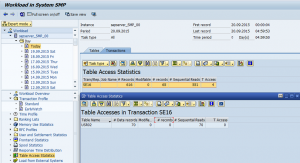
For logging table-level access in SAP systems, we recommended using the Workload Monitor accessible through transaction ST03. You can configure table access logging for up to five transactions including well-known table maintenance transactions such as SE16, SM30 and SM31. The log below from the Workload Monitor displays the number of records viewed or modified using transaction SE16 for the user table USR02 during a specific date. Large record counts could indicate a potential data breach. Correlation with transaction starts performed by users logged in the Security Audit Log or STAD should be possible using conventional SIEM solutions or SAP Enterprise Threat Detection.